Difference between revisions of "Mehamn Accident"
m (some tidy) |
(→Lost and found ID: tidy) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|image=WIDERØE LN-BNK.jpg | |image=WIDERØE LN-BNK.jpg | ||
|image_caption=The accident plane in 1970 | |image_caption=The accident plane in 1970 | ||
| − | |||
|start=11 March 1982 | |start=11 March 1982 | ||
|end=11 March 1982 | |end=11 March 1982 | ||
|map=Map mehamn.png | |map=Map mehamn.png | ||
| − | | | + | |locations=Barents Sea,Mehamn,Finnmark,Norway |
|description=Passenger plane that crashed because of actions of British fighter jet. The cause was covered up by 3 investigation committees, and is still not officially admitted. | |description=Passenger plane that crashed because of actions of British fighter jet. The cause was covered up by 3 investigation committees, and is still not officially admitted. | ||
| − | |constitutes=Air disaster,cover-up | + | |constitutes=Air disaster,Lost and found ID |
| + | |victim_of=cover-up | ||
}} | }} | ||
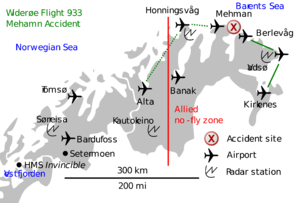
[[image:Widerøe Fligh 933 map.png|thumb|A map showing relevant sites related to Flight 933 and military activity in the area]] | [[image:Widerøe Fligh 933 map.png|thumb|A map showing relevant sites related to Flight 933 and military activity in the area]] | ||
| − | '''Widerøe Flight 933''', also known as the '''Mehamn Accident''', was the crash of a [[de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter]] operated by Norwegian airline [[Widerøe]]. The Twin Otter crashed into the [[Barents Sea]] off [[Gamvik]], [[Norway]] on 11 March 1982, killing all fifteen people on board. The crash was caused by a British fighter plane during a NATO military exercise, within a | + | '''Widerøe Flight 933''', also known as the '''Mehamn Accident''', was the crash of a [[de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter]] operated by Norwegian airline [[Widerøe]]. The Twin Otter crashed into the [[Barents Sea]] off [[Gamvik]], [[Norway]] on 11 March 1982, killing all fifteen people on board. The crash was caused by a British fighter plane during a [[NATO]] military exercise, within a no-fly zone for allied military aircraft. |
| + | |||
| + | The actual course of events is still as of 2024 still denied by the Norwegian government. | ||
==Official narrative== | ==Official narrative== | ||
The results of the four official investigations were that the accident was caused by [[structural failure]] of the [[vertical stabilizer]] during [[clear-air turbulence]]. A mechanical fault in the elevator control system caused the pilots to lose control of pitch; and either a series of stalls or a high-speed gust of wind caused the aircraft to lose altitude without the ability of the crew to counteract, resulting in the failure of the vertical stabilizer.<ref>http://www.stortinget.no/Global/pdf/Dokumentserien/2004-2005/dok24-200405.pdf</ref> | The results of the four official investigations were that the accident was caused by [[structural failure]] of the [[vertical stabilizer]] during [[clear-air turbulence]]. A mechanical fault in the elevator control system caused the pilots to lose control of pitch; and either a series of stalls or a high-speed gust of wind caused the aircraft to lose altitude without the ability of the crew to counteract, resulting in the failure of the vertical stabilizer.<ref>http://www.stortinget.no/Global/pdf/Dokumentserien/2004-2005/dok24-200405.pdf</ref> | ||
| − | + | New information led to two new investigations of the accident – in [[1988]] and [[1997]]. Both investigations were led by Lieutenant General [[Wilhelm Mohr]], who was also in charge of the investigation after the accident in 1982. The conclusion was the same every time – there had been no foreign air traffic in the crash area when the accident occurred.<ref name=vanskelige/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | A [[NRK]] documentary in 2002 led to another commission. The commission concluded in its report that there had not been a collision between the Twin Otter and other aircraft area that could have caused the accident.<ref>https://www.nrk.no/nyheter/distrikt/nrk_troms_og_finnmark/finnmark/mehamnulykken/5070031.html</ref> | ||
| + | ==Geopolitical context== | ||
| + | The accident took place far east of the geographical limit set by the Norwegian authorities for allied military aircraft in Finnmark. If there really had been foreign fighters at the scene of the accident, it would have been a gross violation of the regulations Norwegian politicians had adopted – and it would have given the then [[Soviet Union]] good reason to question other Norwegian self-imposed limitations, such as nuclear and base policy.<ref name=vanskelige/> Later exposures revealed that the NATO flights in the forbidden zone in Eastern Finnmark were part of an operation to test the effectiveness of the Soviet air warning system on the [[Kola Peninsula]].<ref name=vanskelige/> | ||
| + | ==Problems with official narrative== | ||
| + | Almost 50 witnesses on the ground independently claim that they saw alien military aircraft in the area at the time of the crash – many of them can accurately time the observations. The witnesses range from military air controllers who had seen the planes on radar and even talked to the British fighter pilots, to ordinary members of the local population who had caught small glimpses of the fighters' movements. And over the 20 years since the crash, there has been constant reports from anonymous military sources that there is information about foreign aircraft that the public has not been made aware of.<ref name=vanskelige>https://www.skup.no/sites/default/files/metoderapport/2002-43%2520Vanskeligte%2520vitner.pdf</ref> | ||
| + | ===Falsifying witness statements=== | ||
| + | School teacher Grete Mortensen has always claimed that in the first interrogation with the commission, the day after the accident, she said that just after she heard the plane crash, she saw a fighter plane coming from the accident site and flying west over Gamvik. When Grete Mortensen repeated the information to the second commission of inquiry in [[1988]], the commission refused to publish the interrogation in the report. As late as [[1998]], the air craft investigators claimed that Mortensen had not said she had seen any aircraft. Grete Mortensen, however, after several years of negotiations received a copy of the audio recording from the interrogation in [[1982]], showing with all possible clarity that she was telling the truth.<ref name=vanskelige/> | ||
| + | ==Norwegian Intelligence Service== | ||
| + | Per Gavin, at the time of the accident station chief at the military control station at Sørreisa in Troms. As a so-called "Master Controller", he was responsible for the military airspace in northern Norway during the major NATO exercise that took place in the area. He testified to [[NRK]] in 2002 that the military [[Norwegian Intelligence Service]] knew from the very moment of the accident that there had been two British aircraft in the area. He also said that the radar tape of the incident was in the custody of the spook agency.<ref name=vanskelige/> | ||
| + | ==Lost and found ID== | ||
| + | The pilot of the accident plane was never found. But the shoulder insignia from his shirt, torn off an lying orderly on the ocean floor, were found by divers.<ref>Bjørn Nilsen ''Journalist og aktivist'' page 186.</ref> | ||
| + | ==Pressure== | ||
| + | [[NRK]]'s journalist [[Bjørn Nilsen]] was reviled for having published information that pointed to the fact that the whole truth about this case had not been told.<ref name=vanskelige/> | ||
| + | Journalists who tried to investigate were attempted misled by undercover military agents<ref>As told by Bjørn Nilsen in ''Journalist og aktivist''</ref>. | ||
{{SMWDocs}} | {{SMWDocs}} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:26, 29 October 2024
 The accident plane in 1970 | |
 | |
| Date | 11 March 1982 |
|---|---|
| Location | Barents Sea, Mehamn, Finnmark, Norway |
| Description | Passenger plane that crashed because of actions of British fighter jet. The cause was covered up by 3 investigation committees, and is still not officially admitted. |
Widerøe Flight 933, also known as the Mehamn Accident, was the crash of a de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter operated by Norwegian airline Widerøe. The Twin Otter crashed into the Barents Sea off Gamvik, Norway on 11 March 1982, killing all fifteen people on board. The crash was caused by a British fighter plane during a NATO military exercise, within a no-fly zone for allied military aircraft.
The actual course of events is still as of 2024 still denied by the Norwegian government.
Contents
Official narrative
The results of the four official investigations were that the accident was caused by structural failure of the vertical stabilizer during clear-air turbulence. A mechanical fault in the elevator control system caused the pilots to lose control of pitch; and either a series of stalls or a high-speed gust of wind caused the aircraft to lose altitude without the ability of the crew to counteract, resulting in the failure of the vertical stabilizer.[1]
New information led to two new investigations of the accident – in 1988 and 1997. Both investigations were led by Lieutenant General Wilhelm Mohr, who was also in charge of the investigation after the accident in 1982. The conclusion was the same every time – there had been no foreign air traffic in the crash area when the accident occurred.[2]
A NRK documentary in 2002 led to another commission. The commission concluded in its report that there had not been a collision between the Twin Otter and other aircraft area that could have caused the accident.[3]
Geopolitical context
The accident took place far east of the geographical limit set by the Norwegian authorities for allied military aircraft in Finnmark. If there really had been foreign fighters at the scene of the accident, it would have been a gross violation of the regulations Norwegian politicians had adopted – and it would have given the then Soviet Union good reason to question other Norwegian self-imposed limitations, such as nuclear and base policy.[2] Later exposures revealed that the NATO flights in the forbidden zone in Eastern Finnmark were part of an operation to test the effectiveness of the Soviet air warning system on the Kola Peninsula.[2]
Problems with official narrative
Almost 50 witnesses on the ground independently claim that they saw alien military aircraft in the area at the time of the crash – many of them can accurately time the observations. The witnesses range from military air controllers who had seen the planes on radar and even talked to the British fighter pilots, to ordinary members of the local population who had caught small glimpses of the fighters' movements. And over the 20 years since the crash, there has been constant reports from anonymous military sources that there is information about foreign aircraft that the public has not been made aware of.[2]
Falsifying witness statements
School teacher Grete Mortensen has always claimed that in the first interrogation with the commission, the day after the accident, she said that just after she heard the plane crash, she saw a fighter plane coming from the accident site and flying west over Gamvik. When Grete Mortensen repeated the information to the second commission of inquiry in 1988, the commission refused to publish the interrogation in the report. As late as 1998, the air craft investigators claimed that Mortensen had not said she had seen any aircraft. Grete Mortensen, however, after several years of negotiations received a copy of the audio recording from the interrogation in 1982, showing with all possible clarity that she was telling the truth.[2]
Norwegian Intelligence Service
Per Gavin, at the time of the accident station chief at the military control station at Sørreisa in Troms. As a so-called "Master Controller", he was responsible for the military airspace in northern Norway during the major NATO exercise that took place in the area. He testified to NRK in 2002 that the military Norwegian Intelligence Service knew from the very moment of the accident that there had been two British aircraft in the area. He also said that the radar tape of the incident was in the custody of the spook agency.[2]
Lost and found ID
The pilot of the accident plane was never found. But the shoulder insignia from his shirt, torn off an lying orderly on the ocean floor, were found by divers.[4]
Pressure
NRK's journalist Bjørn Nilsen was reviled for having published information that pointed to the fact that the whole truth about this case had not been told.[2]
Journalists who tried to investigate were attempted misled by undercover military agents[5].
References
- ↑ http://www.stortinget.no/Global/pdf/Dokumentserien/2004-2005/dok24-200405.pdf
- ↑ a b c d e f g https://www.skup.no/sites/default/files/metoderapport/2002-43%2520Vanskeligte%2520vitner.pdf
- ↑ https://www.nrk.no/nyheter/distrikt/nrk_troms_og_finnmark/finnmark/mehamnulykken/5070031.html
- ↑ Bjørn Nilsen Journalist og aktivist page 186.
- ↑ As told by Bjørn Nilsen in Journalist og aktivist