Difference between revisions of "False flag"
(simplify and link to the category) |
m (typo) |
||
| (113 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{concept |
| − | [[ | + | |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/False_flag |
| − | + | |image=false-flag-pic.jpg | |
| + | |image_width= | ||
| + | |constitutes=Deep event, Psyop, Third rail topic | ||
| + | |description=False flags are attacks intended to blame a third party. Since a [[JCIT|1979 conference in Jerusalem]], the most common pattern in the West has been bomb attacks which [[authorities]] and the {{ccm}} quickly blame on [[suicide bombings|suicidal]] Muslims, promoting an overarching "[[war on terror]]" narrative, that promotes fear and is used to concoct [[casus bellis]] as needed. | ||
| + | |glossary=False flag attacks are actions carried out in ways calculated to deceive the victim as to the nature of the perpetrator. Historically, these often involved flying literal flags, e.g. from a ship, or wearing uniforms. The procedure has been used as a standard way to try to justify starting a war. Most recently, perhaps the most common false flag in Western nations have been bombs attacks blamed on Muslims designed to fuel fear and promote the "war on terror". | ||
| + | |key_properties=Start/End/ON has perpetrator/Has perpetrator/Description | ||
| + | |key_property_headers=Start/End/Attributed to/Perpetrator(s)/Description | ||
| + | |subjects=Strategy of tension | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | A '''False flag attack''' (or '''false flag operation''') is an act committed with the intent of disguising the actual source of responsibility and pinning blame on another party. An attack on a target will appear to be done by an enemy, but this enemy is aided and the attack is often organised by the attacked target. They may be used as a stand alone [[casus belli]] or part of a longer term [[strategy of tension]], such as happened during the [[Italian]] [[Years of Lead]] during which [[Operation Gladio]] terrorised the [[Italian]] population. The primary modern example is the "[[War On Terror]]" which is being waged worldwide.<ref>https://www.wikiwand.com/en/False_flag</ref><ref>See "Examples" on the bottom of this page</ref> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Origin== |
| + | The term comes from navies warfare in [[1700s]] whereby a vessel flew the flag of a neutral or enemy [[country]] in order to hide its true identity. The tactic used by pirates and private assassins to deceive other ships into allowing them to move closer before attacking them as in famous [[Hollywood]] movies. It became legal in international maritime law, on the condition that the attacking vessel displayed its true flag once an attack had begun.<ref>https://books.google.com/books?id=xn17DwAAQBAJ&pg=PT281</ref><ref>https://www.cjr.org/language_corner/false-flags.php</ref> | ||
| − | === | + | == Purposes == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | Individual events may have multiple congruent purposes (for example, as covert [[assassination]]s, or to discredit a particular group by framing them for the attack,), but campaigns (such as the "[[war on terror]]" or the Italian [[strategy of tension]]) often have broader [[War on Terror/Purposes|purposes]], such as effecting [[social change]] by using [[fear]] as a stressor of a population. |
| − | {{ | + | |
| − | + | == Feasibility == | |
| + | |||
| + | Attribution of [[cyberterrorism|virtual attacks]] is notoriously difficult and predicted to get even harder<ref>https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2018/03/friday_squid_bl_615.html#comments</ref><ref>http://www.theregister.co.uk/2018/03/08/analysis_suggests_norks_not_behind_olympic_destroyer_malware_attack/</ref>, but increased mass communications (especially the [[mass surveillance]] carried out by [[intelligence agencies]] such as the [[NSA]]) mean that large scale false flag attacks in the real world are only feasible for secretive, influential and highly disciplined organisations. They are believed to rarely take place without the cooperation or at least the acquiescence of intelligence agencies. False flag attacks are a risky but regular tool used by [[deep state]] groups adept at co-opting the machinery of national governments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Strategy == | ||
| + | {{YouTubeVideo | ||
| + | |code= Y6LKmhDRWFc | ||
| + | |caption= [[Patrick Clawson]] of the [[Washington Institute for Near East Policy | Washington Institute]] in a 2012 QA. He explains, that in order for the United States getting into a war, there needs to be the initiation of a crisis; basically acknowledging a number of false flag attacks, or provocations that lead to war, in the last 150 years.<ref>https://www.corbettreport.com/false-flags-over-iran saved at [https://web.archive.org/web/20160808021031/https://www.corbettreport.com/false-flags-over-iran/ Archive.org] and [http://archive.is/5yuiL Archive.is]</ref> | ||
| + | |align=left | ||
| + | |width=350px | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | [[Webster Tarpley]] has published extensively on the strategy of false flags. While they are inevitably contain an element of risk - especially for the lower level operatives who are usually lied to about their involvement, and are often [[murder]]ed as part of the cover-up - certain common strategies are employed to maximise the "[[plausible deniability]]" by which higher-ups life to fight - and kill - another day. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Drills === | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{FA|Terror drill}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | "[[Counter-terror drills]]" provide cover for activities as suspect as placing live [[explosives]] in a [[school]] bus.<ref>https://www.yahoo.com/news/cia-leaves-explosives-school-bus-training-exercise-172712978.html</ref> Many high profile terror attacks are near simultaneous with such drills (for example, [[9-11/Drills|9-11]] and [[7 July 2005 London bombings/Drills|7-7]]). Rogue employees can easily make the decision to make these drills "go live" if they deem conditions favourable, for example by remote detonation of bombs unbeknownst to other participants. | ||
| − | + | === Fallback strategies === | |
| − | + | False flags are usually designed with many contingency (fallback) strategies to thwart subsequent investigation by allowing the perpetrators to choose from a maze of {{on}}s and [[Official_opposition_narratives|''opposition'' narratives]] according to how events pan out. Additional countermeasures such as [[assassination]] or [[blackmail]] of [[whistleblower]]s, [[witness]]es or [[journalist]]s are sometimes used to try to preserve secrecy, but these counter-strategies have risks of their own. Exploitation of the target population's psychological weaknesses (such as people's [[fear]], [[naivety]], [[just world bias]], [[cognitive dissonance]] and [[conditioning]]) is an essential part of the effort to minimize the proportion of people who uncover the deception. | |
| − | + | == Psychology == | |
| + | {{FA|Psychology}} | ||
| + | {{YouTubeVideo | ||
| + | |code= UGwSLcuMQD0 | ||
| + | |width=325px | ||
| + | |caption= "How to Create a False Flag in 10 Easy Steps" - [https://www.bitchute.com/video/WLmPiNygSoi7/ Bitchute backup] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | The | + | The [[psychology]] of the the targets of terror (the general public) has been extensively studied by "[[terror experts]]", who have gradually refined the process of how to most successfully tell the "[[big lie]]". Terror drills have been used to condition people, for example stoking [[Islamophobia]].<ref>http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2015/01/02/india-police-muslim-drills_n_6406648.html</ref> |
| − | === | + | === Public Awareness === |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[image:chartoftheday_11551_americans_top_fears_of_2017_n.jpg|left|500px|thumbnail|Evidence of an increasing failure of "[[terrorism]]" to scare people - and of increasing distrust of the {{on}} - was provided by a 2017 survey of the attitudes of 1207 US adults, which revealed their greatest fear to be "corrupt government officials".<ref name=statista>https://www.statista.com/chart/11551/americans-top-fears-of-2017/</ref>]] | |
| − | + | [[Washington's Blog]] reported in April 2013, after the [[Boston Marathon Bombing]] that interest in False Flag attacks was at an all time high, citing data from [[Google Trends]]. In 2017, a survey showed that "[[terrorism]]" was not among US citizens top 20 fears, and that #1 was "corrupt government officials" - with almost 3/4 of people either "afraid" or "very afraid".<ref name=statista/> | |
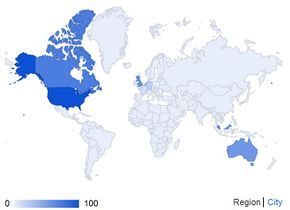
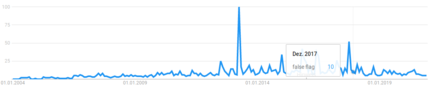
| + | [[image:false_flag_google_trends.png|left|430px|thumbnail|The dramatic spike in searches for "false flag" in April 2013, when the [[Boston Marathon bombings]] did occur.]] The geographical data showed that searches were being made on the term especially in [[USA]], [[Canada]], [[UK]], [[Malaysia]], [[Australia]] and [[Germany]]:<br/> | ||
| − | + | [[image:false_flag_google_trends_geography.jpg|left|290px|thumbnail]] | |
| − | === | + | === September 11th, 2001 === |
| + | {{FA|9-11}} | ||
| − | + | Although widely effective at the time, 9/11 changed the dynamics of false flags because after nearly 15 years of mostly online activism by the [[9/11 Truth movement]] have lead to its being widely doubted. A 2015 survey, for example, found that 33% of [[Canadian]]s were in favor of a Parliamentary review of the [[9/11 Commission Report]], with 26% neither for nor against, and only 19% opposed.<ref>http://www.army.mod.uk/documents/general/2015DIN07-111.pdf</ref><ref>http://rethink911.ca/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ReThink911Petition_Response.pdf</ref> This has lead to a new emphasis on [[internet censorship]] and the removal of [[freedom of speech]] (notably in France in 2015) as ways to try to prevent the unmasking of false flags attacks. | |
| − | The | + | == Selected Recent Examples == |
| + | The most active perpetrators of false flag attacks are believed to be the intelligence agencies of US, UK and Israel.<ref>Chris Bollyn. {{where}}</ref> [[Operation Gladio]] is a good place to start in study of recent examples, since it is relatively well documented and believed to underpin a range of more modern developments (such as [[Operation Gladio/B]]). | ||
| − | === | + | === 1945? - ? Operation Gladio === |
| + | {{FA|Operation Gladio}} | ||
| − | + | [[image:Bologna1.jpg|thumb|right|380px|The remains of the Bologna Central Station in August 1980 after an [[Operation Gladio]] bomb killed 85 civilians.]] | |
| − | + | This was a large operation in many European countries which is still only partially understood. It was most clearly revealed in Italy, after bomb attacks which killed hundreds of civilians were eventually admitted to have been carried out by a team established by [[NATO]] and the [[CIA]]. This operation quite probably gave rise to the [[Turkish deep state]]. The program has continued and expanded internationality and codenamed [[Operation Gladio B|Gladio B]]. | |
| − | === | + | === 1954 Lavon Affair === |
| + | {{FA|Lavon Affair}} | ||
| − | + | In 1954, [[Israel]] used [[Egyptian]] [[Jews]] as a fifth-column to attack US and UK-owned targets in Cairo and Alexandria. In 1954, one such saboteurs was caught planting a bomb. Israel blamed "[[antisemitism]]" in Egypt for the accusations and anyone who dared repeat them, silencing almost all western comment. However, it finally ended five decades of denial in 2005, presenting official citations to surviving agents, saying: "This is historic justice for those who were sent on a mission on behalf of the state and became the victims of a complex political affair."<ref>[http://www.ynetnews.com/Ext/Comp/ArticleLayout/CdaArticlePrintPreview/1,2506,L-3065838,00.html#n "After half a century of reticence and recrimination], Israel ... honored ... agents-provocateur." YNetNews, 30th March 2005.</ref> | |
| − | The | + | The motive is still not entirely clear, though Israel wished to induce the British government to retain its occupying troops in Egypt's Suez Canal zone. Israel also urgently needed manpower to work and defend the land it had seized in 1948, so inducing "anti-semitism", pogroms and expulsions of Jews was to their advantage. The Wikipedia article on the [[Lavon Affair]] is detailed and largely complete, but it claims that the affair was "disastrous for Israel in several ways" - while omitting the serious effects on Egypt and Egyptian Jews. |
| − | + | === 1967 USS Liberty Incident === | |
| + | {{FA|USS Liberty Incident}} | ||
| − | + | [[Image:USS-Liberty-damaged.jpg|380px|right]] | |
| − | + | The [[Israel]]i attack on the USS Liberty illustrates what can happen when false flag attacks fail. Had the USS Liberty been actually sunk according to plan, Israel might have succeeded in plausibly denying culpability. As it was, the survivors report the planes as Dassault Mirage IIIs and Super-Mystere jets, which could only have been Israeli.<ref>[http://www.ifamericansknew.org/us_ints/ul-akins.html The Attack on the USS Liberty and its Cover-up] James Akins was U.S. ambassador to Saudi Arabia. The Center for Policy Analysis on Palestine, Annual Distinguished Lecture, September 1999. If Americans Knew.org.</ref> The torpedo boats were correctly marked as being Israeli. The survivors all state that the USS liberty was flying the US flag, rendering highly implausible the official Israeli narrative that "we made a mistake". Other evidence includes the lack of markings on the Israeli planes and the jamming of US distress frequencies to try to stop the ship radioing for help. A high level cover up and a subservient US [[corporate media]] prevented major repercussions at the time. | |
| − | + | === September 11<sup>th</sup> & Amerithrax === | |
| + | {{FAs|9/11|2001 Anthrax attacks}} | ||
| − | + | [[Image:9-11-wtc-plane-hits.jpg|380px|right]] | |
| − | + | On [[September 11, 2001]], an attack occurred in the eastern US which killed thousands of people. The US government asserted that it was perpetrated by [[19 Hijackers]] under direction of [[Al Qaeda]]. Numerous anomalies, such as the [[WTC7/collapse|collapse]] of [[WTC7 |WTC7, a third tower in the World Trade Center]] which was ''not'' hit by an aeroplane, suggest that this event was a false flag. Many eye-witnesses report that explosives were involved in all three tower collapses. [[FBI]] whistleblower [[Sibel Edmonds]] has revealed a U.S. intelligence alliance between [[al Qaeda]] starting in [[1997]] and ongoing to present time. An attack was launched against the Pentagon, which was subject to a military stand down. The [[official narrative]] fails to explain the innumerable deviations from [[standard operating procedure]] before, during and after the attacks. [[Wikipedia]] editors rapidly [[Wikipedia/Censorship|censor]] any evidence which contradicts the official narrative. The coverup was completed and sealed with the domestic terror [[2001 Anthrax attacks|Anthrax attacks]] that frightened all government and media into a non-critical silence and complicit compliance with the subsequent unleashing of global "[[counter-terrorism]]" policies and [[permanent war]]s. | |
| − | + | == Admitted False Flag Attacks == | |
| + | [[Nation state]]s rarely admit to carrying out False Flag attacks, even when clear evidence exists that is unaccounted for by any other version of events. Some recent attacks which have been admitted, from [[Wikipedia]]'s list of false flag attacks: | ||
| − | * | + | * [[1978]] [[Celle Hole]] one bombing carried out by a West German secret service to further implicate the Red Army Faction, an active terrorist group. Revealed to be a not very serious (nobody hurt, no prison escape) case by the German government in 1986. |
| − | * | + | * [[1970s]] In [[Italy]] right-wing elements are accused of carrying out various terrorist acts as part of a broader [[Strategy of tension]]. There do not appear to be any of the elements of a false-flag element, though the 1972 killing of three Italian police [[Peteano bombing]] blame was initially blamed on their ideological opponents, the [[Lotta Continua]] ("continuous struggle", far left extra-parliamentary organization). Officers of the carabinieri were later indicted and convicted for manipulating the investigation in false directions. An [[Ordine Nuovo]] ("New Order" far right Italian cultural and extra-parliamentary political and terrorist organization founded in 1956) member has been named as the bomber. |
| − | * | + | * [[1970s]] the [[CIA]] [[Project Cherry]]<ref>http://onwardoverland.com/Far_East/cambodianarticles/ciacambodia.html saved at [https://web.archive.org/web/20201213153332/http://onwardoverland.com/Far_East/cambodianarticles/ciacambodia.html Archive.org] saved at [https://archive.is/Ltvmv Archive.is]</ref> is described in [[Wikipedia]] as: "Covert [[assassination]] / [[destabilization]] operation during [[Vietnam war]], targeting Prince (later King) [[Norodom Sihanouk]] and the government of [[Cambodia]]. Disbanded."<ref>http://archive.today/2019.06.16-055612/https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIA_cryptonym</ref> The operation has no seperate article as of 12/[[2020]]. |
| + | {{YouTubeVideo | ||
| + | |code= -43pjRwkVMU | ||
| + | |caption= '''''False Flags and the Dawn of Bioterrorism''''' (29:08) a 2020 short documentary by [[James Corbett]],<ref name=BioterrorAndTranscript>[https://www.corbettreport.com/bioterror/ Episode 388 – False Flags and the Dawn of Bioterrorism [[The Corbett Report]]</ref><ref name=BioterrorYouTube>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-43pjRwkVMU False Flags and the Dawn of Bioterrorism] [[The Corbett Report]] 2020-11-20</ref> a contextual history and critical overview of the threat of the military industrial biological [[technocracy]] and their duplicitous "defensive" threat to humanity. | ||
| + | " ''For the past twenty years, the world has been in the midst of a so-called "war on terror" set in motion by a false flag attack of spectacular proportions. Now the stage is being set for a new spectacular attack to usher in the next stage in that war on terror: the war on bioterrorism. But who are the real bioterrorists? And can we rely on government agencies, their appointed health authorities, and the corporate media to accurately identify those terrorists in the wake of the next spectacular terror attack?'' " | ||
| + | |align=right | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | * [[1962]] [[Operation Northwoods]] was a series of proposals for false-flag attacks, blaming [[Cuba]] for attacks carried out on US people/assets rejected by the Kennedy administration. In the same year [[Operation Mongoose]] was 12 proposals devised by the Department of Defense and against the same target. [[James Bamford]] wrote in his well-cited 2002 book "Body of secrets" that Northwoods "had the written approval of the Chairman and every member of the [[Joint Chiefs of Staff]]". | ||
| − | * | + | * [[1953]] [[Operation Ajax]] and [[Operation Boot]] were covert operations to overthrow the [[Prime Minister of Iran]] and replace him with the Shah. |
| − | * | + | * [[1944]] [[Panzer Brigade 150]] wore American uniforms as they attempted to seize bridges ahead of the Ardennes Offensive, a German counter-attack. Their success was slight though the tactic caused the Americans great alarm. A Wikipedia article on the "Kommandoverband Jaguar German army unit" was deleted when it was discovered to have been largely taken from (and hence a copyright violation of) an article on a Russian web-site [http://beute.narod.ru/Beutepanzer/su/t-34/t-34-85/t-34_85_jaguar.htm here], claiming that Germans in Russian uniforms spent 6 hours in Soviet occupied territory. It is unclear whether this is a true false-flag attack/operation (as intended at both Wikipedia and Wikispooks). It is known that SOE agents sometimes wore German uniforms behind enemy lines and, in 1944, German soldiers were sometimes wearing the better-quality American uniforms. Debatable false-flag, treated here as covert. |
| − | + | * [[1939]] The [[Gleiwitz incident]] in which Germans dressed as Polish briefly seize a German radio station. They briefly broadcast in Polish and left behind the body of a freshly murdered German Silesian known to have been sympathetic to Poles. Genuine false-flag. Pretext for the German invasion of Poland, [[official narrative|official]] start of [[WWII]]. | |
| − | + | * 1939 The [[Shelling of Finland]] by Joseph Stalin and USSR in order to get pretext for a war of aggression named the [[Winter War]]. | |
| − | + | * [[1933]] The [[Reichstag Fire]] was Hitler's pretext for suspending the Weimar Constitution and could have been false flag. Historians disagree as to whether Van der Lubbe acted alone or whether the arson was planned and ordered by the Nazis. | |
| − | ==See Also== | + | == See Also == |
*[[:Category:False Flag]] - The category of false flag attack pages | *[[:Category:False Flag]] - The category of false flag attack pages | ||
| − | ==References== | + | {{SMWDocs}} |
| + | == References == | ||
| + | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
| − | [[Category:False Flag | + | [[Category:False Flag| ]] |
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 23:29, 10 December 2023
A False flag attack (or false flag operation) is an act committed with the intent of disguising the actual source of responsibility and pinning blame on another party. An attack on a target will appear to be done by an enemy, but this enemy is aided and the attack is often organised by the attacked target. They may be used as a stand alone casus belli or part of a longer term strategy of tension, such as happened during the Italian Years of Lead during which Operation Gladio terrorised the Italian population. The primary modern example is the "War On Terror" which is being waged worldwide.[1][2]
Contents
Origin
The term comes from navies warfare in 1700s whereby a vessel flew the flag of a neutral or enemy country in order to hide its true identity. The tactic used by pirates and private assassins to deceive other ships into allowing them to move closer before attacking them as in famous Hollywood movies. It became legal in international maritime law, on the condition that the attacking vessel displayed its true flag once an attack had begun.[3][4]
Purposes
Individual events may have multiple congruent purposes (for example, as covert assassinations, or to discredit a particular group by framing them for the attack,), but campaigns (such as the "war on terror" or the Italian strategy of tension) often have broader purposes, such as effecting social change by using fear as a stressor of a population.
Feasibility
Attribution of virtual attacks is notoriously difficult and predicted to get even harder[5][6], but increased mass communications (especially the mass surveillance carried out by intelligence agencies such as the NSA) mean that large scale false flag attacks in the real world are only feasible for secretive, influential and highly disciplined organisations. They are believed to rarely take place without the cooperation or at least the acquiescence of intelligence agencies. False flag attacks are a risky but regular tool used by deep state groups adept at co-opting the machinery of national governments.
Strategy
| Patrick Clawson of the Washington Institute in a 2012 QA. He explains, that in order for the United States getting into a war, there needs to be the initiation of a crisis; basically acknowledging a number of false flag attacks, or provocations that lead to war, in the last 150 years.[7] |
Webster Tarpley has published extensively on the strategy of false flags. While they are inevitably contain an element of risk - especially for the lower level operatives who are usually lied to about their involvement, and are often murdered as part of the cover-up - certain common strategies are employed to maximise the "plausible deniability" by which higher-ups life to fight - and kill - another day.
Drills
- Full article: Terror drill
- Full article: Terror drill
"Counter-terror drills" provide cover for activities as suspect as placing live explosives in a school bus.[8] Many high profile terror attacks are near simultaneous with such drills (for example, 9-11 and 7-7). Rogue employees can easily make the decision to make these drills "go live" if they deem conditions favourable, for example by remote detonation of bombs unbeknownst to other participants.
Fallback strategies
False flags are usually designed with many contingency (fallback) strategies to thwart subsequent investigation by allowing the perpetrators to choose from a maze of official narratives and opposition narratives according to how events pan out. Additional countermeasures such as assassination or blackmail of whistleblowers, witnesses or journalists are sometimes used to try to preserve secrecy, but these counter-strategies have risks of their own. Exploitation of the target population's psychological weaknesses (such as people's fear, naivety, just world bias, cognitive dissonance and conditioning) is an essential part of the effort to minimize the proportion of people who uncover the deception.
Psychology
- Full article: Psychology
- Full article: Psychology
| "How to Create a False Flag in 10 Easy Steps" - Bitchute backup |
The psychology of the the targets of terror (the general public) has been extensively studied by "terror experts", who have gradually refined the process of how to most successfully tell the "big lie". Terror drills have been used to condition people, for example stoking Islamophobia.[9]
Public Awareness
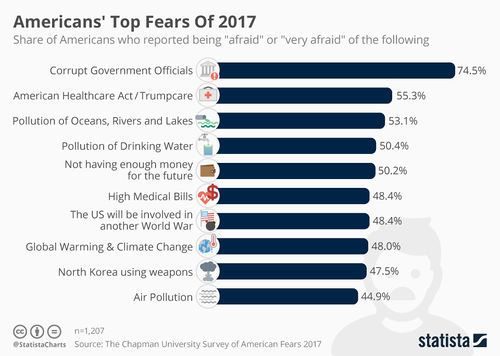
Washington's Blog reported in April 2013, after the Boston Marathon Bombing that interest in False Flag attacks was at an all time high, citing data from Google Trends. In 2017, a survey showed that "terrorism" was not among US citizens top 20 fears, and that #1 was "corrupt government officials" - with almost 3/4 of people either "afraid" or "very afraid".[10]
The geographical data showed that searches were being made on the term especially in USA, Canada, UK, Malaysia, Australia and Germany:
September 11th, 2001
- Full article:
 9-11
9-11
- Full article:
Although widely effective at the time, 9/11 changed the dynamics of false flags because after nearly 15 years of mostly online activism by the 9/11 Truth movement have lead to its being widely doubted. A 2015 survey, for example, found that 33% of Canadians were in favor of a Parliamentary review of the 9/11 Commission Report, with 26% neither for nor against, and only 19% opposed.[11][12] This has lead to a new emphasis on internet censorship and the removal of freedom of speech (notably in France in 2015) as ways to try to prevent the unmasking of false flags attacks.
Selected Recent Examples
The most active perpetrators of false flag attacks are believed to be the intelligence agencies of US, UK and Israel.[13] Operation Gladio is a good place to start in study of recent examples, since it is relatively well documented and believed to underpin a range of more modern developments (such as Operation Gladio/B).
1945? - ? Operation Gladio
- Full article:
 Operation Gladio
Operation Gladio
- Full article:

This was a large operation in many European countries which is still only partially understood. It was most clearly revealed in Italy, after bomb attacks which killed hundreds of civilians were eventually admitted to have been carried out by a team established by NATO and the CIA. This operation quite probably gave rise to the Turkish deep state. The program has continued and expanded internationality and codenamed Gladio B.
1954 Lavon Affair
- Full article: Lavon Affair
- Full article: Lavon Affair
In 1954, Israel used Egyptian Jews as a fifth-column to attack US and UK-owned targets in Cairo and Alexandria. In 1954, one such saboteurs was caught planting a bomb. Israel blamed "antisemitism" in Egypt for the accusations and anyone who dared repeat them, silencing almost all western comment. However, it finally ended five decades of denial in 2005, presenting official citations to surviving agents, saying: "This is historic justice for those who were sent on a mission on behalf of the state and became the victims of a complex political affair."[14]
The motive is still not entirely clear, though Israel wished to induce the British government to retain its occupying troops in Egypt's Suez Canal zone. Israel also urgently needed manpower to work and defend the land it had seized in 1948, so inducing "anti-semitism", pogroms and expulsions of Jews was to their advantage. The Wikipedia article on the Lavon Affair is detailed and largely complete, but it claims that the affair was "disastrous for Israel in several ways" - while omitting the serious effects on Egypt and Egyptian Jews.
1967 USS Liberty Incident
- Full article:
 USS Liberty Incident
USS Liberty Incident
- Full article:
The Israeli attack on the USS Liberty illustrates what can happen when false flag attacks fail. Had the USS Liberty been actually sunk according to plan, Israel might have succeeded in plausibly denying culpability. As it was, the survivors report the planes as Dassault Mirage IIIs and Super-Mystere jets, which could only have been Israeli.[15] The torpedo boats were correctly marked as being Israeli. The survivors all state that the USS liberty was flying the US flag, rendering highly implausible the official Israeli narrative that "we made a mistake". Other evidence includes the lack of markings on the Israeli planes and the jamming of US distress frequencies to try to stop the ship radioing for help. A high level cover up and a subservient US corporate media prevented major repercussions at the time.
September 11th & Amerithrax
- Full articles: 9/11, 2001 Anthrax attacks
- Full articles: 9/11, 2001 Anthrax attacks
On September 11, 2001, an attack occurred in the eastern US which killed thousands of people. The US government asserted that it was perpetrated by 19 Hijackers under direction of Al Qaeda. Numerous anomalies, such as the collapse of WTC7, a third tower in the World Trade Center which was not hit by an aeroplane, suggest that this event was a false flag. Many eye-witnesses report that explosives were involved in all three tower collapses. FBI whistleblower Sibel Edmonds has revealed a U.S. intelligence alliance between al Qaeda starting in 1997 and ongoing to present time. An attack was launched against the Pentagon, which was subject to a military stand down. The official narrative fails to explain the innumerable deviations from standard operating procedure before, during and after the attacks. Wikipedia editors rapidly censor any evidence which contradicts the official narrative. The coverup was completed and sealed with the domestic terror Anthrax attacks that frightened all government and media into a non-critical silence and complicit compliance with the subsequent unleashing of global "counter-terrorism" policies and permanent wars.
Admitted False Flag Attacks
Nation states rarely admit to carrying out False Flag attacks, even when clear evidence exists that is unaccounted for by any other version of events. Some recent attacks which have been admitted, from Wikipedia's list of false flag attacks:
- 1978 Celle Hole one bombing carried out by a West German secret service to further implicate the Red Army Faction, an active terrorist group. Revealed to be a not very serious (nobody hurt, no prison escape) case by the German government in 1986.
- 1970s In Italy right-wing elements are accused of carrying out various terrorist acts as part of a broader Strategy of tension. There do not appear to be any of the elements of a false-flag element, though the 1972 killing of three Italian police Peteano bombing blame was initially blamed on their ideological opponents, the Lotta Continua ("continuous struggle", far left extra-parliamentary organization). Officers of the carabinieri were later indicted and convicted for manipulating the investigation in false directions. An Ordine Nuovo ("New Order" far right Italian cultural and extra-parliamentary political and terrorist organization founded in 1956) member has been named as the bomber.
- 1970s the CIA Project Cherry[16] is described in Wikipedia as: "Covert assassination / destabilization operation during Vietnam war, targeting Prince (later King) Norodom Sihanouk and the government of Cambodia. Disbanded."[17] The operation has no seperate article as of 12/2020.
| False Flags and the Dawn of Bioterrorism (29:08) a 2020 short documentary by James Corbett,[18][19] a contextual history and critical overview of the threat of the military industrial biological technocracy and their duplicitous "defensive" threat to humanity.
" For the past twenty years, the world has been in the midst of a so-called "war on terror" set in motion by a false flag attack of spectacular proportions. Now the stage is being set for a new spectacular attack to usher in the next stage in that war on terror: the war on bioterrorism. But who are the real bioterrorists? And can we rely on government agencies, their appointed health authorities, and the corporate media to accurately identify those terrorists in the wake of the next spectacular terror attack? " |
- 1962 Operation Northwoods was a series of proposals for false-flag attacks, blaming Cuba for attacks carried out on US people/assets rejected by the Kennedy administration. In the same year Operation Mongoose was 12 proposals devised by the Department of Defense and against the same target. James Bamford wrote in his well-cited 2002 book "Body of secrets" that Northwoods "had the written approval of the Chairman and every member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff".
- 1953 Operation Ajax and Operation Boot were covert operations to overthrow the Prime Minister of Iran and replace him with the Shah.
- 1944 Panzer Brigade 150 wore American uniforms as they attempted to seize bridges ahead of the Ardennes Offensive, a German counter-attack. Their success was slight though the tactic caused the Americans great alarm. A Wikipedia article on the "Kommandoverband Jaguar German army unit" was deleted when it was discovered to have been largely taken from (and hence a copyright violation of) an article on a Russian web-site here, claiming that Germans in Russian uniforms spent 6 hours in Soviet occupied territory. It is unclear whether this is a true false-flag attack/operation (as intended at both Wikipedia and Wikispooks). It is known that SOE agents sometimes wore German uniforms behind enemy lines and, in 1944, German soldiers were sometimes wearing the better-quality American uniforms. Debatable false-flag, treated here as covert.
- 1939 The Gleiwitz incident in which Germans dressed as Polish briefly seize a German radio station. They briefly broadcast in Polish and left behind the body of a freshly murdered German Silesian known to have been sympathetic to Poles. Genuine false-flag. Pretext for the German invasion of Poland, official start of WWII.
- 1939 The Shelling of Finland by Joseph Stalin and USSR in order to get pretext for a war of aggression named the Winter War.
- 1933 The Reichstag Fire was Hitler's pretext for suspending the Weimar Constitution and could have been false flag. Historians disagree as to whether Van der Lubbe acted alone or whether the arson was planned and ordered by the Nazis.
See Also
- Category:False Flag - The category of false flag attack pages
Examples
| Page name | Start | End | Attributed to | Perpetrator(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| "Gulf of Tonkin Incident" | 2 August 1964 | 4 August 1964 | Vietnam | US/Navy | Two faked attacks used by the USA as a casus belli to commit ground forces to the Vietnam War. |
| "Jubilee Plot" | Francis Millen Thomas Callan Michael Harkins | An attempt by Irish nationalist patsies to assassinate Queen Victoria and her Cabinate during her Golden Jubilee thanks giving service at Westminster abbey on 20 June 1887 | |||
| "Kosovo student poisoning" | 22 March 1990 | 22 July 1990 | The alleged poisoning of thousands of Kosovan young people by toxic gases or substances in 1990. It came in the run-up to the Kosovo War and gained lots of coverage in the international press. | ||
| "The Storming of the Reichstag" | Attempted false flag incident, where police agents provocateurs attempted to incite a small crowd of right wing protesters to storm Parliament, in an attempt to smear a larger COVID-dissident demonstration the same day. | ||||
| 2001 Mexican legislative assembly attack | 10 October 2001 17:00:00 | 10 October 2001 17:30:00 | Saar Noam Ben Zvi Salvador Guersson | Two Israelis caught with false passports grenades, explosives and guns in the Mexican parliament a month after 9-11. Later released without charge. Western corporate media aware but uninterested. | |
| 2002 Bali bombings | 12 October 2002 23:05:00 | 12 October 2002 23:05:00 | Al-Qaeda Jemaah Islamiyah | Two bombs in Bali that killed 202 people, blamed on Al-Qaeda | |
| 2002 Venezuelan coup attempt | 11 April 2002 | 13 April 2002 | A failed CIA-backed coup attempt against President of Venezuela Hugo Chávez. | ||
| 2005 London bombings | 7 July 2005 08:50:00 | 7 July 2005 09:47:00 | Hasib Hussain Mohammad Sidique Khan Germaine Lindsay Shehzad Tanweer | A series of coordinated attacks on London's public transport system during the morning rush hour, allegedly carried out by four Muslim suicide bombers. | |
| 2011 Alexandria bombing | Army of Islam | An deadly attack on a church in Egypt to stoke tensions during the 2011 regime change. | |||
| 2014 Ukraine coup/Odessa massacre | 2014 Ukraine coup | Events in Odessa culminating in the deaths of 48 (official narrative) and up to 120 (evidence-based alternative narrative) anti-Kiev Junta demonstrators by fire, gun-shots and beatings in and around the Odessa Trade Union building on 2 May 2014 | |||
| 2016 Berlin attack | 19 December 2016 | 19 December 2016 | Islamic State Anis Amri | Reported truck hijacking in Berlin attributed to ISIL. | |
| 2016 Hurriyah car bombing hoax | 30 October 2016 | 30 October 2016 | A real bomb in the Hurriyah area of Baghdad reported as having killed people by commercially-controlled media but exposed as a hoax after CCTV footage appeared online. | ||
| 2017 Barcelona attacks | National Intelligence Center | Attackers were police informants and under intense surveillance. Happened at a convenient time for the Spanish government. | |||
| 2018 missile attack on Russian IL-20 reconnaissance aircraft | Israel trying to start WW3 by having Russian plane shot down in war ruse. | ||||
| 2021 Washington D.C. Riots | Donald Trump "Alt-right" | One of the most fortified positions in the US gets violently overrun by a group of Trump Supporters after a demonstration... without a single shot fired by the mob. Official narrative soon blamed Trump and extremists. Official opposition narrative soon blamed the democratic party trying to fraud Joe Biden into the White House. Several other governments were briefed by intelligence services that the incident seemingly "was being allowed" to happen. | |||
| 2022 Brooklyn Subway Shooting | Frank Robert James | ||||
| 9-11 | 11 September 2001 | 11 September 2001 | Al-Qaeda "9-11/The 19 Hijackers" Khalid Sheikh Mohammed Zacarias Moussaoui Walid bin Attash Mustafa al-Hawsawi Ramzi bin al-Shibh Ammar al-Baluchi | Mossad US/Deep state SDS | A complex and spectacular set of events in New York and Washington. The US government was quick to blame Al Qaeda, though no evidence of guilt was presented and there is much suspicion about what Al Qaeda really is. In the USA 9-11 assisted the Patriot Act's roll back of civil liberties, the stepping up of domestic surveillance and the financial advancement of the military industrial complex. Abroad 9-11 helped launched wars on Iraq and Afghanistan that had been planned long before. |
| 9-11/George Washington Bridge plot | 11 September 2001 | 11 September 2001 | The FBI arrested at least one van of men (two or three) which was found to contain tons of explosives. This was announced on the day, two conflicting reports, but later retracted. No alternative explanation is known to have been given. | ||
| 9-99/Ryazan incident | 22 September 1999 | 23 September 1999 | FSB | Moscow FSB officers discovered wiring up what looked like a bomb in the basement of a building by night. Local FSB unaware. Claimed to be a terror drill but no documentation was presented. Instead documents were sealed and discussion of it prohibited in the Duma. | |
| Achille Lauro hijacking | 7 October 1985 | 10 October 1985 | Palestine Liberation Front | 1985 hijacking of the Italian ocean liner MS Achille Lauro by four men representing the Palestine Liberation Front. Later revealed to in fact be an Israeli "black" propaganda operation. | |
| Bologna bombing | 2 August 1980 10:25:00 | 2 August 1980 10:25:00 | Communism | Operation Gladio | A murderous attack on the Italian public, carried out by the MI6/CIA led Operation Gladio, blamed on communists, as part of a wider program to prevent their electoral success in Italy. |
| Celle Hole | 25 July 1978 | 25 July 1978 | Prison escape organized by secret services, possibly to arrange a "shot while fleeing" | ||
| Cheonan sinking | 26 March 2010 | 26 March 2010 | North Korea | The sinking of the South Korean Corvette 'Cheonan' on 26 March 2010 with the loss of 46 South Korean sailors, quickly blamed on North Korea by the US and its allies. | |
| Day X plot | 2015 | February 2017 | 'Franco A.'? 'Mathias F.'? 'Maximilian T.'? | A failed attack which appears to have been intended as a false flag to be blamed on Syria. | |
| Gleiwitz Incident | 31 August 1939 | 31 August 1939 | Poland | Germany Alfred Naujocks Gestapo | The excuse for an invasion of Poland, starting World War II |
| Gretchen Whitmer/Kidnapping plot | "Alt-right" | Unknown | The "unsuccessful plot" in 2020 to overthrow the Michigan government arranged by the FBI. | ||
| HMS Defender Crimea controversy | 23 June 2021 | 23 June 2021 | Russia | Vladimir Putin Boris Johnson | A diplomatic military controversy between Russia and the UK |
| Hindawi affair | 17 April 1986 | 17 April 1986 | Failed attempt to smuggle a time bomb onto a plane | ||
| J. D. Tippit/Murder | 22 November 1963 | 22 November 1963 | JFK/Assassination/Perpetrators | An accessory murder to the JFK assassination | |
| JFK/Assassination | 22 November 1963 | 22 November 1963 | Lee Harvey Oswald | US/Deep state JFK/Assassination/Perpetrators | The assassination of US President John F. Kennedy was the seminal deep political event of modern times, perhaps even more than 9-11. Both were done by the same group. Subsequently the group assassinated RFK, MLK and many others to try to contain the truth. |
| Jovenel Moïse/Assassination | 7 July 2021 | 7 July 2021 | Unknown | SDS | The assassination of Haitian President Jovenel Moïse. |
| July 2021 Gulf of Oman incident | 29 July 2021 | 29 July 2021 | Iran | Israel Iran | Incident in July 2021 |
| Lavon Affair | July 1954 | October 1954 | Egypt | Mossad | A false flag bombing campaign carried out in Egypt against US, UK and Egyptian targets. Israel was caught and exposed - and officially admitted responsibility some 51 years later. |
| Mukden Incident | 18 September 1931 | 18 September 1931 | China | Japan | A particularly feeble excuse of a false flag used by the Japanese to try to justify their 1931 invasion of Manchuria |
| Nashville explosion | 25 December 2020 | 25 December 2020 | Anthony Quinn Warner | A mysterious explosion that has been memory holed since the US Capitol riots. | |
| Oklahoma City bombing | 19 April 1995 | 19 April 1995 | Timothy McVeigh Terry Nichols | The cabal | A highly suspicious terrorist bombing that was initially blamed on "Muslims", then on lone nuts Timothy McVeigh and Terry Nichols. Many questions remain answered about the official narrative. |
| Operation Embarrass | 14 February 1947 | 1948 | 'The Defenders of Arab Palestine' | MI6 | A false flag bombing campaign MI6 carried out to try to stem Jewish immigration. |
| Operation Gladio/B | 1997 | US/Deep state UK/Deep state | A development of Operation Gladio to help roll out the "war on terror" by promoting US/NATO-sponsored false flag attacks to be blamed on "Muslim terrorists". | ||
| Operation Washtub | CIA Anastasio Somoza García | ||||
| Pan Am Flight 103 | 21 December 1988 | 21 December 1988 | Abdelbaset al-Megrahi | When Pan Am Flight 103 exploded over Lockerbie, Scotland on 21 December 1988, killing all 259 passengers and crew on board, news reports cited UN Assistant Secretary-General, Bernt Carlsson, as its highest-profile victim. US and British intelligence operatives, posing as Lockerbie investigators, ignored the evident targeting of the UN diplomat and instead focused on the jumbo jet. With the result that the wrong country was blamed and an innocent person convicted of the Lockerbie bombing. | |
| Patrick Haseldine/Suppressed Lockerbie evidence ignited 9-11 attacks | 11 September 2001 08:46:00 | 11 September 2001 10:28:00 | Al-Qaeda | ||
| Plan JB 355 | US Franklin D. Roosevelt Claire Lee Chennault | A 1941 plan for dozens or hundreds of US bombers with American crews masked by Chinese markings to bombing Japanese cities | |||
| Russian apartment bombings | 4 September 1999 | 16 September 1999 | Ibn al-Khattab Chechnya Adam Dekkushev Yusuf Krymshakhalov | FSB | A 'Russian 9/11' which boosted support for the second war that was launched in Chechnya |
| Shelling of Mainila | 26 November 1939 | 26 November 1939 | Finland | Soviet Union | A false flag used to launch the Winter War. |
| Syrian Chemical Weapons Attack | 21 August 2013 | 21 August 2013 | Syria | ||
| The Bombers Affair (Luxembourg) | 30 May 1984 | 2 December 1985 | Luxembourg terrorist attacks by the local Gladio stay-behind network | ||
| The Sinking of the Atlas | The Red Hand | Direction Générale de la Sécurité Extérieure | German cargo ship sunk by French agents in 1958. Blamed on fictional Red Hand terrorist organization. | ||
| The Sinking of the SS San Flaviano | CIA | British oil tanker sunk in 1958 by the CIA bombing under false flag. The purpose was make foreign companies like Shell suspend operations and in Indonesia, to weaken the Indonesian economy and destabilize the government. | |||
| The secret war against Sweden | 27 October 1981 | 1994 | Soviet Russia | NATO William Casey Ronald Reagan James Lyons National Underwater Reconnaissance Office Bror Stefenson | A large number of "Soviet" submarine intrusions in Swedish waters in the 1980s, in reality committed by NATO under false flag. The intrusions were about deception and PSYOPs, to change the mindset of the Swedes, to make them adapt to US interests. |
| USS Liberty Incident | 8 June 1967 | 8 June 1967 | Israel | A 1967 false flag attack by Israel that tried and failed to sink the USS Liberty, a United States Navy signals intercept ship. The investigation was told to "conclude that the attack was a case of 'mistaken identity' despite overwhelming evidence to the contrary." Israel paid compensation but always contested that it was accidental. | |
| ... further results | |||||
Related Quotations
| Page | Quote | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patrick Clawson | “One can combine other means of pressure with sanctions. I mentioned that explosion on August 17th. We could step up the pressure. I mean look people, Iranian submarines periodically go down, some day one of them might not come up, who would know why? We can do a variety of things if we wish to increase the pressure... We are in the game of using covert means against the Iranians. We could get nastier.” | Patrick Clawson | September 2012 |
| Francesco Cossiga | “Maroni should do what I did when I was Minister of the Interior. First, leave the high school students alone, because think what would happen if a twelve-year-old was killed or seriously injured. Let them do the university students instead. Withdraw the police force from the streets and universities, infiltrate the movement with agents provocateurs ready for anything, and let the demonstrators devastate the shops, set fire to cars and set fire to cities for ten days. After that, thanks to popular support, the sound of ambulance sirens will overwhelm that of police and carabinieri cars. In the sense that the police should massacre the protesters mercilessly and send them all to hospital. Do not arrest them, since the magistrates would immediately set them free, but beat them to a pulp, and to a pulp even those teachers who foment them. Especially the teachers. Not the old ones, of course, but the little girls teachers, yes.” | Francesco Cossiga | 2008 |
| Mikhail Gorbachev | “The storming of the capitol was clearly planned in advance, and it's obvious by whom” | Mikhail Gorbachev | 7 January 2021 |
| Strategy of tension | “When you were on the Right you were not supposed to attack the State or its representatives. You were supposed to attack civilians, women, children, innocent people from outside the political arena. For one simple reason: To force the Italian public to turn to the State turn to the regime and ask for greater security. This was precisely the role of the right in Italy. It placed itself at the service of the State which created a strategy aptly called the "Strategy of Tension" in so far as they had to get ordinary people to accept that at any moment over a period of 30 years, from 1960 to the mid eighties a state of emergency could be declared. So, people would willingly trade part of their freedom for the security of being able to walk the streets, go on trains or enter a bank. This is the political logic behind all the bombings. They remain unpunished because the state cannot condemn itself.” | Vincenzo Vinciguerra | |
| Robert Stuart | “Let me pin my colours to the mast and say that I am absolutely convinced that the BBC did deliberately and knowingly fake evidence of chemical attacks.” | Craig Murray Robert Stuart |
Related Documents
| Title | Type | Publication date | Author(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Document:All Roads Lead to Dark Winter | report | 1 April 2020 | Whitney Webb | |
| Document:Anatomy of a NATO-sponsored false flag operation | audio transcript | 27 March 2014 | Leaked audio of high-level discussion of a planned Turkish false flag operation. It is an example of classic military/intelligence deception tactics in furtherance of policy already decided upon - in this case the overthrow of the Syrian government of Bashar al Assad. | |
| Document:Another Chemical Weapon False Flag on the Eve of Peace Talks in Brussels | article | 4 April 2017 | Paul Antonopoulos | The Khan Sheikoun gas attack in Idlib province, like that in the Damascus suburb of Ghouta in 2013, can be a very useful means of propaganda |
| Document:Bandar ibn Israel | article | 28 August 2013 | Sharmine Narwani | The collusion of Saudi Arabia's Bandar bin Sultan with Israel in acts of terrorist violence in the Middle East through 2013. |
| Document:Charlie Hebdo déjà vú | article | 14 January 2015 | Adrian Salbuchi | An analysis of the Charlie Hebdo event of January 2015. It connects many dots linking it to a litany of similar outrages and exposing the essentially False flag nature of all of them. |
| Document:False Flags for Israel | webpage | 11 September 2012 | Deanna Spingola | An overview of Israel's long history of False Flag attacks. |
| Document:I've Been Banned From Facebook for Sharing an Article About False Flags | article | 17 November 2017 | Caitlin Johnstone | Caitlin Johnstone's account of her Facebook censorship experience. |
| Document:Peter Dale Scott - COPA 2010 | speech | 2010 | Peter Dale Scott | |
| Document:The Global Drugs Meta-Group | article | October 2005 | Peter Dale Scott | |
| Document:The Spectacle of The False Flag | book | 1 March 2015 | Eric Wilson | |
| Document:The Terror Attacks in France. The Broader Geopolitical Implications | interview | 10 January 2015 | Umberto Pascali | Interview with Umberto Pascali – For Voice of the People, TV Sonce, Skipje, Macedonia |
Rating
This article explains this vital tactic, increasingly being unmasked by independent investigators worldwide.
References
- ↑ https://www.wikiwand.com/en/False_flag
- ↑ See "Examples" on the bottom of this page
- ↑ https://books.google.com/books?id=xn17DwAAQBAJ&pg=PT281
- ↑ https://www.cjr.org/language_corner/false-flags.php
- ↑ https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2018/03/friday_squid_bl_615.html#comments
- ↑ http://www.theregister.co.uk/2018/03/08/analysis_suggests_norks_not_behind_olympic_destroyer_malware_attack/
- ↑ https://www.corbettreport.com/false-flags-over-iran saved at Archive.org and Archive.is
- ↑ https://www.yahoo.com/news/cia-leaves-explosives-school-bus-training-exercise-172712978.html
- ↑ http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2015/01/02/india-police-muslim-drills_n_6406648.html
- ↑ a b https://www.statista.com/chart/11551/americans-top-fears-of-2017/
- ↑ http://www.army.mod.uk/documents/general/2015DIN07-111.pdf
- ↑ http://rethink911.ca/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/ReThink911Petition_Response.pdf
- ↑ Chris Bollyn. [Where?]
- ↑ "After half a century of reticence and recrimination, Israel ... honored ... agents-provocateur." YNetNews, 30th March 2005.
- ↑ The Attack on the USS Liberty and its Cover-up James Akins was U.S. ambassador to Saudi Arabia. The Center for Policy Analysis on Palestine, Annual Distinguished Lecture, September 1999. If Americans Knew.org.
- ↑ http://onwardoverland.com/Far_East/cambodianarticles/ciacambodia.html saved at Archive.org saved at Archive.is
- ↑ http://archive.today/2019.06.16-055612/https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIA_cryptonym
- ↑ [https://www.corbettreport.com/bioterror/ Episode 388 – False Flags and the Dawn of Bioterrorism The Corbett Report
- ↑ False Flags and the Dawn of Bioterrorism The Corbett Report 2020-11-20