Difference between revisions of "Plutocracy"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Video) |
(Added: wikiquote.) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|image_width=500px | |image_width=500px | ||
|namebase=http://www.namebase.net/books21.html | |namebase=http://www.namebase.net/books21.html | ||
| + | |wikiquote=http://en.wikiquote.org/wiki/Plutocracy | ||
}} | }} | ||
The [[United States]] was "designed as a Plutocracy – but even the limited forms of representation allotted to people by the “Founding Fathers” are impossible when you have a massive and largely unaccountable [[shadow government]]."<ref>[[Document:Counter-Intelligence: Spying Deters Democracy]]</ref> | The [[United States]] was "designed as a Plutocracy – but even the limited forms of representation allotted to people by the “Founding Fathers” are impossible when you have a massive and largely unaccountable [[shadow government]]."<ref>[[Document:Counter-Intelligence: Spying Deters Democracy]]</ref> | ||
Revision as of 13:49, 23 November 2018
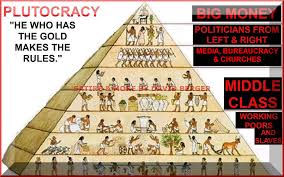 | |
The United States was "designed as a Plutocracy – but even the limited forms of representation allotted to people by the “Founding Fathers” are impossible when you have a massive and largely unaccountable shadow government."[1]
| Robin Upton explains the role of the Bank of England in the history of plutocracy between 8:36 and 12:31 minutes into this video. |
History
The roots of plutocracy go back as far as agriculture, and the increase in social group size leading to the invention of money.[2]
Many thanks to our Patrons who cover ~2/3 of our hosting bill. Please join them if you can.