Difference between revisions of "Gulf of Mexico"
(Created page with "{{place |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gulf of Mexico |image= |image_caption= |constitutes=Sea |location= }} {{SMWDocs}} ==References== {{reflist}} {{Stub}}") |
(unstub) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{place | {{place | ||
|wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gulf of Mexico | |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gulf of Mexico | ||
| − | |image= | + | |image=Fixed gulf map.png |
|image_caption= | |image_caption= | ||
|constitutes=Sea | |constitutes=Sea | ||
|location= | |location= | ||
| + | |description=The "Third Coast" of the [[United States]]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
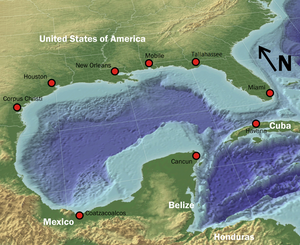
| + | The '''Gulf of Mexico''' (Spanish:Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea] of the [[Atlantic Ocean]],<ref>http://www.deepseawaters.com/Gulf_of_Mexico.htm</ref> largely surrounded by the [[North America]]n continent.<ref name="GNIS1">http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:558730</ref> It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the [[Gulf Coast of the United States]]; on the southwest and south by the [[Mexico|Mexican]] [[States of Mexico|states]] of [[Tamaulipas]], [[Veracruz]], [[Tabasco]], [[Campeche]], [[Yucatan]], and [[Quintana Roo]]; and on the southeast by [[Cuba]]. The [[United States|US]] states of [[Texas]], [[Louisiana]], [[Mississippi]], [[Alabama]], and [[Florida]], which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific coasts). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Gulf of Mexico basin]] is roughly oval in shape and is approximately {{convert|810|nmi|km mi}} wide. It is connected to part of the Atlantic Ocean through the [[Florida Straits]] between the U.S. and Cuba, and with the [[Caribbean Sea]] via the [[Yucatán Channel]] between Mexico and Cuba. Because of its narrow connection to the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf experiences very small [[Tides|tidal ranges]]. The size of the Gulf basin is approximately 1.6 million km<sup>2</sup> (615,000 sq mi). Almost half of the basin consists of shallow continental-shelf waters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most important offshore petroleum-production regions in the world, making up one-sixth of the United States' total production.<ref>https://www.eia.gov/special/gulf_of_mexico/</ref> | ||
| + | |||
{{SMWDocs}} | {{SMWDocs}} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 08:02, 7 June 2021
(Sea) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The "Third Coast" of the United States. |
The Gulf of Mexico (Spanish:Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea] of the Atlantic Ocean,[1] largely surrounded by the North American continent.[2] It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The US states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific coasts).
The Gulf of Mexico basin is roughly oval in shape and is approximately 810 nautical miles (1,500 km; 930 mi) wide. It is connected to part of the Atlantic Ocean through the Florida Straits between the U.S. and Cuba, and with the Caribbean Sea via the Yucatán Channel between Mexico and Cuba. Because of its narrow connection to the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf experiences very small tidal ranges. The size of the Gulf basin is approximately 1.6 million km2 (615,000 sq mi). Almost half of the basin consists of shallow continental-shelf waters.
The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most important offshore petroleum-production regions in the world, making up one-sixth of the United States' total production.[3]
Event
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| Deepwater Horizon | An ecologically disastrous oil spill |