Guayana Esequiba
(Disputed territory) | |
|---|---|
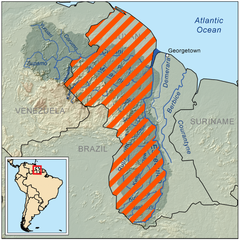 | |
| A territory administered by Guyana and claimed by Venezuela. |
Guayana Esequiba is a territory administered by Guyana and claimed by Venezuela.
The territory was first included in the Viceroyalty of New Granada and the Captaincy General of Venezuela by Spain, but was later included in Essequibo by the Dutch and in British Guiana by the United Kingdom.
Originally, parts of what is now eastern Venezuela were included in the disputed area. The portion today under the administration of Guyana divides the area in six administrative regions (Barima-Waini, Cuyuni-Mazaruni, Pomeroon-Supenaam, Potaro-Siparuni, Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo and Essequibo Islands-West Demerara), while Venezuela treats it as a single entity (Guayana Esequiba or "Zona en Reclamación").
This territory of 159,500 km2 (61,600 sq mi) is the subject of a long-running boundary dispute inherited from the colonial powers and complicated by the independence of Guyana in 1966. The status of the territory is subject to the Treaty of Geneva, which was signed by the United Kingdom, Venezuela and British Guiana on 17 February 1966. This treaty stipulates that the parties will agree to find a practical, peaceful and satisfactory solution to the dispute.[1]
Related Document
| Title | Type | Publication date | Author(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Document:What’s Not Being Said About the Venezuela Oil War | Article | 17 February 2019 | William Engdahl | The Venezuela Oil War Is Really About Huge Oil Reserves in the District of Guayana Esequiba |
References
Wikipedia is not affiliated with Wikispooks. Original page source here