Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership
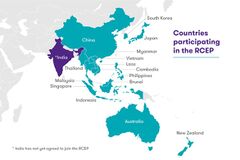 | |
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a free trade agreement in the Asia-Pacific region between the ten ASEAN states (i.e. Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam) and five of their FTA partners – Australia, China, Japan, New Zealand, and South Korea. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population and gross world product, making it the largest trade bloc.[1] It was signed at the Vietnam-hosted virtual ASEAN Summit on 15 November 2020,[2][3] and is expected to take effect within two years, after it has been ratified by the member countries.[4]
The trade pact, which includes a mix of high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries, was conceived at the 2011 ASEAN Summit in Bali,[5] while its negotiations were formally launched during the 2012 ASEAN Summit in Cambodia.[6]
The RCEP is the first free trade agreement between China, Japan, and South Korea (three of the four largest economies in Asia), and is the first multilateral free trade agreement to include China. At the time it was signed, analysts predicted it would help stimulate the economy amid the COVID-19 pandemic, and "pull the economic centre of gravity towards Asia."[7]
References
- ↑ "India stays away from RCEP talks in Bali"
- ↑ "Asia-Pacific nations sign world's largest trade pact RCEP"
- ↑ "15 countries, including Singapore, sign RCEP, the world's largest trade pact"
- ↑ "RCEP: Asia-Pacific nations sign world’s biggest trade pact"
- ↑ "Archived copy"
- ↑ "RCEP: Challenges and Opportunities for India, 25 July 2013, RSIS, Singapore"
- ↑ "What is RCEP and what does an Indo-Pacific free-trade deal offer China?
Wikipedia is not affiliated with Wikispooks. Original page source here