Difference between revisions of "Tor"
m (Text replacement - "1990s " to "1990s ") |
m (cons) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{concept | {{concept | ||
|type=software | |type=software | ||
| − | |logo=TOR router.png | + | |logo=TOR router.png |
| + | |on_constitutes=Privacy | ||
| + | |constitutes=Webbrowser, software, mass surveillance? | ||
|wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tor | |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tor | ||
|start=2002-09-20 | |start=2002-09-20 | ||
|website=https://www.torproject.org | |website=https://www.torproject.org | ||
| − | |description=A piece of software which claims to offer security | + | |description=A piece of software developed and made by the [[US Navy]] and [[DARPA]] which claims to offer security and privacy online. CIA withholding [[FOIA]]-requests on their work with it indicates it might be [[honey trap]]. |
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Tor''' is an acronym from '''''T'''he '''O'''nion '''R'''outer''. | + | '''Tor''' is an acronym from '''''T'''he '''O'''nion '''R'''outer'', a piece of [[open source]] software developed by the US military to complicate identity detection online. Widely used, its ''de facto'' [[cryptographic]] security remains a matter of debate. In September 2014, the [[CIA]] refused a [[FOIA request]] on the ground of exemptions b1 (classified information pertaining to an Executive Order) and b3 (information that another federal statute protects).<ref>http://documents.theblackvault.com/documents/cia/cia-torbrowser.pdf</ref> The [[FBI]] was more responsive in 2015.<ref>https://www.wired.com/2014/12/fbi-metasploit-tor/</ref> |
| + | |||
==Official narrative== | ==Official narrative== | ||
| − | TOR directs [[Internet]] traffic through a free, worldwide, volunteer network consisting of over 6000 relays. It is routed through several such routers, and users strong cryptography which provides effective anonymity. An extract of a | + | TOR directs [[Internet]] traffic through a free, worldwide, volunteer network consisting of over 6000 relays. It is routed through several such routers, and users strong cryptography which provides effective anonymity. An extract of a top secret appraisal by the [[NSA]] characterized Tor as "the King of high-secure, low-latency Internet anonymity" with "no contenders for the throne in waiting".<ref>http://www.theguardian.com/world/interactive/2013/oct/04/tor-high-secure-internet-anonymity</ref> |
==History== | ==History== | ||
[[File:Geographies of Tor.png|thumb|A [[cartogram]] illustrating Tor usage]] | [[File:Geographies of Tor.png|thumb|A [[cartogram]] illustrating Tor usage]] | ||
| − | The core principle of Tor, "onion routing", was developed in the mid-[[1990s]] by [[United States Naval Research Laboratory]] employees, [[mathematician]] [[Paul Syverson]] and [[computer scientist]]s [[Michael G. Reed]] and [[David Goldschlag]], with the purpose of protecting U.S. [[United States Intelligence Community|intelligence]] communications online. Onion routing was further developed by [[DARPA]] in 1997.<ref> | + | The core principle of Tor, "onion routing", was developed in the mid-[[1990s]] by [[United States Naval Research Laboratory]] employees, [[mathematician]] [[Paul Syverson]] and [[computer scientist]]s [[Michael G. Reed]] and [[David Goldschlag]], with the purpose of protecting U.S. [[United States Intelligence Community|intelligence]] communications online. Onion routing was further developed by [[DARPA]] in 1997.<ref>[http://books.google.com/books?id=qM0uxPH8RasC&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+Armed+Forces:+Instrument+of+Peace,+Strength,+Development+and+Prosperity&hl=en&sa=X&ei=_-oAVKD1J8uMyAS41IGYCA&ved=0CCoQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=The%20Armed%20Forces%3A%20Instrument%20of%20Peace%2C%20Strength%2C%20Development%20and%20Prosperity&f=false Fagoyinbo, Joseph Babatunde (2013-05-24). The Armed Forces: Instrument of Peace, Strength, Development and Prosperity. AuthorHouse. ISBN 9781477226476. Retrieved 29 August 2014]</ref><ref>[http://books.google.com/books?id=qGLjvFNuaM4C&printsec=frontcover&dq=WikiLeaks:+Inside+Julian+Assange%27s+War+on+Secrecy&hl=en&sa=X&ei=gesAVP36NNGPyATnhYLoCQ&ved=0CB8Q6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=WikiLeaks%3A%20Inside%20Julian%20Assange%27s%20War%20on%20Secrecy&f=false Leigh, David; Harding, Luke (2011-02-08). WikiLeaks: Inside Julian Assange's War on Secrecy. PublicAffairs. ISBN 1610390628. Retrieved 29 August 2014.]</ref>[http://books.google.com/books?id=PFGelEx4LT4C&lpg=PP1&dq=Malware%20Analyst%27s%20Cookbook%20and%20DVD%3A%20Tools%20and%20Techniques&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q=Malware%20Analyst%27s%20Cookbook%20and%20DVD:%20Tools%20and%20Techniques&f=false Ligh, Michael; Adair, Steven; Hartstein, Blake; Richard, Matthew (2010-09-29). Malware Analyst's Cookbook and DVD: Tools and Techniques for Fighting Malicious Code. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118003367. Retrieved 29 August 2014.]</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ===Developers=== | ||
| + | The [[alpha version]] of Tor, developed by Syverson and computer scientists [[Roger Dingledine]] and [[Nick Mathewson]]<ref name=":0">http://pando.com/2014/07/16/tor-spooks/</ref> and then called The Onion Routing project, or TOR project, launched on 20 September 2002. On 13 August 2004, Syverson, Dingledine and Mathewson presented "Tor: The Second-Generation Onion Router" at the 13th [[USENIX]] Security Symposium. In 2004, the Naval Research Laboratory released the source code for Tor under a free licence, and the [[Electronic Frontier Foundation]] (EFF) began funding Dingledine and Mathewson to continue its development.<ref name=":0"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Matt Edman]], who worked with the Tor Project for a year until 2009, was subsequently employed by a defence contractor working for the FBI to develop anti-Tor malware.<ref>http://www.techeye.net/news/tor-developer-helps-spooks-hack-tor</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Wikileaks== | ||
| + | [[Julian Assange]], who founded [[Wikileaks]] stated in 2006 that he had already "received over one million documents from 13 countries". The ''[[New Yorker]]'' and then ''[[Wired]]'' both claimed that these were not knowingly submitted to the site, but captured by him since as he ran a modified Tor exit node, and the documents had been entrusted to the Tor network.<ref>http://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2010/06/07/no-secrets</ref><ref>http://www.wired.com/2010/06/wikileaks-documents/</ref> Asked to clarify whether this was true by ''[[The Register]]'', Assange denied the charge, stating that "The imputation is incorrect. The facts concern a 2006 investigation into Chinese espionage one of our contacts were involved in. Somewhere between none and handful of those documents were ever released on WikiLeaks. Non-government targets of the Chinese espionage, such as Tibetan associations were informed (by us)."<ref>http://www.theregister.co.uk/2010/06/02/wikileaks_tor_snooping_denial/</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Concerns== | ||
| + | {{YouTubeVideo | ||
| + | |code=pvBAaUPzvBQ | ||
| + | |align=left | ||
| + | |width=400px | ||
| + | |caption= Hundreds of Tor Relays are Being Used to De-anonymize Users - Mental Outlaw | ||
| + | |date=2022 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | Cryptographic security and possible exploits of software aside, the Tor network, the way it is currently operating, is not able to ensure the anonymity for all of its users against an adversary that can monitor large portions of the Internet traffic. | |
| − | ==Hacks== | + | Although Tor is an open source project, the history of the software, its popularity - and the fact that the US government continues to fund it - raises a major red flag. In February 2018 the journalist [[Yasha Levine]] has released e-mail communication received through [[FOIA]] dating back to 2007 from Tor founder Dingledine to his contacts at the [[Broadcasting Board of Governors]] about a technical problem concerning TLS connections which made Tor traffic stand out from all the rest and made it easy to fingerprint and single out people who were using Tor from the background data noise of the internet.<ref>https://surveillancevalley.com/blog/claim-tor-does-not-provide-backdoors-to-the-u-s-government</ref> According to Levine it took years for the Torproject to communicate the problem through their official channels. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Purposes=== | ||
| + | Several individual hackers have developed methods to somewhat compromise the supposed anonymity it provides, and its does not seem unlikely that the [[NSA]] has a suite of software designed to unmask Tor users. If this is in fact the case, then Tor is in fact worse than useless, as it draws attention to the user.<ref>http://www.zdnet.com/article/fbi-used-hacking-team-services-to-unmask-tor-user/#!</ref><ref>https://hackertarget.com/tor-exit-node-visualization/</ref><ref>http://motherboard.vice.com/en_ca/read/badonion-honeypot-malicious-tor-exit-nodes</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | A FOIA request to the [[FBI]] by the [[Black Vault]] indicated a June 2013 record indicating that the FBI was concerned about [[Onion Pi]], an implementation of Tor for the [[Raspberry Pi]], observing that although it "improves the ease and portability of accessing the Tor network, it is too early to tell whether [[extremist]] actors will widely adopt the device to conceal nefarious activity."<ref>http://documents.theblackvault.com/documents/fbifiles/FBI-Tor.pdf</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Hacks=== | ||
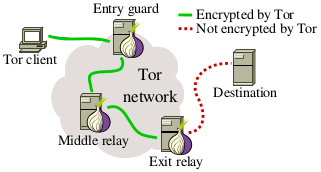
[[image:Tor network.png|right]] | [[image:Tor network.png|right]] | ||
TOR routes internet traffic through many computers and uses multiple layers of cryptography. The last step (handled by an ''exit node'') is of qualitatively different to the other steps. A lot of attacks against the Tor software focus on exit nodes. | TOR routes internet traffic through many computers and uses multiple layers of cryptography. The last step (handled by an ''exit node'') is of qualitatively different to the other steps. A lot of attacks against the Tor software focus on exit nodes. | ||
| − | In 2013 | + | A 2013 research paper came to conclude that: '80% of all types of users may be deanonymized by a relatively moderate Tor-relay adversary within six months' - with far greater success the more resources are available.<ref>http://archive.is/9riI3</ref> In 2013 ''[[Gizmodo]]'' reported that the [[FBI]] admitted "hacking into the tor network" to collect users' IP addresses.<ref>http://gizmodo.com/the-fbi-just-admitted-to-hacking-into-the-tor-network-1310273550</ref> |
| − | In 2015, Roger Dingledine | + | In 2015, Roger Dingledine accused [[Carnegie Mellon University]] of providing its Tor-breaking research in secret to the [[FBI]] in exchange for a payment of “at least $1 million.”<ref>http://www.wired.com/2015/11/tor-says-feds-paid-carnegie-mellon-1m-to-help-unmask-users</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
In July 2016, researchers announced that over 72 days they had found at least 110 malicious Tor nodes which were spying on hidden services.<ref>https://motherboard.vice.com/read/over-100-snooping-tor-nodes-have-been-spying-on-dark-web-sites</ref> | In July 2016, researchers announced that over 72 days they had found at least 110 malicious Tor nodes which were spying on hidden services.<ref>https://motherboard.vice.com/read/over-100-snooping-tor-nodes-have-been-spying-on-dark-web-sites</ref> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Deanonymization== |
| − | + | In 2019, a hack revealed that the [[FSB]] was paying [[SyTech]] to work on de-anonymising Tor.<ref>https://www.zdnet.com/article/hackers-breach-fsb-contractor-expose-tor-deanonymization-project/</ref> | |
{{SMWDocs}} | {{SMWDocs}} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 06:43, 8 September 2023
(Webbrowser, software, mass surveillance?) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | software |
| Start | 2002-09-20 |
| Interest of | • Jacob Applebaum • Roger Dingledine • Matt Edman • Yasha Levine • John Young |
| A piece of software developed and made by the US Navy and DARPA which claims to offer security and privacy online. CIA withholding FOIA-requests on their work with it indicates it might be honey trap. | |
Tor is an acronym from The Onion Router, a piece of open source software developed by the US military to complicate identity detection online. Widely used, its de facto cryptographic security remains a matter of debate. In September 2014, the CIA refused a FOIA request on the ground of exemptions b1 (classified information pertaining to an Executive Order) and b3 (information that another federal statute protects).[1] The FBI was more responsive in 2015.[2]
Contents
Official narrative
TOR directs Internet traffic through a free, worldwide, volunteer network consisting of over 6000 relays. It is routed through several such routers, and users strong cryptography which provides effective anonymity. An extract of a top secret appraisal by the NSA characterized Tor as "the King of high-secure, low-latency Internet anonymity" with "no contenders for the throne in waiting".[3]
History
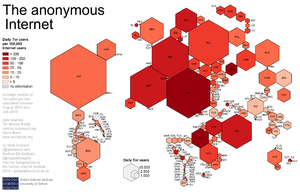
The core principle of Tor, "onion routing", was developed in the mid-1990s by United States Naval Research Laboratory employees, mathematician Paul Syverson and computer scientists Michael G. Reed and David Goldschlag, with the purpose of protecting U.S. intelligence communications online. Onion routing was further developed by DARPA in 1997.[4][5]Ligh, Michael; Adair, Steven; Hartstein, Blake; Richard, Matthew (2010-09-29). Malware Analyst's Cookbook and DVD: Tools and Techniques for Fighting Malicious Code. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118003367. Retrieved 29 August 2014.</ref>
Developers
The alpha version of Tor, developed by Syverson and computer scientists Roger Dingledine and Nick Mathewson[6] and then called The Onion Routing project, or TOR project, launched on 20 September 2002. On 13 August 2004, Syverson, Dingledine and Mathewson presented "Tor: The Second-Generation Onion Router" at the 13th USENIX Security Symposium. In 2004, the Naval Research Laboratory released the source code for Tor under a free licence, and the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) began funding Dingledine and Mathewson to continue its development.[6]
Matt Edman, who worked with the Tor Project for a year until 2009, was subsequently employed by a defence contractor working for the FBI to develop anti-Tor malware.[7]
Wikileaks
Julian Assange, who founded Wikileaks stated in 2006 that he had already "received over one million documents from 13 countries". The New Yorker and then Wired both claimed that these were not knowingly submitted to the site, but captured by him since as he ran a modified Tor exit node, and the documents had been entrusted to the Tor network.[8][9] Asked to clarify whether this was true by The Register, Assange denied the charge, stating that "The imputation is incorrect. The facts concern a 2006 investigation into Chinese espionage one of our contacts were involved in. Somewhere between none and handful of those documents were ever released on WikiLeaks. Non-government targets of the Chinese espionage, such as Tibetan associations were informed (by us)."[10]
Concerns
| Hundreds of Tor Relays are Being Used to De-anonymize Users - Mental Outlaw |
Cryptographic security and possible exploits of software aside, the Tor network, the way it is currently operating, is not able to ensure the anonymity for all of its users against an adversary that can monitor large portions of the Internet traffic.
Although Tor is an open source project, the history of the software, its popularity - and the fact that the US government continues to fund it - raises a major red flag. In February 2018 the journalist Yasha Levine has released e-mail communication received through FOIA dating back to 2007 from Tor founder Dingledine to his contacts at the Broadcasting Board of Governors about a technical problem concerning TLS connections which made Tor traffic stand out from all the rest and made it easy to fingerprint and single out people who were using Tor from the background data noise of the internet.[11] According to Levine it took years for the Torproject to communicate the problem through their official channels.
Purposes
Several individual hackers have developed methods to somewhat compromise the supposed anonymity it provides, and its does not seem unlikely that the NSA has a suite of software designed to unmask Tor users. If this is in fact the case, then Tor is in fact worse than useless, as it draws attention to the user.[12][13][14]
A FOIA request to the FBI by the Black Vault indicated a June 2013 record indicating that the FBI was concerned about Onion Pi, an implementation of Tor for the Raspberry Pi, observing that although it "improves the ease and portability of accessing the Tor network, it is too early to tell whether extremist actors will widely adopt the device to conceal nefarious activity."[15]
Hacks
TOR routes internet traffic through many computers and uses multiple layers of cryptography. The last step (handled by an exit node) is of qualitatively different to the other steps. A lot of attacks against the Tor software focus on exit nodes.
A 2013 research paper came to conclude that: '80% of all types of users may be deanonymized by a relatively moderate Tor-relay adversary within six months' - with far greater success the more resources are available.[16] In 2013 Gizmodo reported that the FBI admitted "hacking into the tor network" to collect users' IP addresses.[17]
In 2015, Roger Dingledine accused Carnegie Mellon University of providing its Tor-breaking research in secret to the FBI in exchange for a payment of “at least $1 million.”[18]
In July 2016, researchers announced that over 72 days they had found at least 110 malicious Tor nodes which were spying on hidden services.[19]
Deanonymization
In 2019, a hack revealed that the FSB was paying SyTech to work on de-anonymising Tor.[20]
A Tor victim on Wikispooks
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Dilawar | A taxi driver who was in the wrong place at the the wrong time. Tortured while in US custody and dead within the week. A leaked autopsy revealed "homicide", but the US authorities have not taken any action in this regard. |
Related Quotations
| Page | Quote | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptome | “Cryptome raises serious questions that nobody else on the left or in the media want to talk about, including how Omidar has created a business from Snowden's cache; what exactly Snowden may have been doing while he was working for the CIA prior to his time at NSA (and what else he may have been doing at NSA itself); and why Snowden and The Intercept continue to proselytize for Tor, the anonymization tool, despite its massive funding from the U.S. government, the Pentagon and the national security state.” | Tim Shorrock | February 2016 |
| Roger Dingledine | “The United States government can’t simply run an anonymity system for everybody and then use it themselves only. Because then every time a connection came from it people would say, “Oh, it’s another CIA agent.” If those are the only people using the network.”” | Roger Dingledine | 2004 |
References
- ↑ http://documents.theblackvault.com/documents/cia/cia-torbrowser.pdf
- ↑ https://www.wired.com/2014/12/fbi-metasploit-tor/
- ↑ http://www.theguardian.com/world/interactive/2013/oct/04/tor-high-secure-internet-anonymity
- ↑ Fagoyinbo, Joseph Babatunde (2013-05-24). The Armed Forces: Instrument of Peace, Strength, Development and Prosperity. AuthorHouse. ISBN 9781477226476. Retrieved 29 August 2014
- ↑ Leigh, David; Harding, Luke (2011-02-08). WikiLeaks: Inside Julian Assange's War on Secrecy. PublicAffairs. ISBN 1610390628. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- ↑ a b http://pando.com/2014/07/16/tor-spooks/
- ↑ http://www.techeye.net/news/tor-developer-helps-spooks-hack-tor
- ↑ http://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2010/06/07/no-secrets
- ↑ http://www.wired.com/2010/06/wikileaks-documents/
- ↑ http://www.theregister.co.uk/2010/06/02/wikileaks_tor_snooping_denial/
- ↑ https://surveillancevalley.com/blog/claim-tor-does-not-provide-backdoors-to-the-u-s-government
- ↑ http://www.zdnet.com/article/fbi-used-hacking-team-services-to-unmask-tor-user/#!
- ↑ https://hackertarget.com/tor-exit-node-visualization/
- ↑ http://motherboard.vice.com/en_ca/read/badonion-honeypot-malicious-tor-exit-nodes
- ↑ http://documents.theblackvault.com/documents/fbifiles/FBI-Tor.pdf
- ↑ http://archive.is/9riI3
- ↑ http://gizmodo.com/the-fbi-just-admitted-to-hacking-into-the-tor-network-1310273550
- ↑ http://www.wired.com/2015/11/tor-says-feds-paid-carnegie-mellon-1m-to-help-unmask-users
- ↑ https://motherboard.vice.com/read/over-100-snooping-tor-nodes-have-been-spying-on-dark-web-sites
- ↑ https://www.zdnet.com/article/hackers-breach-fsb-contractor-expose-tor-deanonymization-project/