Difference between revisions of "Vulture fund"
(Upgrade formatting) |
(More references and legal restrictions) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|constitutes= | |constitutes= | ||
}} | }} | ||
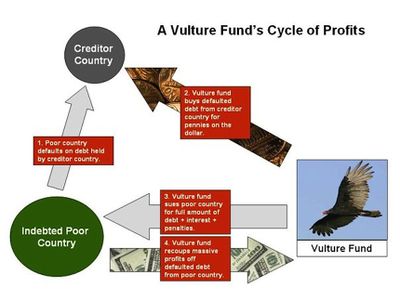
| − | '''Vulture funds''' are usually{{clarify}} a private equity group or fund that buys defaulted [[debt]] that belongs to individuals, companies or nations. They | + | '''Vulture funds''' are usually{{clarify}} a private equity group or fund that buys defaulted [[debt]] that belongs to individuals, companies or nations. They are criticised as being ruthless<ref>http://www.thisismoney.co.uk/money/markets/article-4542838/How-vulture-lord-son-make-billions.html</ref> in pursuing the debt they have purchased, often negating any gains the debtor has made in managing the debt or pursuing debt relief. They also often engage in payments to government, paying well connected [[lobbyist]]s or making large donations to political parties. |
[[image:Vulture Fund explanation.jpg|left|400px]] | [[image:Vulture Fund explanation.jpg|left|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Legal restrictions== | ||
| + | The [[United Kingdom]] was the first country to impose a legal limit on vulture funds. Since 8 April 2010, vulture funds may not collect payments that the [[World Bank]] deems "unsustainable".<ref>Croft, Adrian. [http://uk.reuters.com/article/idUKTRE63748920100408 "New law limits claims by vulture funds"], Reuters UK website, posted 8 April 2010, accessed 10 April 2010.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | On September 9, 2014, the [[UN]] voted 124-11 to create an "historic" new treaty to deal with bankruptcy process of [[nation states]], limiting their exploitation by vulture funds.<ref>[https://www.indybay.org/newsitems/2014/09/09/18761405.php ''International''] "UN Votes for Process to Enact Bankruptcy Treaty and Stop Vulture Funds", 2014</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Victim nations== | ==Victim nations== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 19: | ||
===Peru=== | ===Peru=== | ||
| − | In 1996 [[Paul Elliot Singer]] purchased Peruvian debt for $11M and then threatened to sue unless he received the full $58M. | + | In 1996 [[Paul Elliot Singer]] purchased Peruvian debt for $11M and then threatened to sue unless he received the full $58M.<ref>http://foreignpolicy.com/2014/08/03/a-short-history-of-vultures/</ref> |
===Congo=== | ===Congo=== | ||
| − | [[Peter Grossman]] purchased the Congolese debt for a Bosnian state company, [[EnergoInvest]] for $2.6M. He then successfully sued the DRC for $100M. | + | [[Peter Grossman]] purchased the Congolese debt for a Bosnian state company, [[EnergoInvest]] for $2.6M. He then successfully sued the DRC for $100M.<ref>https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2011/nov/15/vulture-funds-key-players</ref> |
===Argentina=== | ===Argentina=== | ||
Revision as of 10:33, 18 November 2017
 | |
Vulture funds are usually[clarification needed] a private equity group or fund that buys defaulted debt that belongs to individuals, companies or nations. They are criticised as being ruthless[1] in pursuing the debt they have purchased, often negating any gains the debtor has made in managing the debt or pursuing debt relief. They also often engage in payments to government, paying well connected lobbyists or making large donations to political parties.
Contents
Legal restrictions
The United Kingdom was the first country to impose a legal limit on vulture funds. Since 8 April 2010, vulture funds may not collect payments that the World Bank deems "unsustainable".[2]
On September 9, 2014, the UN voted 124-11 to create an "historic" new treaty to deal with bankruptcy process of nation states, limiting their exploitation by vulture funds.[3]
Victim nations
Zambia
Romania loaned $40M to Zambia to buy tractors in 1979, in 1999 unable to keep up the payments they negotiated to settle the debt for $3M but before this could happen Debt Advisory International stepped in and purchased the debt for $4M they then commenced to sue for the original amount plus interest.[4]
Peru
In 1996 Paul Elliot Singer purchased Peruvian debt for $11M and then threatened to sue unless he received the full $58M.[5]
Congo
Peter Grossman purchased the Congolese debt for a Bosnian state company, EnergoInvest for $2.6M. He then successfully sued the DRC for $100M.[6]
Argentina
Examples
- Michael Sheehan - Debt Advisory International, Donegal International
- Paul Singer - Elliot Management Corporation - Paul Singer is a major donor to the Republican Party
- Peter Grossman[7] - FG Capital Management
References
- ↑ http://www.thisismoney.co.uk/money/markets/article-4542838/How-vulture-lord-son-make-billions.html
- ↑ Croft, Adrian. "New law limits claims by vulture funds", Reuters UK website, posted 8 April 2010, accessed 10 April 2010.
- ↑ International "UN Votes for Process to Enact Bankruptcy Treaty and Stop Vulture Funds", 2014
- ↑ http://america.aljazeera.com/articles/2014/3/22/the-end-of-vulturefunds.html
- ↑ http://foreignpolicy.com/2014/08/03/a-short-history-of-vultures/
- ↑ https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2011/nov/15/vulture-funds-key-players
- ↑ https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2011/nov/15/vulture-funds-key-players