Difference between revisions of "Stockholm International Peace Research Institute"
(general expand) |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|interests=peace, arms trade | |interests=peace, arms trade | ||
|leaders= | |leaders= | ||
| − | |logo= | + | |logo=LogoName RGB SIPRI.jpg |
|start=6 May 1966 | |start=6 May 1966 | ||
|abbreviation=SIPRI | |abbreviation=SIPRI | ||
|twitter= | |twitter= | ||
| − | |||
|headquarters=Stockholm, Sweden | |headquarters=Stockholm, Sweden | ||
| + | |members=Jan Eliasson,Vladimir Baranovsky,Jean-Marie Guéhenno,Dan Smith,Patricia Lewis,Espen Barth Eide,Radha Kumar,Jessica Tuchman Mathews,Ramtane Lamamra | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Stockholm International Peace Research Institute''' ('''SIPRI''') provides data about the global [[arms trade]]. | The '''Stockholm International Peace Research Institute''' ('''SIPRI''') provides data about the global [[arms trade]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | SIPRI's stated organizational purpose is to conduct scientific research in issues on conflict and cooperation of importance for international peace and security, with the goal of contributing to an understanding for the conditions for a peaceful solution of international conflicts and sustainable peace. | ||
==Origins== | ==Origins== | ||
In 1964, [[Prime Minister of Sweden]] [[Tage Erlander]] put forward the idea of establishing a peace research institute to commemorate Sweden's 150 years of unbroken [[peace]]. | In 1964, [[Prime Minister of Sweden]] [[Tage Erlander]] put forward the idea of establishing a peace research institute to commemorate Sweden's 150 years of unbroken [[peace]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A Swedish Royal Commission chaired by Ambassador [[Alva Myrdal]] proposed in its [[1966]] report to establish an institute, later named the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, SIPRI. The institute's research should seek to contribute to "the understanding of the preconditions for a stable peace and for peaceful solutions of international conflicts" and the Commission recommended that research be concentrated on armaments, their limitation and reduction, and arms control. The commission also recommended that SIPRI work is of "an applied research character directed towards practical-political questions [which] should be carried on in a constant interchange with research of a more theoretical kind". | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Swedish Riksdag decided that the Institute be established on 1 July 1966 with the legal status of an independent foundation. All SIPRI research is based exclusively on open sources. | ||
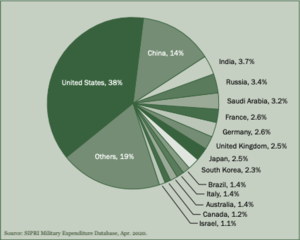
| + | [[File:SIPRI World Military Expenditure 2019.png|thumb|SIPRI is useful for its statistics, like its yearly World Military Expenditure (here for 2019)]] | ||
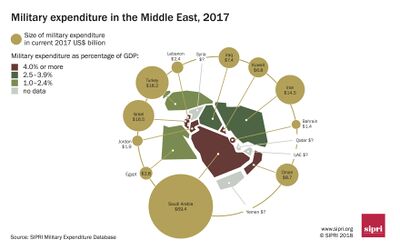
| + | [[File:Fig.1 Military expenditure Middle East.jpg|thumb|400px|Middle East military expenditures.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==People== | ||
| + | The staff of about 70 employees is mainly international, with 25 different nationalities reported in 2019<ref>https://www.sipri.org/news/2020/sipri-releases-annual-review-2019</ref>. The researchers are recruited for specific project periods and represent various academic disciplines. SIPRI also hosts guest researchers who work on issues related to research programmes as well as interns in relevant fields whose programmes of study can contribute to and benefit from SIPRI's research. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The members listed above are the board per 2020<ref>https://www.sipri.org/about/organization/board</ref>. They are not war hawks, but the board composition has a tendency towards apparatchiks (like [[Espen Barth Eide]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Former Governing Board Chairpersons: | ||
| + | * [[Alva Myrdal]] (1966–67) | ||
| + | * [[Gunnar Myrdal]] (1967–73) | ||
| + | * [[Rolf Edberg]] (1974–78) | ||
| + | * [[Hans Blix]] (1978) | ||
| + | * [[Karin Söder]] (1978–79) | ||
| + | * Rolf Björnerstedt (1979–85) | ||
| + | * Ernst Michanek (1985–87) | ||
| + | * Inga Thorsson (1987–91) | ||
| + | * [[Daniel Tarschys]] (1992–2000) | ||
| + | * [[Rolf Ekeus]] (2000–10) | ||
| + | * [[Göran Lennmarker]] (2010–14) | ||
| + | * [[Sven-Olof Petersson]] (2014–2017) | ||
{{SMWDocs}} | {{SMWDocs}} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 04:08, 12 February 2021
 | |
| Abbreviation | SIPRI |
| Formation | 6 May 1966 |
| Headquarters | Stockholm, Sweden |
| Interests | peace, arms trade |
| Sponsored by | Norway/Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Swedish Postcode Foundation |
| Membership | • • Vladimir Baranovsky • • Dan Smith • Patricia Lewis • • Radha Kumar • • Ramtane Lamamra |
The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) provides data about the global arms trade.
SIPRI's stated organizational purpose is to conduct scientific research in issues on conflict and cooperation of importance for international peace and security, with the goal of contributing to an understanding for the conditions for a peaceful solution of international conflicts and sustainable peace.
Origins
In 1964, Prime Minister of Sweden Tage Erlander put forward the idea of establishing a peace research institute to commemorate Sweden's 150 years of unbroken peace.
A Swedish Royal Commission chaired by Ambassador Alva Myrdal proposed in its 1966 report to establish an institute, later named the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, SIPRI. The institute's research should seek to contribute to "the understanding of the preconditions for a stable peace and for peaceful solutions of international conflicts" and the Commission recommended that research be concentrated on armaments, their limitation and reduction, and arms control. The commission also recommended that SIPRI work is of "an applied research character directed towards practical-political questions [which] should be carried on in a constant interchange with research of a more theoretical kind".
The Swedish Riksdag decided that the Institute be established on 1 July 1966 with the legal status of an independent foundation. All SIPRI research is based exclusively on open sources.
People
The staff of about 70 employees is mainly international, with 25 different nationalities reported in 2019[1]. The researchers are recruited for specific project periods and represent various academic disciplines. SIPRI also hosts guest researchers who work on issues related to research programmes as well as interns in relevant fields whose programmes of study can contribute to and benefit from SIPRI's research.
The members listed above are the board per 2020[2]. They are not war hawks, but the board composition has a tendency towards apparatchiks (like Espen Barth Eide).
Former Governing Board Chairpersons:
- Alva Myrdal (1966–67)
- Gunnar Myrdal (1967–73)
- Rolf Edberg (1974–78)
- Hans Blix (1978)
- Karin Söder (1978–79)
- Rolf Björnerstedt (1979–85)
- Ernst Michanek (1985–87)
- Inga Thorsson (1987–91)
- Daniel Tarschys (1992–2000)
- Rolf Ekeus (2000–10)
- Göran Lennmarker (2010–14)
- Sven-Olof Petersson (2014–2017)
Related Quotation
| Page | Quote | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jan Øberg | “There are lots of ways of securing and making peace in the world, but we're not supposed to discuss them. The military-industrial-media-academic-complex prevents us from doing that. You can't do that as a state financed institute. You could look at SIPRI, they don't do peace research anymore if they ever did, they do security studies, peace has been dropped. Most of the peace research institutes in Scandinavia don't do peace research, defined as reducing violence.” | Jan Øberg | November 2024 |
Known members
6 of the 11 of the members already have pages here:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Espen Barth Eide | Attended the 2013 Bilderberg as Norwegian Minister of Foreign Affairs |
| Jan Eliasson | Swedish diplomat |
| Jean-Marie Guéhenno | French globalist diplomat with many ties to the making of defense and security policies. |
| Jessica Mathews | Carnegie Endowment for International Peace President, Far heavier Bilderberg habit than her husband (a US general), former(?) Steering Committee member |
| Emma Rothschild | Panelist on the discussion Is There Work For All? at the 1985 Bilderberg |
| Michael Sahlin | Swedish diplomat on the Swedish Submarine Protection Commission, which was part of a deep state psy-op against the government. |
Sponsors
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| Norway/Ministry of Foreign Affairs | A significant donor to NGOs and planning organizations. Many of the recipients dovetail with NATO objectives like regime changes and controlling the narrative. |
| Swedish Postcode Foundation |