COVID-19/Vaccine/Authorisation
(“COVID-19/Vaccine”, law, list) | |
|---|---|
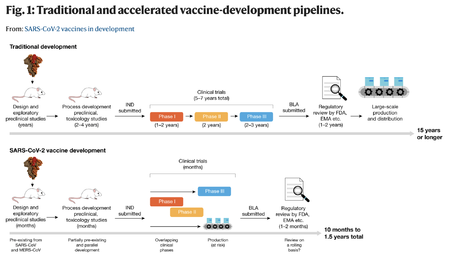 The vaccine approval process was forwarded from 15 years to 10 months | |
| Not all vaccines were authorized in all countries. |
Wikipedia lists countries by authorisation of the different COVID-19/Vaccines by country.[1] To be noted is that not all vaccines are approved everywhere, opening up for future permanent refusal of entry.
In all, it is very noticeable that the trials and approval processes seem to have been a formality - possibly in some cases for already existing products - using a number of novel technologies with unknown effects.
Contents
Change of definition for boosters
In August, 2021, the US Centers for Disease Control redefined a vaccine, from being something that “produces immunity to a specific disease”[2] to something that merely “stimulates the body’s immune response against diseases,”[3] and a vaccination no longer “produces immunity” to a disease, just “protection” from a disease. This change makes the concept sound similar to basic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or any prescription drug one have to keep taking regularly. This vague definition will make it easier for the government to recommend endless boosters for COVID.[4]
Pfizer–BioNTech approval process
- Full article: Pfizer–BioNTech
- Full article: Pfizer–BioNTech
On November 18th 2020 Pfizer and BioNTech announced they had concluded their phase three trial of BNT. They had demonstrated efficacy of 95% making it possible to give it an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. [5]
However, this 95% figure was based upon relative risk reduction. That is the declared percentage difference between the vaccinated group’s 8/18310 chance (0.044%) of developing COVID 19 against a 162/18319 (0.88%) chance of COVID 19 symptoms without the vaccine. It should be noted this only refers to an alleged reduction of COVID 19 symptoms among those who have the virus. The tested endpoints do not demonstrate that the vaccine will either reduce the spread of infection or save lives. It should also be noted that these figures suggest the threat from COVID 19 is vanishingly small.[6][7]
Media outlets, politicians, and public health officials have blared the 95% efficacy. To the casual observer, this would denote 95% reduction in hospitalizations or deaths. When in fact the 95% is calculated, based upon the “Primary Efficacy Endpoints.” In the trial literature these endpoints are described by both companies as non-severe cold/flu symptoms coupled with a positive PCR.
In absolute terms, the effectiveness of the vaccine is (0.88-0.044)% - a risk reduction of 0.84%.[6] In all, this means that according to the preliminary Pfizer-results, someone who takes the Pfizer/BioNtech injection has less than 1% chance of reducing at least one symptom of non-severe “Covid” for a period of 2 months.
In the trials, approximately 5-6 symptoms listed as “side effects” are the same as Covid symptoms. To further bias the trial, Pfizer/BioNtech only started counting “cases” one week after the second dose, and Moderna, 2 weeks after the second dose. Therefore, if these side effects were labelled as “Covid” symptoms instead, even the paltry efficacy of about 1% would be relegated into the negative integers. In others words, the injected group may have been sicker with “Covid” more than the placebo group.[8]
Sputnik V
- Full article: Sputnik V
- Full article: Sputnik V
Not approved in the European Union.
References
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_COVID-19_vaccine_authorizations
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20210826113846/https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vac-gen/imz-basics.htm
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vac-gen/imz-basics.htm
- ↑ https://pjmedia.com/news-and-politics/matt-margolis/2021/09/08/the-cdc-just-made-an-orwellian-change-to-the-definition-of-vaccine-and-vaccination-n1476799
- ↑ https://www.independent.co.uk/news/health/coronavirus-pfizer-vaccine-legal-indemnity-safety-ministers-b1765124.html
- ↑ a b https://off-guardian.org/2021/01/03/what-vaccine-trials/
- ↑ https://off-guardian.org/2021/02/22/synthetic-mrna-covid-vaccines-a-risk-benefit-analysis/
- ↑ https://off-guardian.org/2021/02/22/synthetic-mrna-covid-vaccines-a-risk-benefit-analysis/