Difference between revisions of "1854"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
1844 < 1845 < 1846 < 1847 < 1848 < 1849 < 1850 <1851 < 1852 < 1853 < 1854 > 1855 > 1856 > 1857 > 1858 > 1859 > 1860 > 1861 > 1862 > 1863 > 1864
(Created page with "{{year |image= |image_width= |image_caption= }} {{SMWDocs}} {{Stub}}") |
(unstub) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{year | {{year | ||
| − | |image= | + | |image=Snow-cholera-map.jpg |
|image_width= | |image_width= | ||
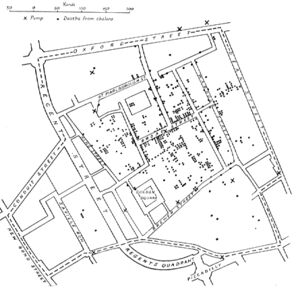
| − | |image_caption= | + | |image_caption=Original map by Dr [[John Snow (physician)|John Snow]] showing the [[Cluster (epidemiology)|clusters]] of [[cholera]] cases in the London epidemic of 1854 |
| + | |description=year 1854 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | == Events == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === January–March === | ||
| + | * [[January 3]] – [[Charles Dickens]] commences writing the novel ''[[Hard Times (novel)|Hard Times]]''. | ||
| + | * [[January 6]] – The fictional detective [[Sherlock Holmes]] is born. | ||
| + | * [[January 9]] – The [[Teutonia Maennerchor Hall|Teutonia Männerchor]] in [[Pittsburgh]], U.S.A. is founded to promote German culture.<ref>[http://www.pghmannerchor.com/history/]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120117054136/http://www.pghmannerchor.com/history/ |date=January 17, 2012 }} "The Teutonia Männerchor was founded in 1854."</ref> | ||
| + | * [[January 20]] – The [[North Carolina General Assembly]] in the United States charters the [[Atlantic and North Carolina Railroad]], to run from [[Goldsboro, North Carolina|Goldsboro]] through [[New Bern, North Carolina|New Bern]], to the newly created [[seaport]] of [[Morehead City, North Carolina|Morehead City]], near [[Beaufort, North Carolina|Beaufort]].<ref>[http://www.historync.org/railroad-ANCRR.htm CommunicationSolutions/ISI, "Railroad — Atlantic & North Carolina"], ''North Carolina Business History'', 2006, accessed 21 May 2015.</ref> | ||
| + | * [[February 11]] – Major streets are lit by [[coal gas]] for the first time by the [[Pacific Gas and Electric Company|San Francisco Gas Company]]; 86 such lamps are turned on this evening in [[San Francisco, California]]. | ||
| + | * [[February 13]] – Mexican troops force [[William Walker (filibuster)|William Walker]] and his troops to retreat to [[Sonora]]. | ||
| + | * [[February 14]] – [[Texas]] is linked by [[Telegraphy|telegraph]] with the rest of the United States, when a connection between [[New Orleans]] and [[Marshall, Texas]] is completed. | ||
| + | * [[February 17]] – The British recognize the independence of the [[Orange Free State]] in Southern Africa; its official independence is declared six days later in the [[Orange River Convention]]. | ||
| + | * [[February 27]] – Britain sends Russia an ultimatum to withdraw from two Romanian provinces it has conquered, [[Moldavia]] and [[Wallachia]]. | ||
| + | * [[February 28]] – The [[Republican Party (United States)]] is founded in [[Ripon, Wisconsin]]. | ||
| + | * [[March]] – The [[British East India Company]] annexes [[Jhansi State]] in India under the [[doctrine of lapse]]. | ||
| + | * [[March 1]] | ||
| + | ** The British [[Inman Line]]'s {{SS|City of Glasgow}} sets out from [[Liverpool]] on passage to the United States with 480 on board; she is lost without trace. | ||
| + | ** German [[psychologist]] [[Friedrich Eduard Beneke]] disappears; 2 years later his remains are found in the canal near [[Charlottenburg]]. | ||
| + | ** The [[Plan de Ayutla]] calls for liberal reforms and the ouster of President [[Antonio López de Santa Anna]] of Mexico. | ||
| + | * [[March 3]] – Australia's first [[telegraph]] line, linking [[Melbourne]] and [[Williamstown, Victoria|Williamstown]], opens. | ||
| + | * [[March 11]] – A [[Royal Navy]] fleet sails from Britain, under [[Vice Admiral]] Sir [[Charles Napier (Royal Navy officer)|Charles Napier]]. | ||
| + | * [[March 20]] – The [[Boston Public Library]] opens to the public in the United States. | ||
| + | * [[March 24]] – Slavery is abolished in [[Venezuela]]. | ||
| + | * [[March 27]] – [[Crimean War]]: The United Kingdom declares war on Russia. | ||
| + | * [[March 28]] – France declares war on Russia. | ||
| + | * [[March 31]] – US Navy [[Commodore (United States)|Commodore]] [[Matthew C. Perry]] signs the [[Convention of Kanagawa]] with the Japanese government (the [[Tokugawa shogunate]]), opening the ports of [[Shimoda, Shizuoka|Shimoda]] and [[Hakodate, Hokkaido|Hakodate]] to American trade. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === April–June === | ||
| + | * [[April 1]] – ''[[Hard Times (novel)|Hard Times]]'' begins serialisation in [[Charles Dickens]]' magazine, ''[[Household Words]]''. | ||
| + | * [[April 16]] – The United States packet ship ''[[Powhattan (1837)|Powhattan]]'' is wrecked off the New Jersey shore, with more than 200 victims. | ||
| + | * [[May 27]] – [[Taiping Rebellion]]: United States [[Minister (diplomacy)|diplomatic minister]] [[Robert Milligan McLane|Robert McLane]] arrives at the Heavenly Capital aboard the American [[warship]] {{USS|Susquehanna|1850|6}}. | ||
| + | * [[May 30]] – The [[Kansas–Nebraska Act]] becomes law (replacing the [[Missouri Compromise]] of 1820), creating the [[Kansas Territory]] and the [[Nebraska Territory]], west of the [[State of Missouri]] and the [[State of Iowa]]. The Kansas–Nebraska Act also establishes that these two new Territories will decide either to allow or disallow [[slavery]], depending on balloting by their residents (these areas would have been strictly "free territory" under the Missouri Compromise, which allowed slavery in the State of Missouri but disallowed it in any other new state north of latitude 36° 30', which forms most of the southern boundary of Missouri. This prohibition of slavery extended all the way from the western boundary of Missouri to the Pacific Ocean). | ||
| + | * [[June]] – The [[Grand Excursion]] takes prominent Eastern United States inhabitants from [[Chicago]] to [[Rock Island, Illinois]] by railroad, then up the [[Mississippi River]] to [[Saint Paul, Minnesota]] by [[steamboat]]. | ||
| + | * [[June 10]] – The first class of the [[United States Naval Academy]] graduates at [[Annapolis, Maryland]]. | ||
| + | * [[June 21]] – [[Battle of Bomarsund]] in the [[Åland Islands]] off the coast of Finland: British [[Royal Navy]] seaman's mate [[Charles Davis Lucas]] throws a live Russian [[artillery shell]] overboard by hand before it explodes, for which he is awarded the first [[Victoria Cross]] in [[1857]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === July–September === | ||
| + | * [[July 4]] – [[James Ambrose Cutting]] takes out the first of his three United States [[patent]]s for improvements to the [[wet plate]] [[collodion process]] ([[Ambrotype]] photography). | ||
| + | * [[July 6]] | ||
| + | ** In [[Jackson, Michigan]], the first convention of the [[Republican Party (United States)|U.S. Republican Party]] is held. | ||
| + | ** [[Sa'id of Egypt|Said Pasha]] succeeds his nephew [[Abbas I of Egypt|Abbas]], as the Pasha of [[Egypt]]. | ||
| + | * [[July 7]] – The [[Bombay Spinning and Weaving Company]] is established as the first [[cotton mill]] in India by Cowasjee Nanabhoy Davar and associates. | ||
| + | * [[July 17]] – The ''[[Bienio progresista]]'' revolutionary coup occurs in Spain. | ||
| + | * [[July 19]] – [[Wood's despatch]] is sent by [[Charles Wood, 1st Viscount Halifax]] to [[Lord Dalhousie]], Governor General of India, proposing radical improvements to the Indian educational system. | ||
| + | * [[August 9]] – [[John of Saxony|Johann]] succeeds to the [[Kingdom of Saxony|throne of Saxony]], on the death of his brother. | ||
| + | * [[August 16]] – [[Battle of Bomarsund]]: Russian troops on the island of Bomarsund, in the [[Åland Islands]], surrender to French–British troops. | ||
| + | * [[August 27]] – English lawyer [[Alfred Wills]] and party set out for the first ascent of the [[Wetterhorn]] in Switzerland, regarded as the start of the "[[golden age of alpinism]]". | ||
| + | * [[August 31]]–[[September 8]] – An epidemic of [[cholera]] in London kills over 10,000. [[John Snow (physician)|Dr John Snow]] traces the source of one outbreak (that killed 500) to a single [[pump|water pump]], validating his theory that [[cholera]] is water-borne, and forming the starting point for [[epidemiology]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[September 20]] – [[Crimean War]]: [[Battle of Alma]] – The French–British alliance wins the first major land engagement of the war. | ||
| + | * [[September 27]] – [[SS Arctic disaster|SS ''Arctic'' disaster]]: The American [[paddle steamer]] {{SS|Arctic}} sinks after a collision with the much smaller French ship {{SS|Vesta}}, 50 miles (80 km) off the coast of [[Newfoundland]], with approximately 320 deaths. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === October–December === | ||
| + | * [[October 1]] – The watch company founded in [[1850]] in [[Roxbury, Massachusetts]], by [[Aaron Lufkin Dennison]], relocates to [[Waltham, Massachusetts|Waltham]], to become the [[Waltham Watch Company]], pioneer in the [[American system of watch manufacturing]]. | ||
| + | * [[October 9]]–[[October 11|11]] – United States diplomats in Europe meet and draft the [[Ostend Manifesto]], setting out a rationale for the U.S. to acquire [[Cuba]] from Spain. | ||
| + | * [[October 6]] – The [[great fire of Newcastle and Gateshead]] in England is ignited by a spectacular explosion. | ||
| + | * [[October 17]] – ''[[The Age]]'' newspaper is founded in [[Melbourne]], Australia. | ||
| + | * [[October 25]] – [[Crimean War]]: [[Battle of Balaclava]] – The allies gain an overall victory, except for the disastrous cavalry [[Charge of the Light Brigade]], from which only 200 of 700 men survive. | ||
| + | * [[November]] | ||
| + | ** [[Florence Nightingale]] and her team of 38 trained volunteer [[nurse]]s, having set out on [[October 21]] from England, arrive at [[Selimiye Barracks]] in [[Üsküdar|Scutari]] in the [[Ottoman Empire]], to care for [[British Army]] troops invalided from the [[Crimean War]]. | ||
| + | ** The [[Mute Rebellion]] breaks out in Sweden. | ||
| + | * [[November 5]] – [[Crimean War]]: [[Battle of Inkerman]] – The Russians are defeated. | ||
| + | * [[November 14]] – [[Great Storm of 1854]] in the [[Black Sea]]: 19 British transport and other ships (plus 2 French) supporting the [[Crimean War]] are wrecked with the loss of at least 287 men. | ||
| + | * [[November 17]] – In [[Egypt]], the [[Suez Canal]] Company is formed. | ||
| + | * [[December 3]] – The [[Eureka Stockade]] Miners' Rebellion breaks out in [[Ballarat]], [[Victoria (Australia)]]. | ||
| + | * [[December 8]] – [[Pope Pius IX]] in the [[apostolic constitution]] ''[[Ineffabilis Deus]]'' defines ''ex Cathedra'' the [[dogma]] of [[Immaculate Conception]], which holds that the [[Blessed Virgin Mary]] was conceived without [[original sin]] | ||
| + | * [[December 10th]] – [[Sa'id Pasha]] officially abolishes slavery in Egypt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Undated === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Ignacy Łukasiewicz]] drills the world's first oil well in Poland, in Bóbrka near [[Krosno County]]. | ||
| + | * Professor [[Benjamin Silliman]] of [[Yale University]] is the first person to [[Fractionation|fractionate]] [[petroleum]] into its individual components, by [[distillation]]. | ||
| + | * The [[Iceland]]ic trade is opened to merchants other than [[Denmark|Danes]]. | ||
| + | * A Russian fort is established at the modern-day site of [[Almaty]]. | ||
| + | * The French fashion label [[Louis Vuitton]] is founded. | ||
| + | * The future Waterbury Clock Company (Incorporated on March 27, 1857) is founded as a department within the Benedict And Burnham Manufacturing Company in [[Waterbury, Connecticut]], the predecessor of [[Timex Group USA]] in timepiece manufacturing. | ||
| + | |||
{{SMWDocs}} | {{SMWDocs}} | ||
| − | {{ | + | ==References== |
| + | {{reflist}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:22, 28 February 2021
 | |
| year 1854 |
Contents
Events
January–March
- January 3 – Charles Dickens commences writing the novel Hard Times.
- January 6 – The fictional detective Sherlock Holmes is born.
- January 9 – The Teutonia Männerchor in Pittsburgh, U.S.A. is founded to promote German culture.[1]
- January 20 – The North Carolina General Assembly in the United States charters the Atlantic and North Carolina Railroad, to run from Goldsboro through New Bern, to the newly created seaport of Morehead City, near Beaufort.[2]
- February 11 – Major streets are lit by coal gas for the first time by the San Francisco Gas Company; 86 such lamps are turned on this evening in San Francisco, California.
- February 13 – Mexican troops force William Walker and his troops to retreat to Sonora.
- February 14 – Texas is linked by telegraph with the rest of the United States, when a connection between New Orleans and Marshall, Texas is completed.
- February 17 – The British recognize the independence of the Orange Free State in Southern Africa; its official independence is declared six days later in the Orange River Convention.
- February 27 – Britain sends Russia an ultimatum to withdraw from two Romanian provinces it has conquered, Moldavia and Wallachia.
- February 28 – The Republican Party (United States) is founded in Ripon, Wisconsin.
- March – The British East India Company annexes Jhansi State in India under the doctrine of lapse.
- March 1
- The British Inman Line's Template:SS sets out from Liverpool on passage to the United States with 480 on board; she is lost without trace.
- German psychologist Friedrich Eduard Beneke disappears; 2 years later his remains are found in the canal near Charlottenburg.
- The Plan de Ayutla calls for liberal reforms and the ouster of President Antonio López de Santa Anna of Mexico.
- March 3 – Australia's first telegraph line, linking Melbourne and Williamstown, opens.
- March 11 – A Royal Navy fleet sails from Britain, under Vice Admiral Sir Charles Napier.
- March 20 – The Boston Public Library opens to the public in the United States.
- March 24 – Slavery is abolished in Venezuela.
- March 27 – Crimean War: The United Kingdom declares war on Russia.
- March 28 – France declares war on Russia.
- March 31 – US Navy Commodore Matthew C. Perry signs the Convention of Kanagawa with the Japanese government (the Tokugawa shogunate), opening the ports of Shimoda and Hakodate to American trade.
April–June
- April 1 – Hard Times begins serialisation in Charles Dickens' magazine, Household Words.
- April 16 – The United States packet ship Powhattan is wrecked off the New Jersey shore, with more than 200 victims.
- May 27 – Taiping Rebellion: United States diplomatic minister Robert McLane arrives at the Heavenly Capital aboard the American warship Template:USS.
- May 30 – The Kansas–Nebraska Act becomes law (replacing the Missouri Compromise of 1820), creating the Kansas Territory and the Nebraska Territory, west of the State of Missouri and the State of Iowa. The Kansas–Nebraska Act also establishes that these two new Territories will decide either to allow or disallow slavery, depending on balloting by their residents (these areas would have been strictly "free territory" under the Missouri Compromise, which allowed slavery in the State of Missouri but disallowed it in any other new state north of latitude 36° 30', which forms most of the southern boundary of Missouri. This prohibition of slavery extended all the way from the western boundary of Missouri to the Pacific Ocean).
- June – The Grand Excursion takes prominent Eastern United States inhabitants from Chicago to Rock Island, Illinois by railroad, then up the Mississippi River to Saint Paul, Minnesota by steamboat.
- June 10 – The first class of the United States Naval Academy graduates at Annapolis, Maryland.
- June 21 – Battle of Bomarsund in the Åland Islands off the coast of Finland: British Royal Navy seaman's mate Charles Davis Lucas throws a live Russian artillery shell overboard by hand before it explodes, for which he is awarded the first Victoria Cross in 1857.
July–September
- July 4 – James Ambrose Cutting takes out the first of his three United States patents for improvements to the wet plate collodion process (Ambrotype photography).
- July 6
- In Jackson, Michigan, the first convention of the U.S. Republican Party is held.
- Said Pasha succeeds his nephew Abbas, as the Pasha of Egypt.
- July 7 – The Bombay Spinning and Weaving Company is established as the first cotton mill in India by Cowasjee Nanabhoy Davar and associates.
- July 17 – The Bienio progresista revolutionary coup occurs in Spain.
- July 19 – Wood's despatch is sent by Charles Wood, 1st Viscount Halifax to Lord Dalhousie, Governor General of India, proposing radical improvements to the Indian educational system.
- August 9 – Johann succeeds to the throne of Saxony, on the death of his brother.
- August 16 – Battle of Bomarsund: Russian troops on the island of Bomarsund, in the Åland Islands, surrender to French–British troops.
- August 27 – English lawyer Alfred Wills and party set out for the first ascent of the Wetterhorn in Switzerland, regarded as the start of the "golden age of alpinism".
- August 31–September 8 – An epidemic of cholera in London kills over 10,000. Dr John Snow traces the source of one outbreak (that killed 500) to a single water pump, validating his theory that cholera is water-borne, and forming the starting point for epidemiology.
- September 20 – Crimean War: Battle of Alma – The French–British alliance wins the first major land engagement of the war.
- September 27 – SS Arctic disaster: The American paddle steamer Template:SS sinks after a collision with the much smaller French ship Template:SS, 50 miles (80 km) off the coast of Newfoundland, with approximately 320 deaths.
October–December
- October 1 – The watch company founded in 1850 in Roxbury, Massachusetts, by Aaron Lufkin Dennison, relocates to Waltham, to become the Waltham Watch Company, pioneer in the American system of watch manufacturing.
- October 9–11 – United States diplomats in Europe meet and draft the Ostend Manifesto, setting out a rationale for the U.S. to acquire Cuba from Spain.
- October 6 – The great fire of Newcastle and Gateshead in England is ignited by a spectacular explosion.
- October 17 – The Age newspaper is founded in Melbourne, Australia.
- October 25 – Crimean War: Battle of Balaclava – The allies gain an overall victory, except for the disastrous cavalry Charge of the Light Brigade, from which only 200 of 700 men survive.
- November
- Florence Nightingale and her team of 38 trained volunteer nurses, having set out on October 21 from England, arrive at Selimiye Barracks in Scutari in the Ottoman Empire, to care for British Army troops invalided from the Crimean War.
- The Mute Rebellion breaks out in Sweden.
- November 5 – Crimean War: Battle of Inkerman – The Russians are defeated.
- November 14 – Great Storm of 1854 in the Black Sea: 19 British transport and other ships (plus 2 French) supporting the Crimean War are wrecked with the loss of at least 287 men.
- November 17 – In Egypt, the Suez Canal Company is formed.
- December 3 – The Eureka Stockade Miners' Rebellion breaks out in Ballarat, Victoria (Australia).
- December 8 – Pope Pius IX in the apostolic constitution Ineffabilis Deus defines ex Cathedra the dogma of Immaculate Conception, which holds that the Blessed Virgin Mary was conceived without original sin
- December 10th – Sa'id Pasha officially abolishes slavery in Egypt.
Undated
- Ignacy Łukasiewicz drills the world's first oil well in Poland, in Bóbrka near Krosno County.
- Professor Benjamin Silliman of Yale University is the first person to fractionate petroleum into its individual components, by distillation.
- The Icelandic trade is opened to merchants other than Danes.
- A Russian fort is established at the modern-day site of Almaty.
- The French fashion label Louis Vuitton is founded.
- The future Waterbury Clock Company (Incorporated on March 27, 1857) is founded as a department within the Benedict And Burnham Manufacturing Company in Waterbury, Connecticut, the predecessor of Timex Group USA in timepiece manufacturing.
Events
| Event | Start | End |
|---|---|---|
| Pax Brittanica | 1815 | 1915 |
| Victorian era | 1840 | 1901 |
| Crimean War | October 1853 | February 1856 |
New Groups
| Group | Image | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huntingdon College |  | Private college | Alabama college |
| University College Dublin |  | Research University | Ireland's largest university |
| Lille University of Science and Technology |  | Includes a number of specialized education and research units | |
| Lincoln University (Pennsylvania) |  | State-related HBCU | Historically black university in Pennsylvania |
| Sydney Grammar |  | Independent Day school | Sydney establishment school with influential old boys network. |
| Hamline University |  | Military ranks Liberal arts | Hamline is known for its emphasis on social justice. |
| Ohio Central College |  | In 1882, future president Warren G. Harding graduated from the college. |
Births
| Title | Born | Place of birth | Died | Summary | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Léo Taxil | 21 March 1854 | 31 March 1907 | Author Journalist | ||
| Alfred Milner | 23 March 1854 | Gießen Grand Duchy of Hesse | 13 May 1925 | Diplomat Deep politician | A deep politician of singular importance in the UK Deep state of the late 19th and early 20th century. |
| E. W. Scripps | 18 June 1854 | 12 March 1926 | Media executive | US newspaper publisher. | |
| George Buchanan | 25 November 1854 | 20 December 1924 | Diplomat |
Many thanks to our Patrons who cover ~2/3 of our hosting bill. Please join them if you can.
References
- ↑ [1]. Archived January 17, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. "The Teutonia Männerchor was founded in 1854."
- ↑ CommunicationSolutions/ISI, "Railroad — Atlantic & North Carolina", North Carolina Business History, 2006, accessed 21 May 2015.