Difference between revisions of "Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease"
(Redirected page to Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease) Tag: New redirect |
(redirect) Tag: Removed redirect |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{concept | |
| + | |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Creutzfeldt%E2%80%93Jakob_disease | ||
| + | |constitutes=disease | ||
| + | |image=Practneurol-2016-001571f02.jpg | ||
| + | |image_caption=Magnetic resonance image of sporadic CJD | ||
| + | |description=A fatal degenerative brain disorder. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, and visual disturbances. Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, weakness, and coma. About 70% of people die within a year of diagnosis. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | '''Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease''' ('''CJD'''), also known as '''subacute spongiform encephalopathy''' or '''neurocognitive disorder due to prion disease''', is a fatal [[neurodegeneration|degenerative]] [[brain disorder]].<ref name=NIH2003/><ref name=CDC2015Main>https://www.cdc.gov/prions/cjd/index.html</ref> Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, and visual disturbances.<ref name=NIH2003/> Later symptoms include [[dementia]], involuntary movements, blindness, weakness, and [[coma]].<ref name=NIH2003/> About 70% of people die within a year of diagnosis.<ref name=NIH2003/> The name Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease was introduced by [[Walther Spielmeyer]] in 1922, after the German neurologists [[Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt]] and [[Alfons Maria Jakob]].<ref>http://www.whonamedit.com/synd.cfm/696.html Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Cause and diagnosis --> | ||
| + | CJD is caused by a type of abnormal protein known as a [[prion]].<ref name=CDC2019>https://www.cdc.gov/prions/cjd/index.html |website=www.cdc.gov</ref> Infectious prions are [[protein folding|misfolded]] proteins that can cause normally folded proteins to also become misfolded.<ref name=NIH2003/> About 85% of cases of CJD occur for unknown reasons, while about 7.5% of cases are [[heredity|inherited from a person's parents]] in an [[autosomal dominant]] manner.<ref name=NIH2003/> Exposure to brain or spinal tissue from an infected person may also result in spread.<ref name=NIH2003/> There is no evidence that sporadic CJD can spread between people via normal contact or [[blood transfusions]], although this is possible in [[variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease]].<ref>https://www.transfusionguidelines.org/transfusion-handbook/5-adverse-effects-of-transfusion/5-4-variant-creutzfeldt-jakob-disease-vcjd</ref> Diagnosis involves ruling out other potential causes.<ref name=NIH2003/> An [[electroencephalogram]], [[Lumbar puncture|spinal tap]], or [[magnetic resonance imaging]] may support the diagnosis.<ref name=NIH2003/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is no specific treatment for CJD.<ref name=NIH2003>https://web.archive.org/web/20170704234755/https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Creutzfeldt-Jakob-Disease-Fact-Sheet</ref> [[Opioids]] may be used to help with pain, while [[clonazepam]] or [[sodium valproate]] may help with involuntary movements.<ref name=NIH2003/> CJD affects about one per million people per year.<ref name=NIH2003/> Onset is typically around 60 years of age.<ref name=NIH2003/> The condition was first described in 1920.<ref name=NIH2003/> It is classified as a type of [[transmissible spongiform encephalopathy]].<ref>https://web.archive.org/web/20170808104028/https://www.cdc.gov/prions/cjd/about.html</ref> Inherited CJD accounts for about 10% of prion disease cases.<ref name=Man2015>https://doi.org/10.3171%2F2015.8.FOCUS15328</ref> Sporadic CJD is different from [[bovine spongiform encephalopathy]] (mad cow disease) and [[variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease]] (vCJD).<ref name=CDC2015Ind>https://web.archive.org/web/20170718154357/https://www.cdc.gov/prions/cjd/index.html|a</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{SMWDocs}} | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | {{reflist}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{PageCredit | ||
| + | |site=Wikipedia | ||
| + | |date=31.08.2021 | ||
| + | |url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Creutzfeldt%E2%80%93Jakob_disease | ||
| + | }} | ||
Revision as of 13:32, 2 September 2021
(disease) | |
|---|---|
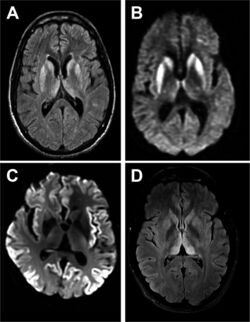 Magnetic resonance image of sporadic CJD | |
| A fatal degenerative brain disorder. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, and visual disturbances. Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, weakness, and coma. About 70% of people die within a year of diagnosis. |
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD), also known as subacute spongiform encephalopathy or neurocognitive disorder due to prion disease, is a fatal degenerative brain disorder.[1][2] Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, and visual disturbances.[1] Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, weakness, and coma.[1] About 70% of people die within a year of diagnosis.[1] The name Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease was introduced by Walther Spielmeyer in 1922, after the German neurologists Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Maria Jakob.[3]
CJD is caused by a type of abnormal protein known as a prion.[4] Infectious prions are misfolded proteins that can cause normally folded proteins to also become misfolded.[1] About 85% of cases of CJD occur for unknown reasons, while about 7.5% of cases are inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant manner.[1] Exposure to brain or spinal tissue from an infected person may also result in spread.[1] There is no evidence that sporadic CJD can spread between people via normal contact or blood transfusions, although this is possible in variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease.[5] Diagnosis involves ruling out other potential causes.[1] An electroencephalogram, spinal tap, or magnetic resonance imaging may support the diagnosis.[1]
There is no specific treatment for CJD.[1] Opioids may be used to help with pain, while clonazepam or sodium valproate may help with involuntary movements.[1] CJD affects about one per million people per year.[1] Onset is typically around 60 years of age.[1] The condition was first described in 1920.[1] It is classified as a type of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy.[6] Inherited CJD accounts for about 10% of prion disease cases.[7] Sporadic CJD is different from bovine spongiform encephalopathy (mad cow disease) and variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD).[8]
A Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease victim on Wikispooks
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| José Baselga | Chief cancer researcher at AstraZeneca dies at 61 of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, possibly an effect of the Covid jab. |
References
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n https://web.archive.org/web/20170704234755/https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Creutzfeldt-Jakob-Disease-Fact-Sheet
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/prions/cjd/index.html
- ↑ http://www.whonamedit.com/synd.cfm/696.html Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/prions/cjd/index.html |website=www.cdc.gov
- ↑ https://www.transfusionguidelines.org/transfusion-handbook/5-adverse-effects-of-transfusion/5-4-variant-creutzfeldt-jakob-disease-vcjd
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20170808104028/https://www.cdc.gov/prions/cjd/about.html
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.3171%2F2015.8.FOCUS15328
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20170718154357/https://www.cdc.gov/prions/cjd/index.html%7Ca
Wikipedia is not affiliated with Wikispooks. Original page source here