Difference between revisions of "Confirmation bias"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(desc) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Confirmation_bias | |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Confirmation_bias | ||
|image=Confirmation bias on search engines.png | |image=Confirmation bias on search engines.png | ||
| + | |image_width=440px | ||
|description=The preference people have to avoid [[cognitive dissonance]] by homing in on information which meets their expectations | |description=The preference people have to avoid [[cognitive dissonance]] by homing in on information which meets their expectations | ||
|constitutes=bias | |constitutes=bias | ||
Latest revision as of 18:24, 1 March 2022
(bias) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Interest of | |
| The preference people have to avoid cognitive dissonance by homing in on information which meets their expectations | |
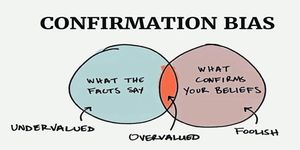
Confirmation bias is a bias which reflects the cognitive dissonance inherent in unexpected ideas. People tend to be more likely to take on board evidence of things they already believe than to accept things which challenge their current worldview and so necessitate a re-think.
Importance
This psychological phenomenon is of great importance in successfully controlling the narrative.
Many thanks to our Patrons who cover ~2/3 of our hosting bill. Please join them if you can.