Difference between revisions of "Media Bias/Fact Check"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
The [[Atlantic Council]] have used data from MBFC.{{cn}} | The [[Atlantic Council]] have used data from MBFC.{{cn}} | ||
| − | The site was used by researchers at the [[University of Michigan]] to create a tool called the "Iffy Quotient", which draws data from ''Media Bias/Fact Check'' and ''[[NewsWhip]]'' to track the prevalence of 'fake news' and questionable sources on social media.<ref>{{Cite web |author=Dian Schaffhauser|url=https://campustechnology.com/articles/2018/10/16/u-m-tracker-measures-reliability-of-news-on-facebook-twitter.aspx |title=U-M Tracker Measures Reliability of News on Facebook, Twitter -- Campus Technology |website=Campus Technology |language=en |access-date=2018-12-03}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://csmr.umich.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/UMSI-CSMR-Iffy-Quotient-Whitepaper-810084.pdf|author1=Paul Resnick|author2=Aviv Ovadya|author3=Garlin Gilchrist|work=School of Information - Center for Social Media Responsibility|title=Iffy Quotient: A Platform Health Metric for Misinformation|publisher=University of Michigan|page=5}}</ref> The site was also used by a research group at the [[Massachusetts Institute of Technology]] in initial training of an AI to fact | + | The site was used by researchers at the [[University of Michigan]] to create a tool called the "Iffy Quotient", which draws data from ''Media Bias/Fact Check'' and ''[[NewsWhip]]'' to track the prevalence of 'fake news' and questionable sources on social media.<ref>{{Cite web |author=Dian Schaffhauser|url=https://campustechnology.com/articles/2018/10/16/u-m-tracker-measures-reliability-of-news-on-facebook-twitter.aspx |title=U-M Tracker Measures Reliability of News on Facebook, Twitter -- Campus Technology |website=Campus Technology |language=en |access-date=2018-12-03}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://csmr.umich.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/UMSI-CSMR-Iffy-Quotient-Whitepaper-810084.pdf|author1=Paul Resnick|author2=Aviv Ovadya|author3=Garlin Gilchrist|work=School of Information - Center for Social Media Responsibility|title=Iffy Quotient: A Platform Health Metric for Misinformation|publisher=University of Michigan|page=5}}</ref> The site was also used by a research group at the [[Massachusetts Institute of Technology]] in initial training of an [[AI]] to do "[[fact checking]]" and detect the [[bias]] of a [[website]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.popsci.com/AI-fake-news|title=This AI can help spot biased websites and false news|last=Verger|first=Rob|date=2018-10-04|website=Popular Science|language=en|access-date=2019-01-01}}</ref> |
==Criticism== | ==Criticism== | ||
Revision as of 10:08, 6 December 2019
Started: November 2015
Founder: Dave Van Zandt
In its own words:
"Dedicated to educating the public on media bias and deceptive news practices"
Constitutes: “fact checker”
Main focus: fake news, bias, media
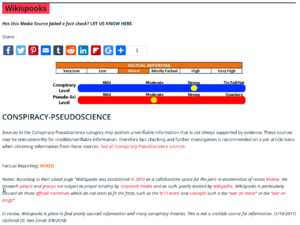
Media Bias/Fact Check (MBFC) is a "fact checker" which scores websites on "conspiracy level", "pseudo-sci level" and "left- or right wing bias, and by quality of factual reporting. MBFC has browser extensions for both Firefox and Chrome.
Official narrative
MBFC reports that it was started by Dave Van Zandt[1] in 2015[2] and has some volunteers who perform source research, writing and assist in fact checking. Van Zandt has a small internet footprint.[3]
Endorsement
The Atlantic Council have used data from MBFC.[citation needed]
The site was used by researchers at the University of Michigan to create a tool called the "Iffy Quotient", which draws data from Media Bias/Fact Check and NewsWhip to track the prevalence of 'fake news' and questionable sources on social media.[4][5] The site was also used by a research group at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in initial training of an AI to do "fact checking" and detect the bias of a website.[6]
Criticism
The Palmer Report published an article in April 2017 entitled Scam site “Media Bias Fact Check” caught cribbing its ratings from Wikipedia.[7]
The Poynter Institute wrote that "Media Bias/Fact Check is a widely cited source for news stories and even studies about misinformation, despite the fact that its method is in no way scientific."[8]
The site was #2 on a list of Zero Hedge's Top 9 “fakest ‘fake-news’ checkers.”[3]
Trusted websites
MBFC's most trusted fact checking websites, as of December 2019, were FactCheck.org, FactChecker, Flack Check, Hoax-Slayer, Open Secrets, PolitiFact, Poynter Institute, Snopes, Sunlight Foundation and Truth or Fiction.[9]
References
- ↑ https://mediabiasfactcheck.com/about/
- ↑ https://mediabiasfactcheck.com/contact/
- ↑ a b https://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-02-20/exposing-9-fakest-fake-news-checkers
- ↑ Dian Schaffhauser. "U-M Tracker Measures Reliability of News on Facebook, Twitter -- Campus Technology". Campus Technology. Retrieved 2018-12-03.Page Module:Citation/CS1/styles.css must have content model "Sanitized CSS" for TemplateStyles (current model is "Scribunto").
- ↑ Paul Resnick; Aviv Ovadya; Garlin Gilchrist. "Iffy Quotient: A Platform Health Metric for Misinformation" (PDF). School of Information - Center for Social Media Responsibility. University of Michigan. p. 5.Page Module:Citation/CS1/styles.css must have content model "Sanitized CSS" for TemplateStyles (current model is "Scribunto").
- ↑ Verger, Rob (2018-10-04). "This AI can help spot biased websites and false news". Popular Science. Retrieved 2019-01-01.Page Module:Citation/CS1/styles.css must have content model "Sanitized CSS" for TemplateStyles (current model is "Scribunto").
- ↑ https://www.palmerreport.com/politics/scam-site-media-bias-fact-check-caught-cribbing-its-ratings-from-wikipedia/2342/
- ↑ https://www.poynter.org/fact-checking/2018/heres-what-to-expect-from-fact-checking-in-2019/
- ↑ https://mediabiasfactcheck.com/fact-check-resources/