Difference between revisions of "Great Transition Initiative"
(import as is) |
(adjusting) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{group |
| − | + | |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Transition | |
| − | '''Great Transition''' | + | |twitter= |
| + | |logo= | ||
| + | |type= | ||
| + | |start=2003 | ||
| + | |website=http://gtinitiative.org/resources/gtessay.html | ||
| + | |founders= | ||
| + | |headquarters= | ||
| + | |constitutes=think tank | ||
| + | |head= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | The '''Great Transition Initiative''' and its predecessor, the [[Global Scenario Group]] (GSG), have described visions of a just and [[sustainable global future]]. The term ''Great Transition'' was originally coined by [[Kenneth E. Boulding]] in ''The Meaning of the 20th Century – The Great Transition'' ([[1964]]) and describes the shift from pre-modern to post-modern culture, and the four possible courses of action that these organizations believe will allow humanity to successfully manage the Great Transition.<ref>https://books.google.co.uk/books/about/The_Meaning_of_the_20th_Century.html?id=u8YSAAAACAAJ&redir_esc=y</ref> | ||
| − | Elements of the Great Transition vision include egalitarian social and ecological values, increased inter-human connectivity, improved [[quality of life]], and a healthy planet, as well as the absence of poverty, war, and environmental destruction. The Great Transition concept was cited by [[List of Prime Ministers of Bhutan|Prime Minister of Bhutan]] [[Jigme Thinley]],<ref>Jigme Thinly, [http://www.cabinet.gov.bt/?page_id=207 "Address by the Prime Minister on Well-Being and Happiness,"] UN Headquarters, New York, April 2, 2012.</ref> Josh Ryan-Collins of the [[New Economics Foundation]],<ref>Josh Ryan-Collins, [ | + | Elements of the Great Transition vision include egalitarian social and ecological values, increased inter-human connectivity, improved [[quality of life]], and a healthy planet, as well as the absence of poverty, war, and environmental destruction. The Great Transition concept was cited by [[List of Prime Ministers of Bhutan|Prime Minister of Bhutan]] [[Jigme Thinley]],<ref>Jigme Thinly, [http://www.cabinet.gov.bt/?page_id=207 "Address by the Prime Minister on Well-Being and Happiness,"] UN Headquarters, New York, April 2, 2012.</ref> Josh Ryan-Collins of the [[New Economics Foundation]],<ref>Josh Ryan-Collins, [https://web.archive.org/web/20140807141842/http://www.neweconomics.org/publications/entry/the-great-transition ''Great Transition''] (London: New Economics Foundation, 2009)</ref> and the Capital Institute.<ref>[http://www.cisymposium.com/ The Capital Institute Symposium: "Beyond Sustainability: The Road to Regenerative Capitalism] New York, June 20–21, 2013, </ref> It was used as a theme for the [[2011]] SmartCSOs conference on strategies for Civil Society Organisations in London.<ref>SmartCSOs, [http://www.veblen-institute.org/Effective-change-strategies-for ''Effective Change Strategies for the Great Transition: Five Leverage Points for Civil Society Organisations''] Berlin: Smart CSOs, 2011).</ref> |
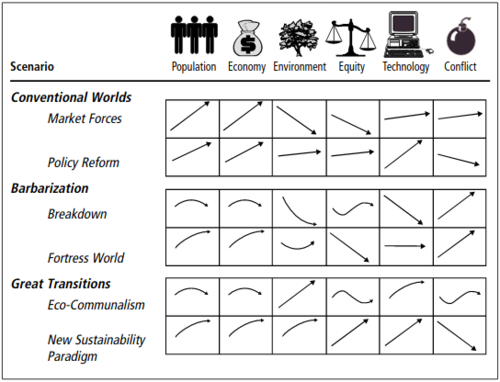
| + | [[File:Great Transitions.png|thumb|500px|right|An info graphic from the 2002 paper "Great Transition - The Promise and Lure of the Times Ahead", of the Global Scenario Group]] | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | The Great Transition was first introduced by the [[Global Scenario Group]] (GSG), an international body of scientists convened in 1995 by the [[Tellus Institute]] and [[Stockholm Environment Institute]] to examine the requirements for a transition to a sustainable global society. The GSG set out to describe and analyze scenarios for the future of the earth as it entered a [[planetary phase of civilization]].<ref>See http://www.gsg.org/gsgpub.html and Paul Raskin, Tariq Banuri, Gilberto Gallopín, Pablo Gutman, Al Hammond, Robert Kates, and Rob Swart, [http://www.greattransition.org/gt-essay ''Great Transition: The Promise and Lure of the Times Ahead''] (Boston: Stockholm Environment Institute, 2002)</ref> | + | The Great Transition was first introduced by the [[Global Scenario Group]] (GSG), an international body of scientists convened in [[1995]] by the [[Tellus Institute]] and [[Stockholm Environment Institute]] to examine the requirements for a transition to a sustainable global society. The GSG set out to describe and analyze scenarios for the future of the earth as it entered a [[planetary phase of civilization]].<ref>See http://www.gsg.org/gsgpub.html and Paul Raskin, Tariq Banuri, Gilberto Gallopín, Pablo Gutman, Al Hammond, Robert Kates, and Rob Swart, [http://www.greattransition.org/gt-essay ''Great Transition: The Promise and Lure of the Times Ahead''] (Boston: Stockholm Environment Institute, 2002)</ref> |
==Great Transition Initiative== | ==Great Transition Initiative== | ||
| + | Further development of Great Transition scenarios is carried on by the Great Transition Initiative (GTI). Launched in 2003, GTI is a global network of several hundred scholars, intellectuals, civil society leaders, and activists working to develop visions and pathways for a “Great Transition" to a future of equity, solidarity and ecological sustainability. The Initiative was relaunched as an online journal and discussion network in [[2014]]. | ||
| − | + | ===Publications=== | |
| − | + | * Parris, Thomas. "[http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00139150209605799#.VZmxB0bLdyE Bytes of Note: A Crystal Ball for Sustainability."] ''Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development''. 44, no. 7 (2002): 3-4. | |
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * Parris, Thomas. "Bytes of Note: A Crystal Ball for Sustainability." ''Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development''. 44, no. 7 (2002): 3-4 | ||
* Rajan, Chella, [http://www.tellus.org/pub/Global%20Politics%20and%20Institutions.pdf ''Global Politics and Institutions'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006. | * Rajan, Chella, [http://www.tellus.org/pub/Global%20Politics%20and%20Institutions.pdf ''Global Politics and Institutions'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006. | ||
* Raskin, Paul. [http://www.tellus.org/pub/Global%20Politics%20and%20Institutions.pdf ''GT Today: A Report from the Future'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006. | * Raskin, Paul. [http://www.tellus.org/pub/Global%20Politics%20and%20Institutions.pdf ''GT Today: A Report from the Future'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006. | ||
*Raskin, Paul. [http://www.greattransition.org/publication/journey-to-earthland ''Journey to Earthland: A Great Transition to Planetary Civilization'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2016. | *Raskin, Paul. [http://www.greattransition.org/publication/journey-to-earthland ''Journey to Earthland: A Great Transition to Planetary Civilization'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2016. | ||
| − | * Revkin, Andy. [http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2002/09/0904_020904_wirimpact.html ''Human Impact on the Earth - How Do We Soften It?''] ''[International Herald Tribune]''. September 4, 2002. | + | * Revkin, Andy. [https://web.archive.org/web/20021003063230/http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2002/09/0904_020904_wirimpact.html ''Human Impact on the Earth - How Do We Soften It?''] ''[[International Herald Tribune]]''. September 4, 2002. |
* Stutz, John. [http://www.tellus.org/pub/The%20Role%20of%20Well-being%20in%20a%20Great%20Transition.pdf ''The Role of Well-Being in a Great Transition'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006. | * Stutz, John. [http://www.tellus.org/pub/The%20Role%20of%20Well-being%20in%20a%20Great%20Transition.pdf ''The Role of Well-Being in a Great Transition'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006. | ||
* White, Allen. [http://www.tellus.org/tellus/publication/transforming-the-corporation ''Transforming the Corporation'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006. | * White, Allen. [http://www.tellus.org/tellus/publication/transforming-the-corporation ''Transforming the Corporation'']. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| Line 40: | Line 35: | ||
* [http://www.gsg.org Global Scenario Group] | * [http://www.gsg.org Global Scenario Group] | ||
* [http://www.popsci.com/ffff Popular Science - Four Futures] - an article in Popular Science about the Great Transition and three other GSG scenarios, with infographics | * [http://www.popsci.com/ffff Popular Science - Four Futures] - an article in Popular Science about the Great Transition and three other GSG scenarios, with infographics | ||
| − | * [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FS7o4g5kzMM | + | * [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FS7o4g5kzMM Visions of a Sustainable World] - a video with highlights from an interview with Dr. [[Paul Raskin]] of GSG and the [[Tellus Institute]] (from a speaker series at [[Yale University]]) |
| − | {{ | + | {{PageCredit |
| + | |site=Wikipedia | ||
| + | |date=06 June 2021 | ||
| + | |url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Transition | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | {{SMWDocs}} | |
| − | + | ==References== | |
| − | + | {{reflist}} | |
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 20:16, 6 June 2021
(Think tank) | |
|---|---|
| Formation | 2003 |
The Great Transition Initiative and its predecessor, the Global Scenario Group (GSG), have described visions of a just and sustainable global future. The term Great Transition was originally coined by Kenneth E. Boulding in The Meaning of the 20th Century – The Great Transition (1964) and describes the shift from pre-modern to post-modern culture, and the four possible courses of action that these organizations believe will allow humanity to successfully manage the Great Transition.[1]
Elements of the Great Transition vision include egalitarian social and ecological values, increased inter-human connectivity, improved quality of life, and a healthy planet, as well as the absence of poverty, war, and environmental destruction. The Great Transition concept was cited by Prime Minister of Bhutan Jigme Thinley,[2] Josh Ryan-Collins of the New Economics Foundation,[3] and the Capital Institute.[4] It was used as a theme for the 2011 SmartCSOs conference on strategies for Civil Society Organisations in London.[5]
History
The Great Transition was first introduced by the Global Scenario Group (GSG), an international body of scientists convened in 1995 by the Tellus Institute and Stockholm Environment Institute to examine the requirements for a transition to a sustainable global society. The GSG set out to describe and analyze scenarios for the future of the earth as it entered a planetary phase of civilization.[6]
Great Transition Initiative
Further development of Great Transition scenarios is carried on by the Great Transition Initiative (GTI). Launched in 2003, GTI is a global network of several hundred scholars, intellectuals, civil society leaders, and activists working to develop visions and pathways for a “Great Transition" to a future of equity, solidarity and ecological sustainability. The Initiative was relaunched as an online journal and discussion network in 2014.
Publications
- Parris, Thomas. "Bytes of Note: A Crystal Ball for Sustainability." Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development. 44, no. 7 (2002): 3-4.
- Rajan, Chella, Global Politics and Institutions. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006.
- Raskin, Paul. GT Today: A Report from the Future. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006.
- Raskin, Paul. Journey to Earthland: A Great Transition to Planetary Civilization. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2016.
- Revkin, Andy. Human Impact on the Earth - How Do We Soften It? International Herald Tribune. September 4, 2002.
- Stutz, John. The Role of Well-Being in a Great Transition. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006.
- White, Allen. Transforming the Corporation. Boston: Tellus Institute, 2006.
External links
- Great Transition Initiative
- Global Scenario Group
- Popular Science - Four Futures - an article in Popular Science about the Great Transition and three other GSG scenarios, with infographics
- Visions of a Sustainable World - a video with highlights from an interview with Dr. Paul Raskin of GSG and the Tellus Institute (from a speaker series at Yale University)
Wikipedia is not affiliated with Wikispooks. Original page source here
References
- ↑ https://books.google.co.uk/books/about/The_Meaning_of_the_20th_Century.html?id=u8YSAAAACAAJ&redir_esc=y
- ↑ Jigme Thinly, "Address by the Prime Minister on Well-Being and Happiness," UN Headquarters, New York, April 2, 2012.
- ↑ Josh Ryan-Collins, Great Transition (London: New Economics Foundation, 2009)
- ↑ The Capital Institute Symposium: "Beyond Sustainability: The Road to Regenerative Capitalism New York, June 20–21, 2013,
- ↑ SmartCSOs, Effective Change Strategies for the Great Transition: Five Leverage Points for Civil Society Organisations Berlin: Smart CSOs, 2011).
- ↑ See http://www.gsg.org/gsgpub.html and Paul Raskin, Tariq Banuri, Gilberto Gallopín, Pablo Gutman, Al Hammond, Robert Kates, and Rob Swart, Great Transition: The Promise and Lure of the Times Ahead (Boston: Stockholm Environment Institute, 2002)