Intercontinental ballistic missile
(missile) | |
|---|---|
 | |
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than 5,500 kilometres (3,400 miles), primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs.
Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target.
The United States, Russia, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, Israel, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Pakistan is the only nuclear-armed state that does not possess ICBMs.[1]
Land-based ICBMs
Operational ICBMs
The United States currently operates 405 ICBMs in three USAF bases.[3] The only model deployed is LGM-30G Minuteman-III. All previous USAF Minuteman II missiles were destroyed in accordance with START II, and their launch silos have been sealed or sold to the public. The powerful MIRV-capable Peacekeeper missiles were phased out in 2005.[4]
The Russian Strategic Rocket Forces have 286 ICBMs able to deliver 958 nuclear warheads: 46 silo-based R-36M2 (SS-18), 30 silo-based UR-100N (SS-19), 36 mobile RT-2PM "Topol" (SS-25), 60 silo-based RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 18 mobile RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 84 mobile RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29), and 12 silo-based RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29).[5]
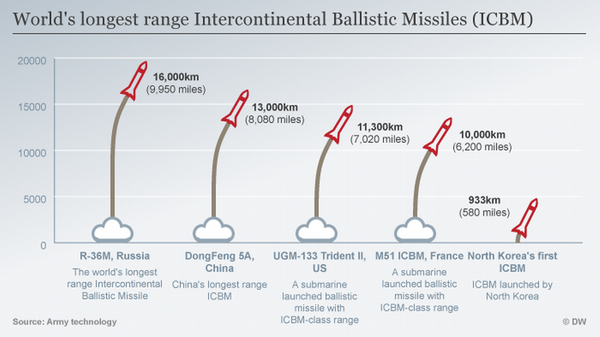
China has developed several long-range ICBMs, like the DF-31. The Dongfeng 5 or DF-5 is a 3-stage liquid fuel ICBM and has an estimated range of 13,000 kilometres. The DF-5 had its first flight in 1971 and was in operational service 10 years later. One of the downsides of the missile was that it took between 30 and 60 minutes to fuel. The Dong Feng 31 (a.k.a. CSS-10) is a medium-range, three-stage, solid-propellant intercontinental ballistic missile, and is a land-based variant of the submarine-launched JL-2.
The DF-41 or CSS-X-10 can carry up to 10 nuclear warheads, which are MIRVs and has a range of approximately 12,000–14,000 km (7,500–8,700 mi).[6][7] The DF-41 is deployed underground in Xinjiang, Qinghai, Gansu and Inner Mongolia. The mysterious underground subway ICBM carrier systems are called the "Underground Great Wall Project".[8]
Israel is believed to have deployed a road mobile nuclear ICBM, the Jericho III, which entered service in 2008. It is possible for the missile to be equipped with a single 750kg nuclear warhead or up to three MIRV warheads. It is believed to be based on the Shavit space launch vehicle and is estimated to have a range of 4,800 to 11,500 km (3,000 to 7,100 mi). In November 2011 Israel tested an ICBM believed to be an upgraded version of the Jericho III.
India has a series of ballistic missiles called Agni. On 19 April 2012, India successfully test fired its first Agni-V, a three-stage solid fuelled missile, with a strike range of more than 7,500 km (4,700 mi). Missile was test-fired for the second time on 15 September 2013. On 31 January 2015, India conducted a third successful test flight of the Agni-V from the Abdul Kalam Island facility. The test used a canisterised version of the missile, mounted over a Tata truck.[9] On 15 December 2022, the first night trial of Agni-V was successfully carried out by SFC from Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha. The missile is now 20 percent lighter because the use of composite materials rather than steel material. The range has been increased to 7,000km.
References
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/290047/ICBM
- ↑ "Israel Tests the Jericho Missile System; Iran Claims They're Being Targeted"
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20170704045256/https://www.state.gov/t/avc/newstart/272337.htm
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20121018115755/http://www.af.mil/news/story.asp?storyID=123011845
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20110514085655/http://russianforces.org/missiles/
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20150110175201/http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-09/02/content_11982723.htm
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20160408175732/http://missilethreat.com/missiles/df-41-css-x-10/?country=china
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20160129152624/http://www.powerandpolicy.com/2012/01/31/chinas-underground-great-wall-subterranean-ballistic-missile/
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20160114090146/http://www.ndtv.com/india-news/agni-5-indias-longest-range-ballistic-missile-successfully-test-fired-735955
Wikipedia is not affiliated with Wikispooks. Original page source here