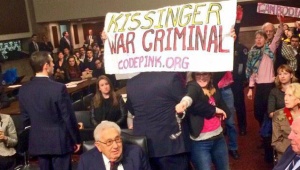Henry Kissinger
Henry Kissinger is a deep politician, former US Secretary of State and National Security Advisor. The US Independent noted the ““War criminal” and Nobel Peace Prize holder; the unique genius of Henry Kissinger.”[1] His travel is limited since he is wanted as a war criminal in various countries.
Contents
Background
In 2003, Kissinger named Fritz G. A. Kraemer as "the greatest single influence of my formative years".[2]
Career
Vietnam
In a phone-call on April 17, 1969, Kissinger advised Richard Nixon that "we might have to go to tactical nuclears and clean it up. All hell will break loose for two months, but at end of road there will be peace in Asia."[3][4]
1973 Chile Coup d'etat
- Full article: Chile/1973 coup d'état
- Full article: Chile/1973 coup d'état
In 1975 Thomas Braden was the principle interviewee in a three-part World In Action documentary, The Rise and Fall of the CIA, in which he stated that Kissinger had been the main operator in the US government's running the 1973 coup d'état."Doctor Kissinger ran the Chile operation, very much like a desk officer. He's that way, he likes to do things himself."
Letelier Assassination
An August 23, 1976 US State Department cable instructed the U.S. embassies in the capitals of Chile, Argentina and Uruguay to "seek appointment as soon as possible with highest appropriate official, preferably the chief of state" and to state that the U.S. government knew that Operation Condor might "include plans for the assassination of subversives, politicians and prominent figures both within the national borders of certain... countries and abroad." Henry Kissinger canceled this warning against international political assassinations. William D. Rogers, Kissinger’s former assistant secretary of state, denied that Kissinger was involved with a September 20th cable instructing the US ambassadors "to take no further action" on the subject of Operation Condor. Kissinger's involvement was revealed in 2010 by a declassified cable from the State Department.[5] Orlando Letelier and Ronni Karpen Moffitt were assassinated in Washington's Embassy Row on September 21st, 1976.[6]
War Criminal status
Some consider Henry Kissinger a war criminal and as in the case of Tony Blair, have tried to arrest him as such.[7][8][9] On September 11, 2001, he was sued, together with other officials from the Nixon Administration by the family of Chilean military commander Rene Schneider who was killed during a botched kidnapping in 1970.[10]
Deep Politics

Kissinger is a regular attender at Le Cercle[11] and attends the Munich Security Conference.
An event carried out
| Event | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Chile/1973 coup | Chile | A CIA military intelligence operation that overthrew of the democratically elected Salvador Allende. |
Related Quotations
| Page | Quote | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia/1975 coup d'état | “There were a number of points of tension between Whitlam's government and the United States intelligence apparatus. Whitlam had close ties with the United States, in 1964 receiving a "Leader" travel grant from the U.S. Department of State to spend three months studying under U.S. government and military officials.
After coming to power, Whitlam quickly removed the last Australian troops from Vietnam. Whitlam government ministers criticised the US bombing of North Vietnam at the end of 1972. The US complained diplomatically about the criticism. In March 1973, US secretary of State William Rogers told Richard Nixon that "the leftists [within the Labor Party would] try to throw overboard all military alliances and eject our highly classified US defence space installations from Australia". In 1973, Whitlam ordered the Australian security organisation ASIS to close its operation in Chile, where it was working as a proxy for the CIA in opposition to Chile's president Salvador Allende. Whitlam's Attorney-General Lionel Murphy used the Australian Federal Police to conduct a raid on the headquarters of the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) in March 1973. CIA Chief of Counter-Intelligence, James Angleton, later said Murphy had "barged in and tried to destroy the delicate mechanism of internal security". Australian journalist Brian Toohey said that Angleton considered then Australian Prime Minister Gough Whitlam a "serious threat" to the US and was concerned after the 1973 raid on ASIO headquarters. In 1974, Angleton sought to instigate the removal of Whitlam from office by having CIA station chief in Canberra, John Walker, ask the director general of ASIO, Peter Barbour, to make a false declaration that Whitlam had lied about the raid in Parliament. Barbour refused to make the statement. In 1974, Whitlam ordered the head of ASIO, Peter Barbour, to sever all ties with the CIA. Barbour ignored Whitlam's order and contact between Australian and US security agencies was driven underground. Whitlam later established a royal commission into intelligence and security. Jim Cairns became Deputy Prime Minister after the 1974 election. He was viewed by US secretary of state Henry Kissinger and defence secretary James Schlesinger as "a radical with strong anti-American and pro-Chinese sympathies". The US administration was concerned that he would have access to classified United States intelligence. Whitlam instantly dismissed ASIS chief WT Robinson in 1975 after discovering ASIS had assisted the Timorese Democratic Union in an attempted coup against the Portuguese administration in Timor, without informing Whitlam's government. Whitlam threatened to reveal the identities of CIA agents working in Australia. He also threatened not to renew the lease of the US spy base at Pine Gap, which was due to expire on 10 December 1975. The US was also concerned about Whitlam's intentions towards its spy base at Nurrungar.” | Wikipedia | 2022 |
| Donald Trump | “Break with tradition, or so it seems. Vilified by the entire Rockefeller and liberal media establishment, but strong evidence he himself is "conservative CIA". Brought to power by "conservative CIA" CNP financiers/members as the Mercers, Steve Bannon and Kellyanne Conway. Trump himself has many long-standing, curious security state and establishment ties, among them: in December 2000 Trump was part of a 94-guest dinner organized by Bilderberg steering committee-, Pilgrims Society-, and 1001 Club-member Conrad Black, where Trump was seen chatting with Henry Kissinger at a table. Happy Rockefeller, the widow of Nelson Rockefeller; Lynn Forester de Rothschild, Richard Perle, Vernon Jordan and later exposed serial pedophiles Jeffrey Epstein and Ghislaine Maxwell all were part of this dinner.” | Joël van der Reijden ISGP Donald Trump | 2020 |
Events Participated in
| Event | Start | End | Location(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilderberg/1957 February | 15 February 1957 | 17 February 1957 | US St Simons Island Georgia (State) | The earliest ever Bilderberg in the year, number 5, was also first one outside Europe. |
| Bilderberg/1957 October | 4 October 1957 | 6 October 1957 | Italy Fiuggi | The 6th Bilderberg meeting, the latest ever in the year and the first one in Italy. |
| Bilderberg/1964 | 20 March 1964 | 22 March 1964 | US Virginia Williamsburg | A year after this meeting, the post of GATT/Director-General was set up, and given Eric Wyndham White, who attended the '64 meeting. Several subsequent holders have been Bilderberg insiders, only 2 are not known to have attended the group. |
| Bilderberg/1971 | 23 April 1971 | 25 April 1971 | US Vermont Woodstock Woodstock Inn | The 20th Bilderberg, 89 guests |
| Bilderberg/1977 | 22 April 1977 | 24 April 1977 | United Kingdom Imperial Hotel Torquay | The 25th Bilderberg, held in Torquay, England. |
| Bilderberg/1978 | 21 April 1978 | 23 April 1978 | US New Jersey Princeton University | The 26th Bilderberg, held in the US |
| Bilderberg/1980 | 18 April 1980 | 20 April 1980 | Germany Aachen | The 28th Bilderberg, held in West Germany, unusually exposed by the Daily Mirror |
| Bilderberg/1981 | 15 May 1981 | 17 May 1981 | Switzerland Palace Hotel Bürgenstock | The 29th Bilderberg |
| Bilderberg/1982 | 14 May 1982 | 16 May 1982 | Norway Sandefjord | The 30th Bilderberg, held in Norway. |
| Bilderberg/1983 | 13 May 1983 | 15 May 1983 | Canada Quebec Château Montebello | The 31st Bilderberg, held in Canada |
| Bilderberg/1984 | 11 May 1984 | 13 May 1984 | Sweden Saltsjöbaden | The 32nd Bilderberg, held in Sweden |
| Bilderberg/1985 | 10 May 1985 | 12 May 1985 | New York US Arrowwood of Westchester Rye Brook | The 33rd Bilderberg, held in Canada |
| Bilderberg/1986 | 25 April 1986 | 27 April 1986 | Scotland Gleneagles Hotel | The 34th Bilderberg, 109 participants |
| Bilderberg/1987 | 24 April 1987 | 26 April 1987 | Italy Cernobbio | 35th Bilderberg, in Italy, 106 participants |
| Bilderberg/1988 | 3 June 1988 | 5 June 1988 | Austria Interalpen-Hotel Telfs-Buchen | The 36th meeting, 114 participants |
| Bilderberg/1989 | 12 May 1989 | 14 May 1989 | Spain Galicia La Toja Island | 37th Bilderberg meeting, 110 guests |
| Bilderberg/1990 | 10 May 1990 | 13 May 1990 | New York US Glen Cove | 38th Bilderberg meeting, 119 guests |
| Bilderberg/1991 | 6 June 1991 | 9 June 1991 | Germany Baden-Baden Steigenberger Hotel Badischer Hof | The 39th Bilderberg, 114 guests |
| Bilderberg/1992 | 21 May 1992 | 24 May 1992 | France Royal Club Evian Evian-les-Bains | The 40th Bilderberg. It had 121 participants. |
| Bilderberg/1994 | 2 June 1994 | 5 June 1994 | Finland Helsinki | The 42nd Bilderberg, in Helsinki. |
| Bilderberg/1995 | 8 June 1995 | 11 June 1995 | Greece Nafsika Astir Palace Hotel Vouliagmeni | The 43rd Bilderberg. Held at the Burgenstock Hotel in Burgenstock, Switzerland. |
| Bilderberg/1996 | 30 May 1996 | 2 June 1996 | Canada Toronto | The 44th Bilderberg, held in Canada |
| Bilderberg/1997 | 12 June 1997 | 15 June 1997 | US Lake Lanier Georgia (State) | The 45th Bilderberg meeting |
| Bilderberg/1998 | 14 May 1998 | 17 May 1998 | Scotland Turnberry | The 46th Bilderberg meeting, held in Scotland, chaired by Peter Carrington |
| Bilderberg/1999 | 3 June 1999 | 6 June 1999 | Portugal Sintra | The 47th Bilderberg, 111 participants |
| Bilderberg/2000 | 1 June 2000 | 4 June 2000 | Belgium Brussels Genval | The 48th Bilderberg, 94 guests |
| Bilderberg/2001 | 24 May 2001 | 27 May 2001 | Sweden Stenungsund | The 49th Bilderberg, in Sweden. Reported on the WWW. |
| Bilderberg/2002 | 30 May 2002 | 2 June 2002 | US Virginia Chantilly Westfields Marriott | The 50th Bilderberg, held at Chantilly, Virginia. |
| Bilderberg/2003 | 15 May 2003 | 18 May 2003 | France Versailles | The 51st Bilderberg, in Versailles, France |
| Bilderberg/2004 | 3 June 2004 | 6 June 2004 | Italy Stresa | The 52nd such meeting. 126 recorded guests |
| Bilderberg/2005 | 5 May 2005 | 8 May 2005 | Germany Rottach-Egern | The 53rd Bilderberg, 132 guests |
| Bilderberg/2006 | 8 June 2006 | 11 June 2006 | Canada Ottawa | 54th Bilderberg, held in Canada. 133 guests |
| Bilderberg/2007 | 31 May 2007 | 3 June 2007 | Turkey Istanbul | The 55th Bilderberg meeting, held in Turkey |
| Bilderberg/2008 | 5 June 2008 | 8 June 2008 | US Virginia Chantilly | The 56th Bilderberg, Chantilly, Virginia, 139 guests |
| Bilderberg/2010 | 3 June 2010 | 6 June 2010 | Spain Hotel Dolce Sitges Barcelona | The 122 guests met in the Hotel Dolce Sitges, Barcelona, Spain. |
| Bilderberg/2011 | 9 June 2011 | 12 June 2011 | Switzerland Hotel Suvretta St. Moritz | 59th meeting, in Switzerland, 129 guests |
| Bilderberg/2012 | 31 May 2012 | 3 June 2012 | US Virginia Chantilly | The 58th Bilderberg, in Chantilly, Virginia. Unusually just 4 years after an earlier Bilderberg meeting there. |
| Bilderberg/2013 | 6 June 2013 | 9 June 2013 | Watford UK | The 2013 Bilderberg group meeting. |
| Bilderberg/2014 | 29 May 2014 | 1 June 2014 | Denmark Copenhagen Marriott Hotel | The 62nd Bilderberg, with 136 guests, held in Copenhagen |
| Bilderberg/2015 | 11 June 2015 | 14 June 2015 | Austria Telfs-Buchen | The 63rd meeting, 128 Bilderbergers met in Austria |
| Bilderberg/2016 | 9 June 2016 | 12 June 2016 | Germany Dresden | The 2016 Bilderberg meeting took place in Dresden, Germany. |
| Bilderberg/2017 | 1 June 2017 | 4 June 2017 | US Virginia Chantilly | The 65th Bilderberg Meeting |
| Bilderberg/2018 | 7 June 2018 | 10 June 2018 | Italy Turin Hotel Torino Lingotto Congress | The 66th Bilderberg Meeting, in Turin, Italy, known for months in advance after an unprecedented leak by the Serbian government. |
| Bilderberg/2019 | 30 May 2019 | 2 June 2019 | Switzerland Montreux | The 67th Bilderberg Meeting |
| Bilderberg/2022 | 2 June 2022 | 5 June 2022 | US Washington DC Mandarin Oriental Hotel | The 68th Bilderberg Meeting, held in Washington DC, after an unprecedented two year hiatus during which a lot of the Bilderberg regulars were busy managing COVID-19 |
| Bilderberg/2023 | 18 May 2023 | 21 May 2023 | Portugal Lisbon Pestana Palace Hotel | The 69th Bilderberg Meeting, held in Lisbon, with 128 guests on the official list. The earliest in the year since 2009. |
| Le Cercle/1970 (Washington) | 2 December 1970 | 2 December 1970 | US Washington DC Rockefeller family mansion | Exact dates uncertain |
| Le Cercle/2011 | Only known info about this meeting is a later invitation letter | |||
| Munich Security Conference/2009 | 2009 | 2009 | Germany Munich Bavaria | The 45th Munich Security Conference |
| Munich Security Conference/2010 | 5 February 2010 | 7 February 2010 | Germany Munich Bavaria | An anti-war demonstration outside described it as "Nothing more than a media-effectively staged war propaganda event, which this year had the purpose of justifying the NATO troop increase in Afghanistan and glorifying the continuation of the war as a contribution to peace and stability." |
| ... further results | ||||
Related Document
| Title | Type | Publication date | Author(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Document:Biden Works to Prolong Ukraine War | blog post | 7 June 2022 | Craig Murray | "Ukraine is objecting to this plan (for Turkey to clear sea lanes of mines and to police the ships carrying grain) because it objects to the removal of the mines, which I should be clear were put down in the sea lanes by Ukraine to prevent amphibious attack on Odessa." |
References
- ↑ http://www.independent.co.uk/news/people/profiles/henry-kissinger-a-diplomatic-colossus-who-is-still-a-key-influence-in-us-amid-syria-crisis-8815533.html
- ↑ http://www.henryakissinger.com/eulogies/100803.html
- ↑ https://consortiumnews.com/2015/08/10/exposing-nixons-vietnam-lies/?print=print
- ↑ http://history.state.gov/historicaldocuments/frus1969-76v19p1/d15
- ↑ http://www.cella.com.br/blog/?p=18469
- ↑ Lynton, Stephen J.; Meyer, Lawrence (September 22, 1976), "Ex-Chilean Ambassador Killed by Bomb Blast", The Washington PostPage Module:Citation/CS1/styles.css must have content model "Sanitized CSS" for TemplateStyles (current model is "Scribunto").
- ↑ http://www.democracynow.org/2015/1/30/codepink_attempts_to_arrest_henry_kissinger
- ↑ https://www.commondreams.org/views02/0611-03.htm
- ↑ http://www.salon.com/2015/04/17/the_ivy_leagues_favorite_war_criminal_why_the_atrocities_of_henry_kissinger_should_be_mandatory_reading/
- ↑ http://cinnabarswan.com/oldsite/essay2.htm
- ↑ https://isgp-studies.com/z-2009-06-01-giancarlo-elia-valoria-P2-lodge-new-head-Licio-Gelli-CIA