Stockholm Network
 | |
| Formation | September 1997 |
| Founder | • Helen Disney • Rick Nye |
| Type | think tank |
| Subpage | •Stockholm Network/Funding •Stockholm Network/History |
The Stockholm Network is a working group of more than 120 market-oriented think tanks from across Europe created by Helen Disney and Rick Nye of pollsters Populus. It calls itself "a one-stop shop for organisations seeking to work with Europe’s brightest policymakers and thinkers" and claims to have "the capacity to deliver local messages and locally-tailored global messages across the EU and beyond."[1] The network churns out thousands of op-eds in the "high-quality European press", produces hundreds of publications and holds several conferences, seminars and meetings to "influence many millions of Europeans every year."[2] Helen Disney, the Stockholm Network's founder and director, describes it as "not a think tank, as such, but a networking service for think tanks across Europe."[3]
Writing in The Times in December 2005, Paul Staines wrote that the Stockholm Network "turns out to be in fact the public face of Market House International, a PR consultancy that tells corporate clients that the network gives it 'local capacity to deliver both local messages and locally tailored global messages in a wide range of countries'." [4]
Contents
History
- Full article: Stockholm Network/History
- Full article: Stockholm Network/History
The Stockholm Network was founded in September 1997[5] From 2001 the network became part of Civitas, which was formerly known as the Health and Welfare Unit of the Institute for Economic Affairs.[6] In late 2003 Helen Disney and Rick Nye, who worked together at the Social Market Foundation, created the private company Market House International, a Public Relations (PR) consultancy, in order to run the Stockholm Network.[7] In 2008 the International Policy Network reportedly left the Stockholm Network.[8] The Liberalni Institute left the Stockholm Network on the 29th January 2009, shortly after the publication of the report on the UK pharmaceutical industry.
Stockholm Network Programmes
The Network is described as a forum for "sharing, exchanging and developing pan-European research and best practice."[9] The Network states that it has three programmes of work as follows:
- Energy and Environment programme
- Intellectual Property and Competition programme
- Health and Welfare programme[10]
In order to promote ideas to stimulate economic growth, the Stockholm Network concentrates on a familiar litany of free market policy measures and ideas: 'Reforming European welfare states' and 'creating a more flexible labour market'; 'Ensuring more consumer-driven healthcare','Encouraging an informed debate on intellectual property rights'; 'Reforming European energy markets to ensure the most beneficial balance between economic growth and environmental quality'; 'Emphasising the benefits of globalisation, trade and competition and creating an understanding of free market ideas and institutions.'[11]
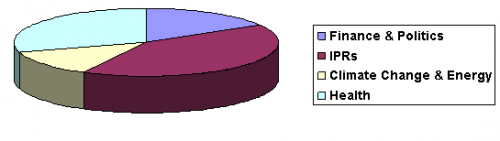
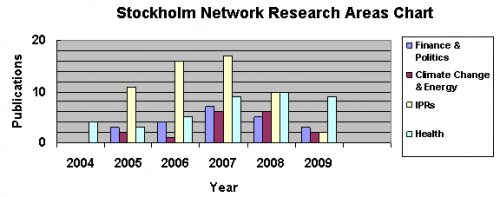
Energy and Environment programme
The SN Energy and Environment Programme was established in 2005 to promote a ‘practical market-oriented approach to meeting our future energy challenges while also addressing environmental and climate change concerns.’ [14]
Climate Change
In the same year, SN commissioned a Populus poll and produced a report which made for ‘uncomfortable reading for campaigners’.[15] Authors Helen Disney and Dan Lewis concluded: ‘Britons don't believe the environment should be at the top of the priority list of policy-makers, but they don't want it to be just an add-on extra either.’[16] The Heritage Foundation used the SN’s findings in its own analysis on climate change claiming ‘…69 percent of British people see businesses as the most effective agents in combating threats to the environment, and 74 percent agreed that technological innovation, rather than government intervention, is the best way of dealing with future environmental challenges.’[17] In 2008, the SN published Carbon Scenarios describing three ‘different possible futures that result from the differentiated substance and implementation of possible climate policies’. [18] One of the paper’s contributors, Mark Lynas, explained one potential scenario in the Guardian:
- ’Instead of all the complexity of regulating squabbling nations and billions of people, the price mechanism does the work: companies simply pass on their increased costs to consumers, and demand for carbon intensive products begins to fall.’[19]
Wondering ‘whether business as usual – on climate policy as much as economics – will condemn us all to climate oblivion’, [20] Lynas neglected to mention that representatives from BP and Shell had also participated in the project.[21] In a piece for the New Statesman, Lynas attacks climate sceptics for being affiliated with US-based conservative think tanks:
"’Many climate-change sceptics like to think they are proudly independent people, refusing to be cowed by UN-sponsored orthodoxy from the IPCC. In fact, the arguments of climate sceptics have largely been moulded by a far more sinister force - the US-based conservative think tanks. A recent academic survey of environmentally sceptical books found that 92 per cent were linked with these think tanks, which include the Heritage Foundation, the Cato Institute and the Competitive Enterprise Institute. Since the early 1990s, these and other industry-funded front groups have been leading an anti-environmental backlash, changing the tenor of the political debate on environmental issues and bombarding the media and the public with disinformation.’[22]
Lynas makes no reference to the Stockholm Network’s own connections to the Heritage Foundation and the Cato Institute and the funding it receives from industry giants such as Exxon Mobil (see sections on History, Funding and US Connections).
Intellectual Property and Competition programme
The SN Intellectual Property and Competition Programme was set up in January 2005 aiming to:
- ‘make the field of intellectual property more mainstream and accessible to the general public’
- ‘increase the interaction between specialists focusing on different aspects of intellectual property rights’
- ‘encourage discussion, as well as debates, on different burning IP issues’
- ‘promote European competitiveness’[23]
Critics claim the programme is ‘inconsistent with their radical free-market ideology’ as it ‘pursues far-reaching corporate patent protection rather than free markets.’ [24] But the SN’s Meir Pugatch insists ‘evidence shows definitively that patent protection promotes innovation.’[25] Pugatch reiterated this message at the Debating Pharmaceutical IPRs meeting in February 2007, which was co-sponsored by the UN Conference on Trade and Development and co-chaired by Helen Disney.[26] He also stressed the ‘importance of public-private partnerships’ and claimed that ‘Patent protection is more important today than ever’ – before mentioning that the Stockholm Network is part funded by the pharmaceutical industry. [27]
IPRs and Health: Pfizer and the Patent Debate
Along with financial support from Pfizer, the SN is also linked to the drugs giant through Pfizer Forum – ‘an advertorial program that was launched in The Economist in February, 1994, and now appears in leading policy and business publications worldwide.’ [28] Helen Disney has worked for the forum[29] and Meir Pugatch, SN’s Director of Research & Head of the Intellectual Property (IP) and Competition Programme and IP consultant for Timbro, has been its chair since 2003. [30] Pugatch was also responsible for establishing and chairing the Israeli Pharmaceutical and Biotechnological Think-Tank', consisting of representatives from the Government and the pharmaceutical industry (including Pfizer). [31] Other authors who have written for Pfizer Forum include SN members from the International Policy Network, the Adam Smith Institute, Centre for the New Europe, Civitas and Timbro. [32] Catherine Windels, who used to work for Pfizer and The Heritage Foundation, formerly served on the board patrons of the SN which she helped found. [33]
Pfizer was opposed to proposals to change the USA's legal structure for patents through the Patent Reform Act 2007, claiming it ‘weakened patent rights’ and reduced damages to be paid out for patent infringement.[34] Patent law changes were considered to be a victory for software firms’and a ‘defeat for research based drugmakers.’ .[35] The SN entered the debate, comparing the American model to the European Union's patent system which it described as ‘circular and ineffective at best’. The network ‘unusually, refusing[ed] to take sides,’ presumably in an effort to balance the competing interests of ‘various knowledge-based industry giants’ such as Microsoft and Pfizer, who both offered financial support to the SN in that year.[36][37].
Health and Welfare programme
The Stockholm Network's Health and Welfare Programme was set up at the end of 2005. Key aims and objectives include:[38]
- Providing a comprehensive resource on European think tank initiatives in the field of Health and Welfare
- Promoting competition and choice in healthcare, through reform of European health systems and markets
- Promoting more flexible labour markets in Europe
- Promoting market oriented reform of Europe's failing pensions systems
Prior to the establishment of the programme, Helen Disney and other ‘leading experts' – mostly members of other think tanks in the SN – had already spelled out the Malthusian ‘reality’ of European healthcare systems after analysing data from a SN and Populus commissioned study. Representatives from Timbro; the Italian free-market think tank; Istituto Bruno Leoni; the French economic think tank, Molinari Economic Institute; and the Hague-based think tank, Edmund Burke Foundation, were among the ‘experts’ who concluded ‘Europe’s health systems are no longer sustainable and will have to be overhauled.’ [39]An additional Populus poll and publication, which saw Disney collaborating with representatives from the Health Policy Institute and the Institute for Free Society among others, [40] concluded that health consumers would travel abroad to get treatments denied in their home countries and argued for an integrated health service market. Unsurprisingly, the SN welcomed the European Commission’s ensuing draft directive on patient mobility.[41]
Debates
The Science-Democracy Debate
In 2005, the Stockholm Network co-sponsored the ‘Westminster Fringe Debate’ with the motion “Democratisation of science would not be in the public interest”. According to the organisers:
“Science is driven by curiosity. Would any attempt to put that under greater public scrutiny deaden scientific inquiry or must scientists now come to terms with the fears and priorities of society at large? And is public accountability a meaningful concept in science? Scientists may not know what they are going to discover when they start experimenting or to what use it may ultimately be put. Are the public qualified to determine the priorities of scientific research? Is that untrammelled freedom for science out of date and dangerous?”[42]
Lord Dick Taverne from Sense About Science and Colin Blakemore, who was Chief Executive of the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) at the time, supported the motion which was carried.[43]
US Connections
The Stockholm Network is listed on the website for the Atlas Economic Research Foundation (AERF) [44], an American organisation based near Washington that “serves as a catalyst and connector to link free-market organizations and individuals to the ideas, people and resources they need to promote a free society.”[45] The AERF, which has received $680,000 from Exxon Mobil since 1998 (see Atlas Economic Research Foundation), has created an 'international network of free-market public policy institutes' and compiles a directory of its affiliates.[46] Other listed think tanks that are part of the AERF's 'freedom network' and the Stockholm Network include Instituto Acton; the Adam Smith Institute; Instituto Bruno Leoni; Center for Liberal-Democratic Studies; Centre for Liberal Strategies; Centre for the New Europe; Centre for Research into Post-Communist Economies; Civita; CIVITAS; European Ideas Network; International Policy Network; Libertarian Alliance; Policy Exchange; and Timbro.[47] The American Enterprise Institute; the Heritage Foundation and the Cato Institute are amongst the US-based 'freedom network' members.[48]
One of the Stockholm Network's first employees, Nicole Gray Conchar, had previously worked for the Cato Institute,[49] and from 2007 to 2008, the institute was one of the SN’s funders.[50] Catherine Windels, who used to work for Pfizer and The Heritage Foundation, formerly served on the board patrons of the SN which she helped found.[51] The foundation was also one of the SN’s funders from 2005 to 2006.[52].
Funding
- Full article: Stockholm Network/Funding
- Full article: Stockholm Network/Funding
The Stockholm Network has published a list of corporations who have made contributions to the network in its annual report for the three years between 2005-2008.[53][54][55]. As of June 2010 the latest annual report on the SN website is for 2007-2008.[56] Although the Stockholm Network don't allow any figures to be made public on the importance of each contributor a look at the interests of the network's larger supporters bears a close resemblance to the research agenda of the network.
Members
The British connection
The network was founded in London and Stockholm, though it is operated out of London and has a large contingent of UK members, however many of the UK members have left the network. Some of the British member organisations are listed as part of the British conservative movement, Movement Conservatism, including the Institute of Economic Affairs, Reform, the Adam Smith Institute, Policy Exchange, Civitas, International Policy Network.[57]
Former British Members
Adam Smith Institute - member of the SN in the years 2006-7[58] and 2007-8[59] | Centre for European Reform, No Longer Members[60] | David Hume Institute | Hayek Society | Institute of Economic Affairs, left in 2005[61] | International Policy Network | Libertarian Alliance | Nurses for Reform (Asked to leave the network in 2009)[62] | Policy Institute (though its successor body Reform Scotland is a member)| Project Empowerment | Globalization Institute
Current British Members
Business for New Europe | Centre for Policy Studies | Centre for Research into Post-Communist Economies | Civitas | E.G. West Centre | Global Vision | Open Europe | Policy Exchange | Politeia | Reform | Reform Scotland | Social Affairs Unit | Centre for Social Justice[63]
British Members
Full list of members
Adam Smith Institute, UK - member of the SN in the years 2006-7[64] and 2007-8[65] | Adam Smith Society, Italy | Adriatic Institute for Public Policy | Albanian Liberal Institute, Albania | Anders Chydenius Foundation, Finland | Association for Liberal Thinking, Turkey | Association for Modern Economy, Macedonia | Avenir Suisse, Switzerland | Bertil Ohlin Institute, Sweden | Bulgaria Society for Individual Liberty, Bulgaria | Causa Liberal, Portugal | Centre for Democracy and Free Enterprise, Czech Republic | Centre for Economic Development, Bulgaria | Centre for Economic Development, Slovakia | Centre for Economics and Politics, Czech Republic | Centre for Entrepreneurship and Economic Development, Montenegro | Centre for European Reform, UK | Centre for Institutional Analysis and Development | Centre for Liberal Strategies, Bulgaria | Centre for Liberal-Democratic Studies, Serbia | Centre for Policy Studies, UK | Centre for Political Thought, Poland | Centre for Research into Post-Communist Economies, UK | Centre for Social and Economic Research, Poland | Centre for the New Europe | Centre for the Study of Democracy, Bulgaria | Centro Einaudi, Italy | Cercles Liberaux, France | CIDAS, Italy | Civic Institute, Czech Republic | Civita, Norway | CIVITAS, United Kingdom | Conservative Institute of M. R. Stefanik, Slovakia | Council on Public Policy, Germany | David Hume Institute, United Kingdom | E.G. West Centre, UK | Economic Policy Research Institute, Macedonia | Ekome, Greece | Eudoxa, Sweden | Euro 92 (think tank), France | European Ideas Network, Brussels | European Independent Institute, The Netherlands | EVA (think tank), Finland | F. A. v. Hayek Institute, Austria | Fondazione Luigi Einaudi, Italy | Foundation for Market Economy, Hungary | Frédéric Bastiat Stichting, The Netherlands | Free Market Centre, Serbia | Freedom Institute, Ireland | Friedrich Naumann Stiftung, Germany | Friedrich von Hayek Gesellschaft, Germany | Fundacio Catalunya Oberta, Spain | Fundacion Internacional para la Libertad (FIL), Spain | Gdansk Institute for Market Economics, Poland | Hayek Foundation, Russia | Hayek Foundation, Slovakia | Hayek Society, Hungary | Hayek Society, LSE, London | Health Consumer Powerhouse, Belgium | Health Reform, Czech Republic | Hellenic Leadership Institute | IFRAP, France | Independent Institute of Socio-Economic and Political Studies, Belarus | INEKO, Slovakia | Institut Constant de Rebecque, Switzerland | Institut Economique Molinari, Belgium | Institut Hayek, Belgium | Institut Karla Havlicka Borovskeho, Czech Republic | Institut Montaigne, France | Institut Turgot, France | Institute for Economic Studies Europe, Aix-en-Provence | Institute for Free Enterprise, Germany | Institute for Free Society, Slovakia | Institute for International Relations, Croatia | Institute for Market Economics (IME), Bulgaria | Institute for Strategic Studies and Prognosis, Montenegro | Institute for Transistional Democracy and International Security, Hungary | Institute of Economic Affairs, UK (According to a Telegraph blog by Alex Singleton, the IEA left the Stockholm Network prior to January 2009)[66] | Institute of Economic Analysis, Russia | Institute of Economic Studies, Iceland | Institute of Economics (Ekonomski Institut), Croatia | Instituto Juan de Mariana, Spain | Instytut Liberalno-Konserwatywny, Poland | International Centre for Economic Research, Italy | International Council for Capital Formation, Brussels | International Policy Network, United Kingdom (According to a Telegraph blog by Alex Singleton, the IPN left the Stockholm Network prior to January 2009)[67] | Istituto Acton, Italy | Istituto Bruno Leoni, Italy | Jaan Tonisson Institut, Estonia | Jerusalem Institute for Market Studies, Israel | Konrad Adenauer Foundation, Germany | Liberales Institut, Switzerland | Liberales, Belgium | Liberalni Institute, Czech Republic | Libertarian Alliance, United Kingdom | Libertas (think tank) | Liberty Ideas, Austria | Lithuanian Free Market Institute | Ludwig von Mises Institute Europe, Brussels | Ludwig von Mises Institute, Romania | M.E.S.A. 10, Slovakia | Magna Carta Foundation, Italy | New Economic School, Georgia | New Economics School, Russia | New Social Market Economy Foundation, Germany | Nova Civitas, Belgium | Nova Res Publica, Italy | Nurses for Reform, created in 2006. | Open Europe, United Kingdom | Open Republic Institute | Poder Limitado, Spain | Policy Exchange, United Kingdom | Policy Institute, United Kingdom | Politeia, United Kingdom | Project Empowerment, United Kingdom | Ratio Institute, Sweden | Reform, United Kingdom | Riinvest Institute for Development Research, Kosovo | Romania Think Tank | Romanian Centre for Economic Policies | Sauvegarde Retraites (Save the Pensions), France | Social Affairs Unit, London | Stiftung Marktwirtschaft, Germany | Taxpayers' Alliance | Telders Foundation, Netherlands | The Copenhagen Institute, Denmark | Globalization Institute, United Kingdom | Think Tank for International Governance Research, Austria | Thomas More Institute, Belgium | Timbro, Sweden | Ukrainian Centre for Independent Political Research | Venezie Institute, Italy | Walter Eucken Institut, Germany
People
Management
The Stockholm Network does not have a board and is owned and run by Helen Disney.[68]
Staff Numbers
| Year | Staff Numbers | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1997-1998 | 3 Staff Members[69] | ||
| 1998-1999 | ? Staff Members | ||
| 1999-2000 | ? Staff Members | ||
| 2000-2001 | ? Staff Members | ||
| 2001-2002 | ? Staff Members | ||
| 2002-2003 | ? Staff Members | ||
| 2003-2004 | ? Staff Members | ||
| 2004-2005 | ? Staff Members | ||
| 2005-2006 | 5 Full Time & 4 Part Time Staff Members[70] | ||
| 2006-2007 | 6 Full Time & 5 Part Time Staff Members[71] | ||
| 2007-2008 | 15 Staff Members[72] | ||
| 2008-2009 | ? Staff Members | ||
| 2009-2010 | 5 Staff Members & 4 Fellows[73] |
Staff May 2010
- Helen Disney, Chief Executive and Founder
- Dr Meir Pugatch, Director of Research
- Dr Cristina Palomares, Chief Operating Officer
Research Officers
- Dr David Torstensson (Senior Researcher)
- Rachel Chu (Research Officer)
Fellows
- Paul Domjan (Energy Fellow)
- Jacob Arfwedson (Research Fellow), Joined 2006
- Paul Healy Policy Analyst
- Nasrin Hassam Accounts[74]
Patrons and Directors 2002-2006
In April 2002 the SN listed the following as "patrons and directors":
- Catherine Barr Windels, Patron
- PJ Anders Linder, Patron
- Hardy Bouillon ,President of the Centre for the New Europe
- David Green Director, Civitas: Institute for the Study of Civil Society
- Mattias Bengtsson, Director, Timbro
- Elisabeth Lulin, Director, Paradigmes[75]
By May 2005 Hardy Bouillon was no longer listed although the rest of the list is unchanged,[76] by January 2006 Catherine Barr Windels and PJ Anders Linder were no longer listed and no new patrons or directors were added to the list.[77]
Stockholm Network Private Company Directors 2006-Present
The PR firm Market House International was set up to 'host' the Stockholm Network. The company was changed to being directly names as the Stockholm Network in 2006.[78][79]. The companies incorporation documents list the following directors:
Former Personnel
- Anne Jensen, Project Officer, IP, Competition and Trade programme (2004-2007)
- Sacha Kumaria, is the Stockholm Network's Assistant Director.
- Peter Nolan Director of Environmental Affairs. (Left 2006)
- Terry O'Dwyer, Manager, Health and Welfare programme (2004-2006)
- Tim Evans, Director of Development (2005-2009)
- Francesca Ficai, Senior Researcher (Joined in October 2006 following a spell working for two Labour MP's)
- Shane Frith, Managing Director (Left the Network in August 2007)
- Simon Moore, Research Officer (2006-2009) (Joined following Internship)
- Katie Perrior, Media Director (July 2005-2008) (Before Joining the SN Katie Perrior 'worked for the Conservative Party Chairman and Conservative shadow home secretary during high profile campaigns'.[82] Following a spell at the SN Perrior worked on Boris Johnson's 2008 Mayoral campaign[83][84])
- Susie Squier, Office Manager (2007-2009) Joined following an internship, Left to join the Taxpayers Alliance and then to advise Iain Duncan Smith)
- Cara Walker, Head of Communications (2005-2009)(Formerly Iain Duncan Smith's secretary then directed the Atlantic Bridge think tank 2003-2005, in 2005 she worked on Michael Howard's election campaign, she joined the Stockholm Network in the same year, in 2009 she Left to join the Centre for Social Justice)
Resources
- Karen Horn, The Free-Marketeers get up. Even when the economy is in bad shape more and more think tanks get launched, Institut Economic Molinari, 11-June-2005, Accessed 26-April-2010
- SourceWatch Stockholm Network on SourceWatch
- Corporate Europe Observatory, "Covert industry funding fuels the expansion of radical rightwing EU think tanks", July 2005.
- Paul Staines, "You want policy? In cash?", The Times (London), 20 December 2005, Page 19.
- Helen Disney, Karen Horn, Pavel Hrobon, Johan Hjertqvist, Alastair Kilmarnock, Andreas Mihm, Alberto Mingardi, Cécile Philippe, David Smith, Eline van den Broek, Gerrold Verhoeks Impatient for Change: European attitudes to healthcare reform 13 May 2004.
- James Stanfield, RE: Stockholm Network, E-mail to Steven Harkins, E.G.West Centre, 10-May-2010, 9:26am
- Claire Rusbridge, FW: Stockholm Network, E-mail to Steven Harkins, Institute of Economic Affairs, 12-May-2010, 6:05pm
- Catherine Hoye, RE: Stockholm Network, E-mail to Steven Harkins, Centre for European Reform, 10-May-2010, 11:43am
- Helen Disney, RE:Stockholm Network Members, Stockholm Network, E-mail to Steven Harkins,
- Helen Disney, RE:Stockholm Network Members, Stockholm Network, 27-May-2010, 10:04, E-mail to Steven Harkins
References
- ↑ Stockholm Network. Stockholm Network: FAQs, Stockholm Network, Accessed 9 April 2010.
- ↑ Stockholm Network. Stockholm Network: About Us, Stockholm Network, Accessed 9 April 2010
- ↑ Corporate Europe Observatory,Email from Helen Disney to Corporate Europe Observatory, Corporate Europe Observatory, May 31st 2005, accessed 23 Apr 2010
- ↑ Paul Staines, You want policy? In cash?', The Times (London), 20 December 2005, Page 19.
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2006-2007:10 Years of the Stockholm Network, ISSUU, Accessed 04-May-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, About Us, Stockholm Network, Web Archive 01-April-2002, Accessed 09-May-2010
- ↑ Market House International, Certificate of Incorporation of a Private Limited Company, Companies House, 05-November-2003
- ↑ Alex Singleton, Free-market network demands bail-out for pharmaceutical industry, The Telegraph, 19-January-2009, Accessed 27-April-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network Stockholm Network: Policy Issues, Stockholm Network, Accessed 9 April 2010.
- ↑ Stockholm Network Programmes and Events Accessed 28 April 2010.
- ↑ Stockholm Network Stockholm Network: Policy Issues, Stockholm Network, Accessed 9 April 2010.
- ↑ Data displayed in this chart are based on the collection of publications available on SN’s website in April 2010. Programmes and events; media coverage and press releases; and publications from the think tank library are not included. There are several publications covering both health and research on IPRs.
- ↑ Data displayed in this chart are based on the collection of publications available on SN’s website in April 2010. Programmes and events; media coverage and press releases; and publications from the think tank library are not included. There are several publications covering both health and research on IPRs.
- ↑ Stockholm Network. Energy and Environment Programme Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ MacSmith, A. The Independent. Britain hosts energy summit while failing to meet its emission targets. 1 November 2005. Accessed 3 May 2010.
- ↑ MacSmith, A. The Independent. Britain hosts energy summit while failing to meet its emission targets. 1 November 2005. Accessed 3 May 2010.
- ↑ McNamara, S. and Lieberman, B. The Heritage Foundation. [1] 1 June 2007. Accessed 3 May 2010.
- ↑ Stockholm Network. Carbon Scenarios Accessed 3 May 2010.
- ↑ Lynas, M. The Guardian. Climate Change is Inevitable. We can only avert oblivion. 12 June 2008.
- ↑ Lynas, M. The Guardian. Climate Change is Inevitable. We can only avert oblivion. 12 June 2008.
- ↑ Domjan, P. and Isyanova, G. The Stockholm Network. Carbon Scenarios: Blue Sky Thinking for a Green Future. 2008.
- ↑ Lynas, M. New Statesman.The global warming deniers. 3 July 2008. Accessed 3 May 2010.
- ↑ The Stockholm Network. Intellectual Property Accessed 5 May 2010.
- ↑ Corporate Europe Observatory.Covert industry funding fuels the expansion of radical rightwing EU think tanks. July 2005. Accessed 5 May 2010.
- ↑ New, W. Intellectual Property Watch. Informative Debate On IP And Drug Price Model, Flexibilities 26 February 2010. Accessed 5 May 2010.
- ↑ UNITED NATIONS CONFERENCE ON TRADE AND DEVELOPMENT. Debating Pharmaceutical IPRs - A joint UNCTAD - Stockholm Network event Accessed 5 May 2010.
- ↑ New, W. Intellectual Property Watch. Informative Debate On IP And Drug Price Model, Flexibilities 26 February 2010. Accessed 5 May 2010.
- ↑ Pfizer Forum. Pfizer Forum. Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Helen Disney Website. Helen Disney Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Dr. Meir Perez Pugatch.Pugatch CV Accessed 21 April 2010.
- ↑ Dr. Meir Perez Pugatch.Pugatch CV Accessed 21 April 2010.
- ↑ Pfizer Forum.Pfizer Forum: Authors Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Zoom Info: Catherine Windels. Catherine Windels Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Pharma Marketletter. Patent law changes: victory for software firms, defeat for research based drugmakers. 17 September 2007. Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Pharma Marketletter. Patent law changes: victory for software firms, defeat for research based drugmakers. 17 September 2007. Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Pharma Marketletter. Patent law changes: victory for software firms, defeat for research based drugmakers. 17 September 2007. Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2007-08, ISSU, Accessed 20-April-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Networks. Health and Welfare Accessed 8 April 2010.
- ↑ Helen Disney, Karen Horn, Pavel Hrobon, Johan Hjertqvist, Alastair Kilmarnock, Andreas Mihm, Alberto Mingardi,Cécile Philippe, David Smith, Eline van den Broek, Gerrold Verhoeks. Impatient for Change European attitudes to healthcare reform 12 May 2004. Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Helen Disney, David Hill, Pavel Hrobon, Adam Kruszewski, Henrieta Madarová, Rick Nye, Martin Stefunko. Poles Apart? Eastern European attitudes to healthcare reform. 19 May 2005. Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Helen Evans. Nurses for Reform Blog.Brussels comes to the rescue of NHS patients: London think tank heralds cross-border health directive. 9 January 2008. Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Saunders, P. 4 April 2005. Institute of Science in Society. Science versus Democracy? Accessed 17 April 2010
- ↑ Saunders, P. 4 April 2005. Institute of Science in Society. Science versus Democracy? Accessed 17 April 2010
- ↑ Atlas Economic Research Foundation]. Freemarket Think Tanks Accessed 17 April 2010.
- ↑ Atlas Economic Research Foundation. Mission & Vision Accessed 17 April 2010.
- ↑ Atlas [Alas Network: About] Accessed 3 May 2010.
- ↑ AERF.[The Freedom Network] Accessed 3 May 2010.
- ↑ AERF.[The Freedom Network] Accessed 3 May 2010.
- ↑ HDisney, Revision as of 13:28, 7 August 2008, Wikipedia, Accessed 27-April-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2007-08, ISSU, Accessed 20-April-2010
- ↑ Zoom Info: Catherine Windels. Catherine Windels Accessed 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2005-06, ISSU, Accessed 20-April-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2005-06, ISSU, Accessed 20-April-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2006-07, ISSU, Accessed 20-April-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2007-08, ISSU, Accessed 20-April-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Join the Network, The Stockholm Network, Accessed 01-June-2010
- ↑ Tim Montgomerie, The growth of Britain's conservative movement, ConservativeHome, 14 March 2009.
- ↑ 10 Years of the Stockholm Network, The Stockholm Network Annual Report 2006/2007, The Stockholm Network, p. 13
- ↑ The Stockholm Network Annual Report 2007/2008, The Stockholm Network
- ↑ Catherine Hoye, RE:Stockholm Network, E-mail to Steven Harkins 10-May-2010 11:43am
- ↑ Clare Rusbridge, FW: Stockholm Network, E-mail to Steven Harkins, 12-May-2010 6:05pm
- ↑ Helen Disney, RE:Stockholm Network Members, Stockholm Network, 27-May-2010, 10:04, E-mail to Steven Harkins
- ↑ Think Tank Details, United Kingdom, Stockholm Network, Accessed 22-May-2010
- ↑ 10 Years of the Stockholm Network, The Stockholm Network Annual Report 2006/2007, The Stockholm Network, p. 13
- ↑ The Stockholm Network Annual Report 2007/2008, The Stockholm Network
- ↑ Alex Singleton, Free-market network demands bail-out for pharmaceutical industry, Telegraph, January 19th, 2009, acc 20 May 2010
- ↑ Alex Singleton, Free-market network demands bail-out for pharmaceutical industry, Telegraph, January 19th, 2009, acc 20 May 2010
- ↑ FAQs, Stockholm Network website, acc 17 Apr 2010
- ↑ HDisney, Revision as of 13:28, 7 August 2008, Wikipedia, Accessed 27-April-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2005-2006, ISSU, 2006, Accessed 01-July-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, 2006-2007, ISSU, 2007, Accessed 01-July-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2007-2008, ISSU, 2008, Accessed 01-July-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Staff Profiles, Stockholm Network, Accessed 13-May-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Staff Profiles, Stockholm Network, Accessed 13-May-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, About Us, Stockholm Network, Web Archive 01-April-2002, Accessed 09-May-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Patrons and Directors, Stockholm Network, 02-March-2005, Accessed via web archive 10-May-2010
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Directors and Patrons, Stockholm Network, 01-January-2006, Accessed via web archive 10-May-2010
- ↑ Market House International, Certificate of Incorporation of a Private Limited Company, Companies House, 05-November-2003
- ↑ Market House international Changes its name to The Stockholm Network, Certificate of Incorporation on Change of Name, Companies House, 06-February-2006
- ↑ 288a Appointment of Helen Disney as Director, Stockholm Network New Director 05-November-03, Companies House, 05-12-2003
- ↑ 288a Appointment of Rick Nye as Secretary, Stockholm Network Secretary Appointed 05-12-2003, Companies House, 05-November-2003
- ↑ Stockholm Network, Annual Report 2005-06, ISSU, Accessed 20-April-2010
- ↑ Katie Perrior, Meet the Directors, InHouse PR, Accessed 25-June-2010
- ↑ Katie Perrior, Lobbyists should make the most of Boris' willingness to listen, PR Week, 5-June-2008, Accessed 25-June-2010