Difference between revisions of "US/Military"
m (→Pollution: add video) |
m (not done, but good enough for now) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|code=t9uqiRb_lRk | |code=t9uqiRb_lRk | ||
|align=left | |align=left | ||
| − | |width= | + | |width=500px |
|caption= America’s Massive Global Military Presence Explained - TLDR News | |caption= America’s Massive Global Military Presence Explained - TLDR News | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
The US Military has divided the entire world into operational areas. There are currently 11 unified combatant commands, and each is established as the highest echelon of military commands, in order to provide effective command and control of all U.S. military forces, regardless of branch of service, during peace or during war time.<ref>http://www.au.af.mil/au/awc/awcgate/crs/rl30245.pdf page 2</ref> | The US Military has divided the entire world into operational areas. There are currently 11 unified combatant commands, and each is established as the highest echelon of military commands, in order to provide effective command and control of all U.S. military forces, regardless of branch of service, during peace or during war time.<ref>http://www.au.af.mil/au/awc/awcgate/crs/rl30245.pdf page 2</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 41: | Line 39: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 17:01, 16 March 2024
(Armed Forces) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Headquarters | Pentagon |
| Leaders | • Joint Chiefs of Staff • US/Secretary of Defense • US/President |
| Subgroups | • U.S. Army • U.S. Navy • U.S. Air Force • U.S. Marine Corps • U.S. Space Force • U.S. Coast Guard |
| Interests | Operation Ranch Hand |
| Interest of | Danny Sjursen |
See also the the Department of Defense
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States of America. The president of the United States is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces and forms military policy with the Department of Defense (DoD) and Department of Homeland Security (DHS), both federal executive departments, acting as the principal organs by which military policy is carried out.
The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard.[1] Special forces are coordinated in the U.S. Special Operations Command and the more sinister Joint Special Operations Command.
Contents
Pollution
| America’s Massive Global Military Presence Explained - TLDR News |
The United States military is one of the biggest polluters on earth,[2][3] with more impact than 140 countries combined.[4][5] It is the biggest consumer of fossil fuels on the planet when looking by organization;[citation needed] it spends $20.2 billion annually on air conditioning (!) in Iraq and Afghanistan alone, according to estimates by Pentagon officials.[6]
According to an EPA list, almost 900 of the nearly 1,200 Superfund sites across the United States are abandoned military facilities or locations that were used to support military needs. One such base, Camp Lejeune in Jacksonville, North Carolina, was held accountable for the contamination of the area’s groundwater. The military base was deemed responsible for dumping a large amount of carcinogens in the groundwater between 1953 and 1987. But only in February 2018 the federal government allowed affected individuals to file for official compensation claims.[7]
In war zones the US military has been using depleted uranium against enemy forces and burn pits to get rid of all material. Both have serious, understated health impacts on soldiers, environment (even globally) and population.
Unified Combatant Command
- Full article:
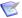 Unified Combatant Command
Unified Combatant Command
- Full article:
The US Military has divided the entire world into operational areas. There are currently 11 unified combatant commands, and each is established as the highest echelon of military commands, in order to provide effective command and control of all U.S. military forces, regardless of branch of service, during peace or during war time.[8]
An event carried out
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| Operation Ranch Hand | U.S. military herbicidal/chemical warfare operation during the Vietnam War |
A Document by US/Military
| Title | Document type | Publication date | Subject(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| File:Inside-the-wire-reference-guide.pdf | handbook | 2 February 2012 | Afghanistan/2001 Invasion | A US Army pocket reference guide given to all US military personnel serving in Afghanistan from February 2012. It provides advice on how to prevent so-called 'green-on-blue' attacks, where Afghan security forces turn their weapons on the coalition soldiers who have trained them. |
Examples
| Page name | Description |
|---|---|
| US/Air Force | |
| US/Army | |
| US/Coast Guard | |
| US/Marine Corps | |
| US/Navy |
Related Quotations
| Page | Quote | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barack Obama/Presidency | “Obama will not purge a civilian or political appointee because they have bought into Obama's ideology," - "The White House protects their own. That's why they stalled on the investigation into Fast and Furious, Benghazi and ObamaCare. He's intentionally weakening and gutting our military, Pentagon and reducing us as a superpower, and anyone in the ranks who disagrees or speaks out is being purged.” | Paul E. Vallely | 2013 |
| Toxoplasma gondii | “You want to know something terrifying? Here's something terrifying and not surprising. The U.S. military knows about Toxo and its effect on behavior. They're interested in Toxo. They're officially intrigued. An I would think they would be intrigued, studying a parasite that makes mammals perhaps do things that everything in their fiber normally tells them not to do because it's dangerous. But suddenly, with this parasite on board, the mammal is a little more likely to go and do it. Who knows? But they're aware of Toxo.” | Professor in neurology and neurosurgery Robert Sapolsky | 2 December 2009 |
Employees on Wikispooks
Event Participated in
| Event | Start | End | Location(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pacific Eclipse | 9 December 2019 | 10 December 2019 | Washington DC Phoenix Honolulu | December 2019 pandemic planning exercise. Using mathematical modelling to create scary-sounding predictions for a smallpox epidemic, the real purpose of the exercise was to indoctrinate the participants from 200 organizations in the necessity of coerced "interventions" to avoid a doomsday scenario. The indoctrination came to fruition during the fake official narrative during Covid. |
Related Documents
| Title | Type | Publication date | Author(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Document:The Pentagon’s “2015 Strategy” For Ruling the World | article | 3 July 2015 | Mike Whitney | A critique of the 2015 US National military strategy document |
| Document:US charged with war crimes in Syria prison siege | Article | 27 January 2022 | Bill Van Auken | Syria’s state media agency Sana quoted the country’s Foreign Ministry as denouncing the actions of the US and its puppet Kurdish-led militia as tantamount to “war crimes”. It demanded the immediate withdrawal of both US troops from northeastern Syria and the Turkish military from the northwest of the country. |
| File:2015 US National Military Strategy.pdf | military strategy document | July 2015 | Joint Chiefs of Staff | Offical 2015 strategy of the US military concerning its equipment, deployments and doctrines. |
| File:Defense Strategic Guidance.pdf | report | January 2012 | US Department of Defense | |
| File:Owning the Weather.pdf | paper | 1 August 1996 | Col Tamzy J. House James B. Near Jr. Lt Col William B. Shields Ronald J. Celentano David M. Husband Ann E. Mercer James E. Pugh | An official document of the US Air Force dealing with research and development of weather modification programs on a 25 year view. Its publication coincided with the start of an upsurge in public awareness and disquiet about 'Chemtrails' |
References
- ↑ https://www.defense.gov/explore/story/Article/2046035/trump-signs-law-establishing-us-space-force/
- ↑ https://www.ecowatch.com/military-largest-polluter-2408760609.html
- ↑ https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/06/190620100005.htm
- ↑ https://www.indiatimes.com/technology/science-and-future/us-armed-forces-are-bigger-polluters-than-140-countries-increasing-climate-change-in-the-world-370042.html saved at Archive.org saved at Archive.is
- ↑ https://theecologist.org/2019/jun/27/us-military-pollution
- ↑ http://www.npr.org/2011/06/25/137414737/among-the-costs-of-war-20b-in-air-conditioning saved at Archive.org saved at Archive.is
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20190411235936/https://pollution.news/2018-09-27-why-the-us-military-is-the-worlds-largest-polluter.html saved at Archive.is
- ↑ http://www.au.af.mil/au/awc/awcgate/crs/rl30245.pdf page 2