Difference between revisions of "The Twitter Files"
m (typos) |
m (→Astroturfing) |
||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
In [[2017]], Pentagon officials asked Twitter to "whitelist" several accounts that the Pentagon was using to spread messages in the [[Middle East]]. | In [[2017]], Pentagon officials asked Twitter to "whitelist" several accounts that the Pentagon was using to spread messages in the [[Middle East]]. | ||
In response, Twitter granted the account permissions similar to those reserved for verified accounts. The FBI was reported to be communicate messages from other clandestine US intelligence [[spooks]], including those of the U.S. intelligence community and the DHS’s [[Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency]], even receiving criticism from Twitter why they have [[FBI]] officials solely tasked with searching for Tweets. The DHS was announced to investigate elections in [[2017]] as a new priority battling "[[disinformation]]". | In response, Twitter granted the account permissions similar to those reserved for verified accounts. The FBI was reported to be communicate messages from other clandestine US intelligence [[spooks]], including those of the U.S. intelligence community and the DHS’s [[Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency]], even receiving criticism from Twitter why they have [[FBI]] officials solely tasked with searching for Tweets. The DHS was announced to investigate elections in [[2017]] as a new priority battling "[[disinformation]]". | ||
| + | ===Deepfakes== | ||
| + | Twitter Site Integrity Team whitelisted accounts from United States Central Command (CENTCOM) used to run online influence campaigns in other countries, including Yemen, Syria, and Kuwait. This whitelisting prevented the accounts from being flagged. Many of the accounts didn't disclose their affiliation with the military, and posed as ordinary users. One of the accounts used a photo identified by Stanford as being a [[deepfake]], and thus fake picture made with [[AI]] technology.<ref>https://www.newsnationnow.com/business/tech/twitter-aided-pentagon-influence-operations-report/</ref> | ||
In [[2020]], the CISA created a operational faction called the Election Integrity Partnership (EIP) and included the [[Stanford]] Internet Observatory, the [[University of Washington]]’s Center for an Informed Public, the [[Atlantic Council]]’s Digital Forensic Research Lab, and [[Graphika]], a social media analytics firm. The EIP was superficially meant to "bypass the First Amendment for government-aligned agencies" to interfere with the government limits on combating [[free speech]].<ref>https://www.aljazeera.com/economy/2022/12/21/twitter-secretly-boosted-us-military-propaganda-investigation</ref><ref>https://nypost.com/tag/twitter-files/</ref> | In [[2020]], the CISA created a operational faction called the Election Integrity Partnership (EIP) and included the [[Stanford]] Internet Observatory, the [[University of Washington]]’s Center for an Informed Public, the [[Atlantic Council]]’s Digital Forensic Research Lab, and [[Graphika]], a social media analytics firm. The EIP was superficially meant to "bypass the First Amendment for government-aligned agencies" to interfere with the government limits on combating [[free speech]].<ref>https://www.aljazeera.com/economy/2022/12/21/twitter-secretly-boosted-us-military-propaganda-investigation</ref><ref>https://nypost.com/tag/twitter-files/</ref> | ||
Revision as of 04:57, 10 September 2023
 | |
| Date | December 2, 2022 - 17 March 2023 |
|---|---|
| Perpetrators | Matt Taibbi, Bari Weiss, Lee Fang, Michael Shellenberger, David Zweig |
| Interests | • twitter • internet censorship • big tech • Hunter Biden's laptop |
| Description | Elon Musk buying Twitter resulted in the exposure of internal Twitter Inc documents |
The Twitter Files emerged in December 2022 exposing collusion and conspiracy to censor between Twitter, Democratic Party members of the United States Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, and the federal government.[1][2]
Contents
Official narrative
- Full article:
 Wikipedia/Problems
Wikipedia/Problems
- Full article:
| Fox News host Tucker Carlson breaks down what was really learned from Elon Musk's 'Twitter Files' on the Hunter Biden laptop story on 'Tucker Carlson Tonight. |
Wikipedia wrote; "The Twitter Files are a series of releases of select internal Twitter, Inc. documents published from December 2022 through March 2023 on Twitter. CEO Elon Musk gave the documents to journalists Matt Taibbi, Bari Weiss, Lee Fang, and authors Michael Shellenberger, David Zweig and Alex Berenson shortly after he acquired Twitter on October 27, 2022. Taibbi and Weiss coordinated the publication of the documents with Musk, releasing details of the files as a series of Twitter threads.
The releases have prompted debate over the nature of blacklisting, vows for congressional investigation, calls for the full release of all documents for the sake of transparency, and calls to improve content moderation processes at Twitter.
After the first set of files was published, many technology journalists said that the reported evidence did not demonstrate much more than Twitter's policy team having a difficult time making a tough call, but resolving the matter swiftly, while right-wing voices said the documents confirmed Twitter's liberal bias. According to Rolling Stone, while a significant portion of the Twitter Files were devoted to Twitter's handling of takedown requests by Democrats and federal officials, Republican officials also "routinely asked Twitter to take down posts they objected to". In a June 2023 court filing, Twitter attorneys strongly rejected any suggestion that the Files showed what Musk and many Republicans claimed."[3]
Concerns
- Full article:
 Deep state/2017 Popularisation
Deep state/2017 Popularisation
- Full article:
The investigative journalism for the releases was done by journalists Matt Taibbi, a former contributing editor for Rolling Stone magazine, and Bari Weiss, a former editor at both The New York Times and The Wall Street Journal, Lee Fang and David Zweig, former New York Times reporter Alex Berenson, and author and environmentalist Michael Shellenberger.
The Epoch Times reported since the infighting of the SDS since 2016 which - very coincidently - aligned with the popularisation of the term deep state, western governments have realised the potential of social media to derail government official narratives, causing a tightening on censorship. Whether the censorship was planned as part of a official opposition narrative is not known.
“After the 2016 upsets of Brexit and the election of Trump, however, the establishment soured on free speech. Both events were seen as undermining NATO, and both were blamed on foreign influence on social media—specifically Russia. The U.S. and UK governments in particular saw the need to identify and purge Russian influence operations online and set up a government–private apparatus to do so.”
Peter Svab, The Epoch Times (17 January 2023) [4]
Revelations
- Full article: Twitter/Censorship
- Full article: Twitter/Censorship

Twitter appeared to censor or remove content on various subjects, including irregularities in the 2020 elections, mail-in voting issues, and various aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic. The company was pressed by government political operatives to purge such content and its purveyors from the platform, though most of the time it was cooperating with the censorship requests willingly, the documents indicate.[5] Leading deep state functionaries appeared to be CEO, Jack Dorsey, Yoel Roth and Parag Agrawal.
Silencing critics
Around November 2020, Democrat House member Adam Schiff his office sent a list of requests to Twitter, including removing "all content" about committee staff and suspending "many" accounts, including accounts by RealClearInvestigations reporter Paul Sperry. Schiff's office alongside the United States House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence accused Sperry of harassing and promoting "false QAnon plots". Sperry denied and threaten to sue and there was no evidence given according to him. Schiff's request was apparently a response to Sperry's articles speculating about the identity of the White House whistleblower, who alleges dark deals being waged between President Donald Trump and Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy. Sperry reported, using unnamed sources, that the whistleblower could be Eric Ciaramella, a CIA analyst.
After refusing to ban Sperry, his account was banned months later for still undisclosed reasons, according to Taibbi.[6][7]
FBI threats
The FBI was reported in the files to be threatening Twitter board of directors in personal conversations with the fact that, if, the FBI wishes regarding who and who could be banned on the site were not fulfilled the "intelligence agencies were very unhappy". The FBI asked Twitter numerous times to comply with its requests, and if they are not met, Twitter would have to "explain" to the agency. If Twitter's position on an issue was to differ from that of the government, the company would be threatened to be noted as a foreign hostile agent, which the board of directors took so serious, they toed the government line.[8][9]
In spite of the fact that the FBI was cautioning Twitter to reporting plain users for being Russian spies, numerous of the censorship demands were essentially records of accounts with small to no prove of being Russian. At times, Twitter attempted to inquire for more data, noticing that it couldn't discover any prove on its conclusion, but regularly it essentially complied. At a certain point, Twitter simply couldn't handle all requests, as FBI agents were e-mailing plain Microsoft Word files such as .docs to give e-mail addresses of "Russian accounts". [10][11][12]
Corporate Media control
- Full article:
 Corporate media/Deep state control
Corporate media/Deep state control
- Full article:
Corporate media appeared to be controlled - if not - handled by the 3-letter agencies. An unnamed intelligence agency threatened that the media would get reports that Twitter was ignoring some extremely important issues, such as possible foreign influence activities. For example, a censorship request targeted an account "allegedly operated by Russian intelligence", although Twitter - again - received no evidence of that.
Even CIA former officers Twitter had contracted for these cases commented that "due to the lack of technical evidence on our part, I usually give up and wait for more evidence," indicating an even more urgent unexplained need for the intelligence agencies to act this way.[13]
Hunter Biden
- Full article: Hunter Biden laptop
- Full article: Hunter Biden laptop
Twitter executives, particularly Yoel Roth, Head of trust and safety, were regularly invited to meetings with the FBI and other intelligence agencies for briefings on the online activities of foreign intelligence agencies. Prior to the US 2020 election, Roth had been told to expect a “hack-and-leak” Russian media psyop October, involving Hunter Biden.
Although posting links of the story of Hunter Biden laptop being found broke no rules of Twitter, Roth internally said the story was probably a Russian operation and was obtained through "hacking" - with no evidence given - not clarifying why that would be enough to ban users for reporting on that.[14][15][16]
COVID 19
- Full article: COVID-19/Censorship
- Full article: COVID-19/Censorship
David Zweig reported Twitter found incalculable occurrences of tweets labeled as 'misleading' or taken down completely, in some cases activating account suspensions, essentially since they veered from CDC direction or contrasted from CDC recommendations. Politicians and activists with above average user engagement were also shadowbanned, including Robert F. Kennedy Jr, at other moments people that simply wanted to share being scared to take a Covid 19 Vaccine were also banned from using the site, using an automated set of words to detect opinions on the site.[17][18]
Astroturfing
In 2017, Pentagon officials asked Twitter to "whitelist" several accounts that the Pentagon was using to spread messages in the Middle East. In response, Twitter granted the account permissions similar to those reserved for verified accounts. The FBI was reported to be communicate messages from other clandestine US intelligence spooks, including those of the U.S. intelligence community and the DHS’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, even receiving criticism from Twitter why they have FBI officials solely tasked with searching for Tweets. The DHS was announced to investigate elections in 2017 as a new priority battling "disinformation".
=Deepfakes
Twitter Site Integrity Team whitelisted accounts from United States Central Command (CENTCOM) used to run online influence campaigns in other countries, including Yemen, Syria, and Kuwait. This whitelisting prevented the accounts from being flagged. Many of the accounts didn't disclose their affiliation with the military, and posed as ordinary users. One of the accounts used a photo identified by Stanford as being a deepfake, and thus fake picture made with AI technology.[19]
In 2020, the CISA created a operational faction called the Election Integrity Partnership (EIP) and included the Stanford Internet Observatory, the University of Washington’s Center for an Informed Public, the Atlantic Council’s Digital Forensic Research Lab, and Graphika, a social media analytics firm. The EIP was superficially meant to "bypass the First Amendment for government-aligned agencies" to interfere with the government limits on combating free speech.[20][21]
At a certain point, automated programs set up with the EIP even (temporarily) banned the Twitter accounts of the New York Post and then-White House spokeswoman Kayleigh McEnany for posting the blacklisted link to the Post’s Hunter Biden laptop story.[22]
Twitter Internal investigation
Twitter, conducted an investigation and found virtually zero Russian activity ahead of the 2020 election, per internal communications. CISA refused to admit to have done anything.[23][24][25]
“CISA does not censor speech, period. CISA’s mission is to build resilience to disinformation and foreign malign influence activities that threaten critical infrastructure, including election infrastructure,” a CISA spokesperson told The Epoch Times via email. “We work in a non-partisan manner with state and local election officials to equip the American public with accurate information about the conduct and security of their elections. Online content platform operators, as always, make their own decisions regarding the content on their platforms.””
Peter Svab, The Epoch Times (17 January 2023) [4]
Corporate Media cover up
Oliver Darcy of CNN said "The Twitter Files tell us nothing new. There’s no shocking revelation in there about government censorship or covert manipulation by political campaigns. They merely bring to the surface the internal deliberations of a company dealing with complex issues in ways consistent with its values.” Fox News ran a story on the other corporate media outlets highlighting their refusal to discuss the content of the files itself.[26]
References
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-63963779
- ↑
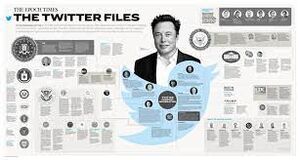
 The Epoch Times - 2023 - Click on the picture twice to enhance it.
The Epoch Times - 2023 - Click on the picture twice to enhance it. - ↑ https://www.wikiwand.com/en/Twitter_Files
- ↑ a b https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bYjC1Kklpoo
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://www.livemint.com/news/world/twitter-files-2-the-10-big-revelations-on-right-wing-users-11670553671487.html
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://twitter.com/zerohedge/status/1615559645539581952
- ↑ https://english.ahram.org.eg/NewsContent/50/1204/484018/AlAhram-Weekly/Opinion/Revelations-from-the-Twitter-Files.aspx
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://www.wsj.com/articles/twitter-files-revelations-are-instructive-but-not-surprising-media-cultural-elites-misinformation-disagreement-musk-11670856198
- ↑ https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-sci-tech/twitter-files-explained-what-are-they-and-what-to-make-of-them/
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://www.foxnews.com/media/what-elon-musks-twitter-files-uncovered-about-tech-giant
- ↑ https://www.newsnationnow.com/business/tech/twitter-aided-pentagon-influence-operations-report/
- ↑ https://www.aljazeera.com/economy/2022/12/21/twitter-secretly-boosted-us-military-propaganda-investigation
- ↑ https://nypost.com/tag/twitter-files/
- ↑ https://myvalleynews.com/blog/2023/01/22/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files/
- ↑ https://www.theepochtimes.com/us/infographic-key-revelations-of-the-twitter-files-4986669
- ↑ https://unherd.com/thepost/the-most-surprising-revelation-about-elon-musks-twitter-files/
- ↑ https://www.jpost.com/international/article-724599
- ↑ https://www.foxnews.com/media/twitter-files-cnn-abc-nbc-cbs-blackout-coverage-elon-musk?intcmp=tw_fnc