Difference between revisions of "Commonwealth of Nations"
(Destubbed.) |
m |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{group | {{group | ||
|wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commonwealth_of_Nations | |wikipedia=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commonwealth_of_Nations | ||
| + | |description=Organisation, mostly consisting of former [[British Empire]] nations. | ||
|constitutes=International organisation | |constitutes=International organisation | ||
|type=international | |type=international | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
|headquarters=Marlborough House, London | |headquarters=Marlborough House, London | ||
|leaders=Commonwealth Secretary-General, Chairperson of the Commonwealth of Nations | |leaders=Commonwealth Secretary-General, Chairperson of the Commonwealth of Nations | ||
| + | |members=Antigua and Barbuda, | ||
| + | Australia, The Bahamas, Bangladesh, Barbados, Belize, Botswana, Brunei, Cameroon, Canada, Cyprus, Dominica, Eswatini, Fiji, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Grenada, Guyana, India, Jamaica, Kenya, Kiribati, Lesotho, Malawi, Malaysia, Maldives, Malta, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Nauru, New Zealand, Nigeria, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, Rwanda, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Samoa, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Singapore, Solomon Islands, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Togo, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Tuvalu, Uganda, United Kingdom, Vanuatu, Zambia | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{YouTubeVideo | {{YouTubeVideo | ||
|code=T6eSsaoLSfE | |code=T6eSsaoLSfE | ||
| + | |width=320px | ||
|caption=Britains Invisible Empire (full lecture) - [[EIR]] / September 1997 | |caption=Britains Invisible Empire (full lecture) - [[EIR]] / September 1997 | ||
| − | }}'''The Commonwealth of Nations''', generally known simply as the '''Commonwealth''', is a political association of | + | }}'''The Commonwealth of Nations''', generally known simply as the '''Commonwealth''', is a political association of 56 member states, nearly all former territories of the [[British Empire]].<ref>''[https://web.archive.org/web/20121130144205/http://www.maldiveshighcommission.org/ "High Commission of the Maldives in the UK"]''</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ==History== | ||
| + | The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the [[20th century]] with the decolonization of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the ''British Commonwealth of Nations'' through the [[Balfour Declaration]] at the [[1926]] [[Imperial Conference]]. [[Queen Elizabeth II]] is the head of the Commonwealth - [[Charles Mountbatten-Windsor|Charles, Prince of Wales]] her designated successor. Member states are said to have no open legal obligations to one another, just being connected through their use of the English language and historical ties. Although the two exceptions are [[Mozambique]] and [[Rwanda]] which had colonial ties to [[Portugal]] and [[Germany]]/[[Belgium]] respectively. | ||
The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20 per cent of the world's land area. The total population is estimated to be | The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20 per cent of the world's land area. The total population is estimated to be | ||
2,418,964,000 as of 2016, equivalent to nearly a third of the global population, making it the second largest intergovernmental organisation by population behind the [[United Nations]]. | 2,418,964,000 as of 2016, equivalent to nearly a third of the global population, making it the second largest intergovernmental organisation by population behind the [[United Nations]]. | ||
| − | [[ | + | ==Oath of Allegiance== |
| + | In [[Australia]], [[New Zealand]] and [[Canada]] government officials (including [[police]] and [[military]] at times) have to swear an [[Oath of Allegiance]] to the monarch of the country, currently [[King Charles III]].<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oath_of_Allegiance_(New_Zealand)</ref><ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oath_of_Allegiance_(Canada)</ref><ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oath_of_Allegiance_(Australia)</ref><ref>http://classic.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/nsw/consol_reg/pr2015166/s141.html</ref> [[King Charles III]] is king of 15 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 36 other members are republics, and five others have different monarchs. | ||
{{SMWDocs}} | {{SMWDocs}} | ||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:18, 30 August 2023
(International organisation) | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Formation | 1949 |
| Headquarters | Marlborough House, London |
| Leaders | • Commonwealth Secretary-General • Chairperson of the Commonwealth of Nations |
| Type | international |
| Interest of | Crimes of Britain |
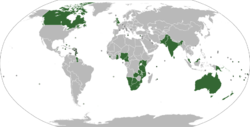
| Membership | • Antigua and Barbuda • • The Bahamas • Bangladesh • Barbados • Belize • Botswana • Brunei • Cameroon • Canada • Cyprus • Dominica • Eswatini • Fiji • Gabon • Gambia • • Grenada • Guyana • India • Jamaica • Kenya • Kiribati • Lesotho • Malawi • Malaysia • Maldives • Malta • Mauritius • Mozambique • • Nauru • New Zealand • Nigeria • Pakistan • Papua New Guinea • Rwanda • Saint Kitts and Nevis • Saint Lucia • Saint Vincent and the Grenadines • Samoa • Seychelles • Sierra Leone • Singapore • Solomon Islands • South Africa • Sri Lanka • Tanzania • Togo • Tonga • • Tuvalu • Uganda • • Vanuatu • Zambia |
| Organisation, mostly consisting of former British Empire nations. | |
| Britains Invisible Empire (full lecture) - EIR / September 1997 |
The Commonwealth of Nations, generally known simply as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, nearly all former territories of the British Empire.[1]
History
The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonization of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference. Queen Elizabeth II is the head of the Commonwealth - Charles, Prince of Wales her designated successor. Member states are said to have no open legal obligations to one another, just being connected through their use of the English language and historical ties. Although the two exceptions are Mozambique and Rwanda which had colonial ties to Portugal and Germany/Belgium respectively.
The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20 per cent of the world's land area. The total population is estimated to be 2,418,964,000 as of 2016, equivalent to nearly a third of the global population, making it the second largest intergovernmental organisation by population behind the United Nations.
Oath of Allegiance
In Australia, New Zealand and Canada government officials (including police and military at times) have to swear an Oath of Allegiance to the monarch of the country, currently King Charles III.[2][3][4][5] King Charles III is king of 15 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 36 other members are republics, and five others have different monarchs.
Known members
All 56 of the members already have pages here:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Antigua and Barbuda | Small island nation in the Caribbean Sea, formerly part of the British Empire. |
| Australia | A large island nation in the southern hemisphere which is pioneering universal surveillance of its citizenry. |
| Bangladesh | 8th most populated country in the world. Formerly part of the British Empire. |
| Barbados | Scenic Caribbean island nation. Formerly part of the British Empire |
| Belize | The only Central American country which is a Commonwealth realm. |
| Botswana | Country in Southern Africa. Formerly part of the British Empire, Botswana is one of the most sparsely populated countries in the world. |
| Brunei | Small kingdom in South-East-Asia |
| Cameroon | West African state |
| Canada | If tar sands are counted, Canada possesses the 3rd largest oil reserves of any nation state. |
| Cyprus | A small, divided, island in the Mediterranean. Greek Cyrpus was aggressively pushing the COVID-19/Vaccine in May 2021. |
| Dominican Republic | Caribbean country; shares the island of Hispaniola with Haiti. |
| Eswatini | Small African Kingdom; surrounded by South Africa. |
| Fiji | One of the world's first nation states to mandate Covid vaccination for certain adults. |
| Gabon | French speaking country on the west coast of Africa. |
| Gambia | The smallest country in mainland Africa. |
| Ghana | Formerly known as the "Gold Coast", Ghana has one of the most stable governments in Africa. A member of the African Union and the Commonwealth of Nations |
| Grenada | A Caribbean island, that had a coup in the 1980s. |
| Guyana | The only UK colony on the mainland on South America. |
| India | The "Jewel in the Crown" of the British Empire. Until independence in 1947 it was ruled from London under the auspices of a British-appointed Viceroy whose powers were absolute. |
| Jamaica | Caribbean island |
| Kenya | Former UK colony in East Africa |
| Kiribati | Small island nation in Oceania. |
| Lesotho | Small landlocked nation in Africa. |
| Malawi | Former UK colony in East Africa |
| Malaysia | Kingdom in Southeast Asia. Known for air disasters. |
| Maldives | Small country of Islands in the Indian Ocean. Main source of income for most is tourism. |
| Malta | Island nation in the Mediterranean sea |
| Mauritius | Island nation in the Indian Ocean. Now a tax haven. |
| Mozambique | South East African state, former Portuguese colony, now in the British Commonwealth. |
| Namibia | A diamond rich territory, formerly occupied by South Africa |
| Nauru | An island nation in Oceania |
| New Zealand | An island state next to Australia which "has become a preferred bolthole for the ultra rich". Aggressively used contact tracing and lockdowns during the COVID-19 event. |
| Nigeria | Africa's most populous nation state, with large reserves of oil and gas. |
| Pakistan | Like Afghanistan, former colony of the UK Pakistan is haunted by CIA drone attacks. Its nuclear weapons cache and border disputes with India also don't help. Supposedly Osama Bin Laden was killed here, in the rich, western city of Abbottabad. |
| Papua New Guinea | |
| Rwanda | |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | A Commonwealth island nation in the Caribbean Sea |
| Saint Lucia | A Commonwealth island nation in the Caribbean Sea |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | A Commonwealth island nation in the Caribbean Sea |
| Samoa | Pacific island nation that might have been the site of dry run for Covid. |
| Seychelles | |
| Sierra Leone | A global cocaine trafficking hub in West Africa |
| Singapore | Densely populated country in Asia. Tough immigration and opium laws. Former UK colony. |
| Solomon Islands | An island nation in Oceania |
| South Africa | A former British and Dutch colony |
| Sri Lanka | Small country in Asia, an attack blamed on IS killed more than 200 people in 2019 just after COVID erupted. |
| Tanzania | Former UK colony in East Africa. The president, John Magufuli, who in 2020 resisted WHO pressure to institute a COVID lockdown, died in 2021. |
| The Bahamas | |
| Togo | Small country in West Africa. |
| Tonga | Polynesian island kingdom. |
| ... further results | |
References
- ↑ "High Commission of the Maldives in the UK"
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oath_of_Allegiance_(New_Zealand)
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oath_of_Allegiance_(Canada)
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oath_of_Allegiance_(Australia)
- ↑ http://classic.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/nsw/consol_reg/pr2015166/s141.html