Difference between revisions of "Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty"
(Inaugurating) |
m (tidy references,description) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Event | {{Event | ||
|image=CTBT_Participation.svg.png | |image=CTBT_Participation.svg.png | ||
| + | |constitutes=treaty | ||
|image_width=300px | |image_width=300px | ||
|image_caption=Participation in the [[CTBT]] | |image_caption=Participation in the [[CTBT]] | ||
|wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comprehensive_Nuclear-Test-Ban_Treaty | |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comprehensive_Nuclear-Test-Ban_Treaty | ||
| + | |locations=New York City | ||
| + | |description=A multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear explosions | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty''' ('''CTBT''') is a multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear explosions, for both civilian and military purposes, in all environments. It was adopted by the [[United Nations General Assembly]] on 10 September 1996 but has not entered into force as eight specific states have not ratified the treaty.<ref>''[https://fas.org/nuke/control/ctbt/chron1.htm "Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty Chronology"]''</ref> | The '''Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty''' ('''CTBT''') is a multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear explosions, for both civilian and military purposes, in all environments. It was adopted by the [[United Nations General Assembly]] on 10 September 1996 but has not entered into force as eight specific states have not ratified the treaty.<ref>''[https://fas.org/nuke/control/ctbt/chron1.htm "Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty Chronology"]''</ref> | ||
==Participation== | ==Participation== | ||
| − | The CTBT was adopted by the [[UN General Assembly]] on 10 September 1996. It opened for signature in New York on 24 September 1996,<ref>United Nations Treaty Collection (2009). ''[http://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&id=488&chapter=26&lang=en "Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty"]'', Retrieved 23 August 2009.</ref> when it was signed by 71 States, including five of the eight then nuclear-capable states. As of October 2016, 166 states have ratified the CTBT and another 17 states have signed but not ratified it.<ref> | + | The CTBT was adopted by the [[UN General Assembly]] on 10 September 1996. It opened for signature in New York on 24 September 1996,<ref>United Nations Treaty Collection (2009). ''[http://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&id=488&chapter=26&lang=en "Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty"]'', Retrieved 23 August 2009.</ref> when it was signed by 71 States, including five of the eight then nuclear-capable states. As of October 2016, 166 states have ratified the CTBT and another 17 states have signed but not ratified it.<ref>http://www.ctbto.org/the-treaty/status-of-signature-and-ratification/</ref><ref>http://www.washingtonpost.com/national/national-security/supercomputers-offer-tools-for-nuclear-testing--and-solving-nuclear-mysteries/2011/10/03/gIQAjnngdM_story.html?wpisrc=nl_tech</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | The CTBT will enter into force 180 days after the 44 states listed in Annex 2 of the treaty have ratified it. These "Annex 2 states" are states that participated in the CTBT’s negotiations between 1994 and 1996 and possessed nuclear power reactors or research reactors at that time.<ref> | + | The CTBT will enter into force 180 days after the 44 states listed in Annex 2 of the treaty have ratified it. These "Annex 2 states" are states that participated in the CTBT’s negotiations between 1994 and 1996 and possessed nuclear power reactors or research reactors at that time.<ref>https://web.archive.org/web/20110927013430/http://www.ctbto.org/press-centre/highlights/2008/the-russian-federations-support-for-thecomprehensive-nuclear-test-ban-treaty/14-october-2008-page-2/?textonly=1</ref> |
===Laggard states=== | ===Laggard states=== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 24: | ||
* [[India]] | * [[India]] | ||
* [[North Korea]] and | * [[North Korea]] and | ||
| − | * [[Pakistan]] have not signed it.<ref> | + | * [[Pakistan]] have not signed it.<ref>https://digitalarchive.wilsoncenter.org/document/116347</ref> |
{{SMWDocs}} | {{SMWDocs}} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:43, 6 August 2021
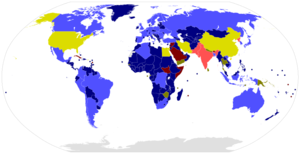 Participation in the CTBT | |
| Location | New York City |
|---|---|
| Description | A multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear explosions |
The Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (CTBT) is a multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear explosions, for both civilian and military purposes, in all environments. It was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 10 September 1996 but has not entered into force as eight specific states have not ratified the treaty.[1]
Participation
The CTBT was adopted by the UN General Assembly on 10 September 1996. It opened for signature in New York on 24 September 1996,[2] when it was signed by 71 States, including five of the eight then nuclear-capable states. As of October 2016, 166 states have ratified the CTBT and another 17 states have signed but not ratified it.[3][4]
The CTBT will enter into force 180 days after the 44 states listed in Annex 2 of the treaty have ratified it. These "Annex 2 states" are states that participated in the CTBT’s negotiations between 1994 and 1996 and possessed nuclear power reactors or research reactors at that time.[5]
Laggard states
Eight Annex 2 states have not ratified the CTBT:
- China
- Egypt
- Iran
- Israel and the
- United States have signed but not ratified the Treaty;
- India
- North Korea and
- Pakistan have not signed it.[6]
Related Document
| Title | Type | Publication date | Author(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Document:Labour Built the Bomb | Article | 10 July 2017 | Bill Ramsay | The prompt for this short essay is not Labour's nuclear legacy: it is what took place in the UN General Assembly last Friday when the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty passed into international law. |
References
- ↑ "Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty Chronology"
- ↑ United Nations Treaty Collection (2009). "Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty", Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- ↑ http://www.ctbto.org/the-treaty/status-of-signature-and-ratification/
- ↑ http://www.washingtonpost.com/national/national-security/supercomputers-offer-tools-for-nuclear-testing--and-solving-nuclear-mysteries/2011/10/03/gIQAjnngdM_story.html?wpisrc=nl_tech
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20110927013430/http://www.ctbto.org/press-centre/highlights/2008/the-russian-federations-support-for-thecomprehensive-nuclear-test-ban-treaty/14-october-2008-page-2/?textonly=1
- ↑ https://digitalarchive.wilsoncenter.org/document/116347